Fundamental of Computers

Introduction to Computer
Engineering
ENCE200
Engineers and Computers
Storage, and manipulation of data
Communication over networks (e-mail, web)
Desktop publishing (desktop publishing is the process of using the computer and specific types of software to combine text and graphics to produce documents such as newsletters, brochures, books, etc.)
Numeric, symbolic computations
Building software applications
Computer System
A computer is a machine that manipulates data according to on a set of instructions.
System Elements:
Computing Elements:
Central Processing Unit, CPU.
Disk spaces,
Input devices: keyboard, sensors
Output devices: monitors, printers
Main parts of a computer
Processor
• ALU
• Control
Memory
• RAM
• ROM
Devices (I/O)
• Input
• Output
Processor Units
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) or the processor is the part that carries out the instructions of a computer program.
ALU: Is a digital circuit which performs the arithmetic and the logical operations.
Control Unit: It controls the flow of information through the processor, and coordinates the activities of the other units within it.
Processor Specifications
Cache: Cache operates as a temporary storage area where frequently accessed data can be stored for rapid access. (6 MB)
Clock Speed: The number of data transfers it performs per clock cycle. (2.2 GHz)
Bus Speed: The clock speed of the bus.(1333 MHz)
Number of Cores: the number of processing cores. 2 Duo
Hardware Model of a Personal Computer
Central Processing Unit
Busses
Input/Output
Keyboard
Monitor
Ports
Mass Storage
Hard Disk
CD-ROM
DVD
Data
Busses
Data
Instruction
Instruction
Random Access
Data
Data Instruction
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Zoom-in a System Component [1]
8
Voltage Range of Binary Signals[1]
HIGH (1)
LOW (0)
INPUT
5.0 Volts
4.0 Volts
3.0 Volts
2.0 Volts
1.0 Volts
0.0 Volts
OUTPUT
9
HIGH (1)
LOW (0)
Rapid change in Computer Technology
Processor logic capacity: about 30% per year
clock rate: about 20% per year
So… advanced functions (e.g., multimedia functions in some Pentiums) and high-speed features (multiple pipelines, larger caches)
Memory
DRAM capacity: about 60% per year (4x every 3 years)
Memory speed: about 10% per year
Cost per bit: improves about 25% per year
So… larger memory => more challenging applications (e.g., atmospheric modeling, astrophysics modeling)
Disk capacity: about 60% per year
So … huge disk capacities => large data storage (video, music files, large data for various applications)
Some Definitions:
Bit: A variable that can have only two possible values.
Byte: A byte (B) consists of a grouping of eight binary digits ("bits"), and is typically considered the smallest addressable unit of data.
RAM: (Random Access Memory) RAM is used to run certain basic programs and functions that your computer needs to operate correctly, and functions only while the computer is receiving power.
ROM: (Read Only Memory) : a type of unchangeable memory residing in chips on motherboard. ROM contains the bare minimum of instructions needed to start your computer.
Hard Disk Drive: The mechanism that controls the positioning, reading, and writing of the hard disk.
Basic Data Types
Data Type boolean char
Contains
True or False
Default false
Unicode Char /u0000 byte short
Int long
Signed integer 0
Signed integer 0
Signed integer 0
Signed integer 0 float double
IEEE 754 floating point
IEEE 754 floating point
0.0
0.0
32
64
8
16
32
Size (bit(s))
1
16
64
Range
N.A.
\u0000 to
\uFFFF
-128 to 127
-32768 to 32757
-2147483648 to
2147483648
-
9223372036854
775808 to
9223372036854
775807
-1.4e-45 to
3.402e+38
-4.9e -32 to
1.79e+308
Table for Quantifying Storage
Term
Byte
Kilobyte
Megabyte
Gigabyte
Terabyte
Abbreviation
B
KB
MB
GB
TB
Number of Bytes/bits
8 bits
1024= 2^10
1,048,576=2^20
2^30
2^40
Operating System
Operating System (OS.) is an interface between hardware and user which is responsible for the management and coordination of activities and the sharing of the resources of a computer.
Examples:
Linux
Mac Os X (Unix based)
Microsoft Windows
Solaris
Services Provided from OS.
Facilities for storing, manipulating data
Facilities for running software applications
Facilities for Communication with others
“It allows you to use the computer without any knowledge of coding. Without an operating system, the hardware would not work until you write your own code.”
Operating Systems (continued)
Earliest OS were designed for single user
Extensions: Multiple user in small connected networks could share information
Now: The computers across World Wide Web (internet) are able to communicate
Computer Networks
When 2 or more computers are connected, through electronic circuits or wireless transmissions of various designs and technologies for the purpose of exchanging data or communicating information between them.
Types of Networks by their size:
LAN: local- area network: covering a small physical area, like a home, office.
