Unit 1
advertisement

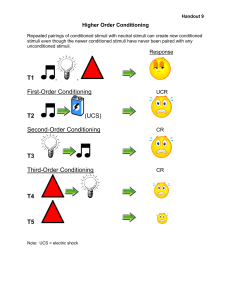
Psyco 486 Learning and Behavioural Theory in Advertising and Marketing Advertising Psychology • Relatively new field • Aims • Differences from market research What We’re Covering • The focus: learning and behavioural theory • Some cross-over into cognitive content • Applications: advertising, marketing Why a Behavioural Approach? Level of Investigation Type of Learning Mechanisms Whole organism Behavioural Neural circuits and neurotransmitters Neural systems or networks Neurons and synapses Molecular, cellular And genetic What Psychologists Work With • Facts • Inferences • Constructs Methodological Issues • Confounds – Demand characteristics – Contingency awareness Controls • Perceptual – Colours, sounds, etc. – Preferences (innate, learned) • Subjects • Brand exposure • General advertising exposure Deception • Misdirection • Post-study questionnaire Techniques • Experimental/laboratory • Naturalistic/applied Learning • • • • Habituation/Sensitization Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Associations • Linking together of: – Events – Memories – Actions and consequences • Central to study of learning and behaviour Rules of Association for Stimuli • Primary (Aristotle’s) – Contiguity, similarity, contrast • Secondary (Thomas Brown) – Length of exposure, vividness, frequency, consitutional differences, emotional state, health, prior habits, freedom from strong associations with other stimuli Associationism • Sensations – Experiences • Memory – Ideas • Mental representations Hierarchy duplex idea complex idea complex idea simple idea simple idea simple idea simple idea simple idea simple sensation simple sensation simple sensation simple sensation simple sensation Classical Conditioning: Basics • Unconditional – Stimuli and responses whose properties are not dependent upon prior training • Conditional (i.e., “dependent”) – Stimuli and responses whose properties occur only after training • US, UR, CS, CR • Associations Stimulus-Substitution • CS takes properties of US • CR equals/approximates UR Sign Tracking • Basics • Supports stimulus substitution • Behavioural categories/classes Preparatory Response Theory • Allows body to prepare for future event • Based on past experience • Survival value Nature of the CR-UR • Compensatory CRs • SOP and AESOP models Temporal Arrangement Short Delay Long Delay Trace Simultaneous Backwards