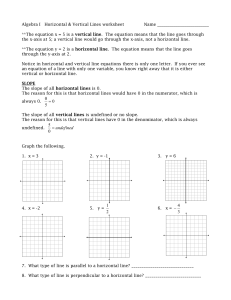
Chapter 3 Lesson 3 Day 1
advertisement

Manufacturing Methods What differences do you see in manufacturing methods among these three images from before the Civil War, after the Civil War, and during modern times? The number of workers, the raw materials used, the kinds of machinery, and the work environment. How do you think the ownership of these workplaces has changed? As workplaces became larger and more modern, ownership shifted from families of modest means to wealthy entrepreneurs. Business Terms • economies of scale The concept of economies of scale says that the cost of manufacturing falls as goods are produced more quickly in larger quantities. After the Civil War, corporations achieved this by investing in new technologies, expanding their workforces, and purchasing machinery. • fixed costs A company’s fixed costs are the debts the company must service whether it is in operation or not. Loans, mortgages, and taxes are fixed costs. • operating costs A company incurs operating costs while it is actively producing goods. Workers must be paid. Raw materials and other supplies must be bought and shipped to the factory to keep operations going. Factories • Why do many factories run day and night, all year long? A factory that is idle is still costing the owners money but is not producing any goods or revenue. Big Business • Big businesses can achieve efficiencies associated with economies of scale in several ways. One is specialization—of workers and of machines. Another is paying lower prices by purchasing resources in large quantities. Business Organizations • corporation a business that has shared ownership in the form of stock with hired management, high fixed costs, and low operating costs • partnership a business owned and managed by two or more people with low fixed costs and high operating costs • sole proprietorship a business owned and managed by an individual with low fixed costs and very high operating costs Big Business What advantage does a big business have when it comes to operating costs? As fixed costs go up, its operating costs go down more than those of the small business. How did consumers benefit directly from the rise of corporations? Because goods were produced at a lower cost, corporations could sell them more cheaply than small businesses and still make a profit. As a result, consumers saved money on certain items What drawbacks do you think may have been associated with big business manufacturing from a consumer’s point of view? The absence of personal attention provided by small businesses and the lack of originality or quality that often comes with corporate production. Business Terms • pool an agreement between companies to set prices at an agreed upon base level • monopoly command of an entire market by an individual company • trust a managing arrangement in which an individual makes decisions regarding the property or assets of another person • holding company a company that owns shares in and manages the assets of other companies but does not make any products Vertical Integration • Owning It All Vertical integration increases efficiency while making a company larger. Companies vertically integrate when they purchase all of the businesses on which they depend, such as those that supply raw materials, equipment, or services such as shipping. • Carnegie Steel Entrepreneur Andrew Carnegie’s steel company engaged in vertical integration. Carnegie bought coal mines, limestone quarries, and iron ore fields, all of which were vital to the production of steel, as well as the rail and shipping companies that haul raw materials or finished products. Vertical Integratin Discussion How could vertical integration prove to be more efficient and cost effective for both the producer and the consumer? The producer’s ownership of businesses that contribute to the operation of the parent company cuts down on supplier expenses, and the resulting savings can be transferred to the consumer. Horizontal Integration • Combining Companies Horizontal integration allows one business to dominate a certain field. It occurs when a strong company combines with other companies in the same business—often competing firms—to form one large corporation. • Standard Oil John D. Rockefeller built his company, Standard Oil, into the nation’s largest oil refiner. With horizontal integration, he acquired his competitors. Eventually he had a monopoly—control of the entire market. Horizontal Integration Discussion How did horizontal integration work to consolidate an industry? It turned an industry with many competing firms into an industry with far fewer firms, perhaps even leaving one company with a monopoly. Horizontal Integration Discussion • Horizontal integration was often a successful strategy for strong companies, but what challenges might it have posed to the company doing the integrating? • When a smaller, weaker company merges with another company, the company doing the integrating had to assume control of any weaknesses that existed within the faltering company and may have had to overcome financial or structural challenges to turn the merger into a success. Horizontal Integration Discussion • What big American industry has employed both horizontal and vertical integration in modern times? • The automotive industry; for example, General Motors [GM] has acquired several other carmakers and has also bought out other supplier companies as well, such as the company that makes all of the radios they install in their automobiles [Delco] Microsoft bought out several software developers, but also suppliers such as microprocessor manufacturers. Business Discussion • If a paper mill bought a new papermaking machine, what fixed and operational costs might it incur? • Fixed: loan to buy the machine; taxes on the purchase. Operating: raw materials, including trees; workers’ wages; shipping costs. Business Discussion • What are the fixed costs that most households have? Taxes, mortgage, or rent • What are some operating costs of a household? Electricity, water, and heating or cooling