Systematics: The Science Of Biological Diversity Chapter 12
advertisement
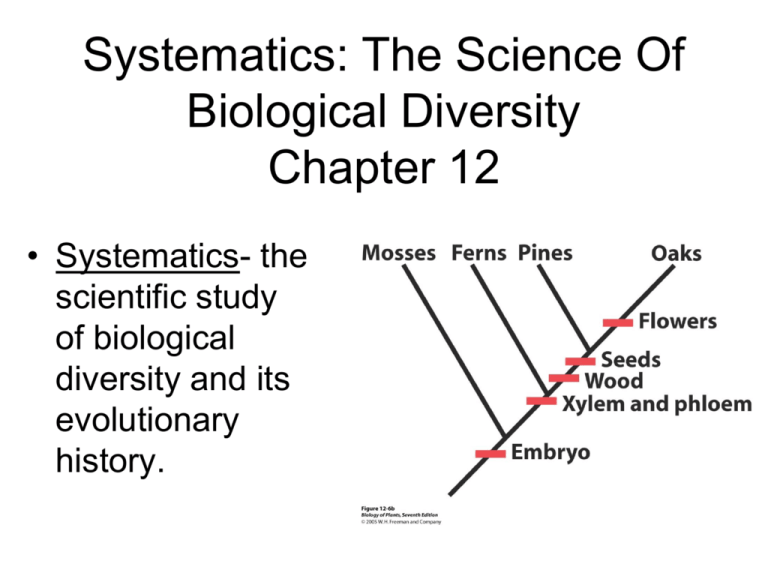
Systematics: The Science Of Biological Diversity Chapter 12 • Systematics- the scientific study of biological diversity and its evolutionary history. Theophrastus (370-285 B.C.) • Father of Botany, student of Aristotle. • Classified plants based on form. – Tree – Shrub – Undershrub – Herb Atropa belladonna- Solanaceae Carol von Linné (1707-1778) • Swedish naturalist. • Systema Naturae & Species Plantarum. – Plant descriptions. – Plant binomials- a two-term system of nomenclature. • Genus and species (specific epithet). • Example- catnip. – Nepeta cataria L. – “Nepeta floribus interrupte spicatus pedunculatis” Nepeta cataria- Lamiaceae Taxonomy • Taxonomy- (gr. taxis- arrangement, nomos- law) the science of the classification of organisms. – Identifying, naming, classifying organisms. • Domain • Kingdom • Phylum- phyta • Class- phyceae • Order- ales • Family- aceae • Genus • Species Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Eukaryote Lineages Origin of Cells Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Species Concepts International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) • Aim- to provide a stable method of naming taxonomic groups. – Principle I- botanical nomenclature is independent of zoological and bacteriological nomenclature. – Principle II- names of taxonomic groups are determined by means of nomenclatural types. – Principle III- nomenclature of a taxonomic group is based upon priority of publication. • Naming- the purpose of giving a name to a taxonomic group is not to indicate its characters or history, but to supply a means of referring to it and to indicate its rank. Taxonomic Terminology • Taxon- a taxonomic group of any rank (plural: taxa). • Synonym- two or more names that apply to the same taxon. • Basionym- the original name of a taxon. • Author/s- the first person or persons to describe a taxon. • Revisionary author/s- the person or persons that modified the name. • Etymology- the derivation, origin, or history of a word. • Type Specimen- a specimen designated to serve as a reference point for a scientific name. – Holotype – Lectotype Taxonomic Names • Species names consists of the genus name, plus the specific epithet. • Members of a species may be grouped into subspecies or varieties. How do you identify plants? • Ask an expert. • Use a herbarium. • Compare plant with a written description. • Use books to picture I.D. specimens. – Photographs and illustrations. • Use a dichotomous key. Dichotomous Keys • A method employed for identifying unknown organisms. • A dichotomous key is constructed of a series of couplets, each consisting of two separate statements. 1. Flowers white .................. Plant A 1. Flowers red or yellow ..... 2 2. Petals red ............ Plant B 2. Petals white ........ Plant C