Pelvis & Perineum Quiz: Anatomy & Clinical Scenarios
advertisement

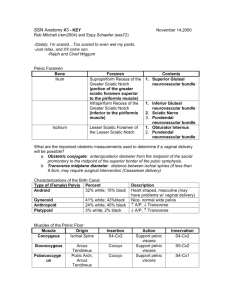
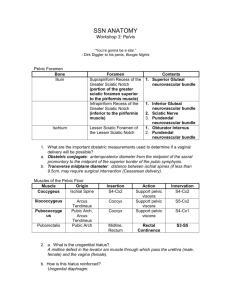
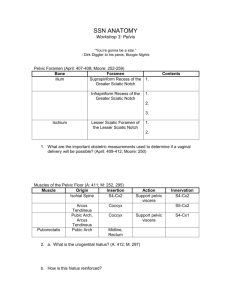
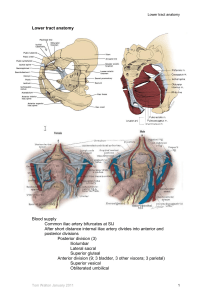
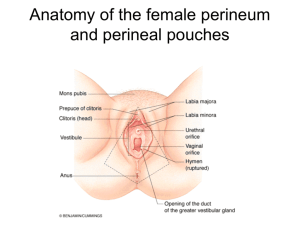
Pelvis and Perineum Quiz YOU WILL HAVE 60 SECONDS PER QUESTION Question #31 A three-day-old baby is undergoing a circumcision procedure. Which of the following nerves will the attending physician anesthetize? A. Cavernous n. B. Dorsal nerve of the penis C. Genitalfemoral n. D. Ilioinguinal n. E. Superficial perineal n. Question #32 As a catheter is placed in the penile urethra, which of the following structures most immediately surrounds the catheter? A. Colles fascia B. Corpus spongiosum C. Deep (Buck’s) fascia D. Loose areolar tissue E. Tunica albuginea Question #33 A 30-year-old female undergoing a hysterectomy has her suspensory ligament cut. Which of the following arteries has also been compromised? A. Internal pudendal B. Superior vesical C. Ovarian D. Vaginal E. Uterine Question #34 Identify the highlighted structure: A. Middle rectal artery B. Ovarian artery C. Obturator artery D. Inferior vesical artery E. Uterine artery Question #35 A 15-year-old boy, after being punched in the abdomen, has a large hematoma deep to his Scarpa’s fascia. Which of the following areas could the hematoma also pass into? A. Corpora cavernosa B. Deep perineal pouch C. Ischio-anal fossa D. Lesser pelvis E. Superficial perineal pouch Pelvis and Perineum Forum Questions Question #1 A patient undergoing surgery requires a pudendal nerve block. Where would you inject the anesthetic agent? What landmark(s) would be used to guide the injection? What are the branches of the pudendal that would be affected and what structures are affected? Question #2 A 32-year old patient is being evaluated for potential complications during vaginal delivery. What pelvic measurements would be necessary? What are the potential shapes of the pelvic inlet of this patient? What would be the distinguishing features between the male and the female pelvis? Pelvic Measurements Pelvic Shapes Male and Female Pelvis Question #3 A 28-year old patient undergoes a midline episiotomy. What pelvic and perianal structures are involved in this procedure? If the perineal body is disrupted during the procedure what are potential complications for this patient in the future (describe each)? Episiotomy Perineal Body Fascia attaching to the perineal body: • Colle’s fascia • Perineal membrane • Deep investing fascia Muscles attaching to the perineal body: • • • • Transverse Perineal (super and deep) Bulbospongiosus External anal sphincter Pubococcygeus Question #4 A 10-year old male patient is seen in the emergency room. The patient accidently fell and straddled his bike and since the time of the accident he has had pain and swelling of his perineal and scrotal area. After further examination it is determinde that the patient has a ruptured urethra. Where are the potential anatomic locations for a urethral rupture? What anatomy would be disrupted or intact with each type of rupture? What would be the potential signs and symptoms associated with each? Question #5 A 54-year old patient with a history of atherosclerotic disease is seen in the emergency room complaining of pain in his pelvic region. Upon further testing he is diagnosed with an obstructed middle rectal vein. What vessels would provide collateral circulation? Trace the path of blood from each collateral vessel. This scenario can also be used for the following arteries: uterine, iliolumbar/circumflex iliac, lateral sacral, middle rectal, inferior gluteal. Blood Supply to the Pelvis Question #6 A patient is in the emergency room following a high speed accident in which the pelvis sustained injury. The patient is diagnosed with a fractured pelvis: What structures are in danger if the fracture is of the superior pubic ramus? What future issues might arise from such a repaired injury? Pelvic Fractures Question #7 A 64-year old patient is seen for a routine physical examination. In what way are the female pelvic viscera examined? What structures can be assessed? The physician notes that the patient’s uterus is lower in the vaginal canal than expected. This anatomic finding would mostly likely be a direct result from injury to what structures? (be prepared to describe the normal and pathologic structures). Pelvic Examination Prolapse Question #8 A 45-year old patient with portal hypertension is seen by his primary care physician and complains of blood in his stool. Following examination he is diagnosed with hemorrhoids. What would be the signs, symptoms and anatomic features to distinguish as to the patients type of hemorrhoids? Question #9 A patient experiencing erectile dysfunction is seen in the urology clinic. Upon further evaluation the patient also expresses a heavy sensation in his lower pelvis. What types of physical examinations might be performed and what anatomy would be assessed? The urologist also performed a cystoscopy on the patient, during the examination what anatomy would be assessed? Digital Rectal Examination Question #10 A 25-year gunshot victim is seen in the emergency room. Upon physical examination it is determined that the bullet entered the gluteal region near the piriformis muscle. What anatomic structures are in danger of being damaged? Question #11 A 33-year old patient is seen by her primary care physician concerned about an inflammation of her superficial inguinal lymph nodes. What areas should be inspected as possible sites of infection? Superficial Inguinal Nodes