Chemical equation = chemical recipe

EL: To understand the law of conservation of mass the different types of , how to write chemical equations and how to identify the 5 main types of reactions.
Focus: Conservation of mass, writing equations and chemical reactions
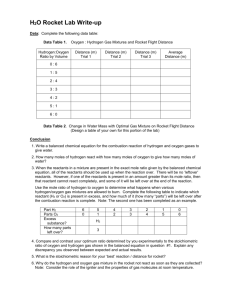
The mass of substances produced (products) by a chemical reaction is always equal to the mass of the reacting substances (reactants).
Let’s test this law!
In groups (3-4 people) carry out the investigation wearing your personal protective equipment using the method provided
Record your results and share your findings by writing them on the board.
Answer the questions on the sheet as well as “How do the result of other groups compare to yours? Explain”
Chemical equation = chemical recipe
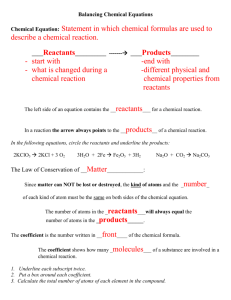
A chemical equation describes the ingredients used during a chemical reaction and the products formed. It is, if you like, similar to a recipe.
The ingredients or reactants appear on the left of the equation while the products appear on the right.
Reactants are always used up during a chemical reaction while the products increase in quantity.
Hydrogen peroxide breaks down to form oxygen gas and water. The word equation for this reaction is shown below:
Hydrogen peroxide ==> oxygen gas + water
the reactant - hydrogen peroxide - is on the left of the arrow
the products - oxygen gas and water - are on the right.
Methane burns to form carbon dioxide and water.
The word equation for this reaction is shown below.
Methane + oxygen ==> carbon dioxide + water.
Note that when a substance burns, it is actually reacting with oxygen.
So oxygen must appear on the left side of the equation as a reactant even though it is not stated in the description above.
a) Magnesium burns in oxygen to form a white powder known as magnesium oxide.
b) Hydrogen and oxygen gases react to form water.
c) Sugar reacts with oxygen in our body to produce carbon dioxide and water.
d) Zinc metal and hydrochloric acid react together to produce hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
* Complete “writing worded equations” worksheet
Scientists describe a chemical reaction by writing a chemical equation using symbols to represent the atoms taking part.
The symbols that are used to represent the substances are called Chemical formula.
There are two types of Chemical formula
Molecular Formulas or Ionic Formulas
Chemical Equations
This equation tells us that two molecules of hydrogen gas react with one molecule of oxygen gas to produce two molecules of water.
The equation has two sides.
• left of the arrow we put the reactants - the chemicals that react together.
• right side of the arrow we put the products - the chemicals that are formed or produced.
If we were to draw this reaction in pictures it would look like this.
• We can see that two molecules of hydrogen react with one molecule of oxygen to produce two molecules of water
• There is a 2 in front of the water and the hydrogen molecule in the equation to "BALANCING the equation".
• There is a special Law in Nature that states that
"Matter can not be created or destroyed" . It is called "The Law Of Conservation Of Mass ".
• What this means is that we have to have the same number of each atom on each side of the arrow in the equation and the mass of the reactants equal the mass of the products.
When writing the formula of an ionic compound a few steps must be followed.
Step 1 - Write the formula of each ion and its charge.
Step 2 - Balance the positive and the negative charges.
Step 3 - Use subscripts to write the formula.
Step 4 - Use brackets if the ion has more than one capital letter and more than one ion is required.
Example 1 What is the formula of aluminium sulfate.
Step 1 - Al +3 and SO
4
-2
Step 2 - Balance the positive and negative charges.
In order to balance 3+ and 2- we have to find the lowest common multiple.
In this case it is 6.
In order to get 6+ we need 2 Aluminium ions.
In order to get 6- we need 3 sulfate ions.
Step 3 and 4 Write the formula using subscript.
Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
Note how we used brackets around the sulfate ion. That's because sulfate is an ion with two capital letters and we need more than one sulfate ion.
http://www.dynamicscience.com.au/tes ter/solutions/chemistry/ionicformexeacti vity.html
-
-
-
-
Watch the following clip from You tube types of chemical reactions to learn more about 4 of the 5 main types of chemical reactions
Synthesis
Decomposition
Single replacement
Double replacement reactions.
You will be performing these reactions in coming lessons
Combustion reactions are those in which the substance reacts with oxygen and heat is released .
Common combustion reactions
›
›
›
Burning of gas in stoves the fuel(octane) burnt to provide energy to a car
Respiration
Watch this demo
methane bubbles combustion reaction