WAN: Covers a broad area (i.e., any network whose communications links cross metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries [2]
Network Architecture
There are two common architecture for computer networks:
Client- Server networks:
Client-server computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between service providers( servers) and service requesters, called clients.
Peer-peer networks: P2P, a distributed network architecture composed of participants that make a portion of their resources (such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth) directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination instances (such as servers or stable hosts).
Client- Server Approach
Wired Technologies for Computer Networks
Twisted –pair :The most widely used medium for telecommunication. Twisted-pair wires are ordinary telephone wire.
Data Transmission Speed: from 2 million bits per second to 100 million bits per second.
Coaxial cable: are widely used for cable television systems, office buildings, and other worksites for local area networks.
Data Transmission Speed: from 200 million bits per second to 500 million bits per second
Wired Technologies for Computer Networks( continued)
Fiber optic: consist of one or more thin filaments of glass fiber wrapped in a protective layer.
Data Transmission Speed: The speed of fiber optics is hundreds of times faster than coaxial cables and thousands of times faster than twisted-pair wire.
Different Types of Networks
Intranets :A set of networks, using Internet protocols, and
IP based tools such as web browsers and file transfer applications, under a control of administrative entity. extranets: is a network limited to a single organization or entity.
Internet: The a global system of interconnected governmental, academic, public, and private computer networks.
Network Hardware Components
Network Card: A piece of computer hardware to allow communication between computers.
Repeater: The device that clean the signals from noises, transmits it at a higher power level.
Routers: It forwards packets between networks.
Switches: This is distinct from a hub in that it only forwards the frames to the ports involved in the communication rather than all ports connected
Hub: When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied unmodified to all ports of the hub for transmission. The destination address in the frame is not changed to a broadcast address
Issues with Computer Networks
Develop techniques for computers to communicate
(software/hardware)
Especially important for multimedia communication made through protocols
Reliability is especially important –ensure data received successfully
Need for mathematical modeling
Internet
Internet
The world’s largest computer network. It means the network of networks.
History: 1969 the DOD project on building an Advanced
Research Projects Agency Networks (ARPANET), how to keep U.S. military sites in communication in case of war.
1994: It has 20 million users in more than 50 countries
2004: 800 million users
Internet (Continued…)
1968 - DARPA
(Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) contracts with BBN
(Bolt, Beranek & Newman) to create ARPAnet
1970 - First five nodes:
UCLA
Stanford
UC Santa Barbara
U of Utah, and
BBN
1974 - TCP specification by Vint Cerf
1984 – On January 1, the Internet with its 1000 hosts converts en masse to using TCP/IP for its messaging
Common Definitions
IP: An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical label that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes.
IPv4 addresses are usually represented in dot-decimal notation (four numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots, e.g. 208.77.188.166).
IP address
Continued …
Browser: A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web.
Host: ( internet node) is a computer node, that is connected to the internet.
Server: A host that host information resources as well as application software for providing network services, is a server.
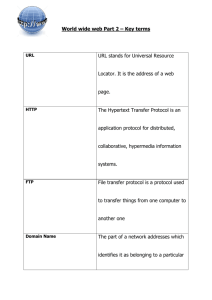
URLs: Stands for "Uniform Resource Locator." A URL is the address of a specific Web site or file on the Internet.
It cannot have spaces or certain other characters
Continued …
Router: Is an electronic device used to connect two or more computers or other electronic devices to each other, and usually to the Internet.
Firewall: A Hardware or software, or a combination of both that blocks an unauthorized access.
Proxy: In computer networks, a proxy server is a server
(a computer system or an application program) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers.
Internet Service Provider: (ISP) Is a company that provides
Modem
A modem (modulator-demodulator) is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information.
Cable Modem (1999)
600-1500 kbits/sec
DSL (2004)
1.5 Mbits/sec
WLAN-Wireless Local Area Network
Protocols
A set of rules which is used by computers to communicate with each other across a network. A protocol is a convention or standard that controls or enables the connection, communication, and data transfer, data formatting between computing end points.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers or
IEEE is a non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related to electricity.
Common Internet Protocols
ISO
TCP/IP
HTTP
SSH
Telnet
FTP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/
Internet Protocol (IP)
IP: How the data are to be physically transmitted from one computer to another.
TCP: Ensures that data being using IP are received without errors.
Note: TCP/IP form the foundation of many other high level application-oriented protocols.
Examples:
FTP: file transfer protocol
Telnet
SSH: Secure shell
Http: Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used for retrieving the hypertext
OSI
Open System Interconnection Reference Model
Is an abstract description for layered communications and computer network protocol design.
Network layers
Connection in TCP/IP
TCP/IP VS. OSI
Number of Hosts on the Internet
Host: Any computer connected to the internet- or any type of data network. A network host can host information resources as well as application software for providing network services.
Date
Aug 81
May. 82
Aug. 83
Oct. 84
Nov. 85
Dec. 86
Jul. 88
No. of hosts Date
213 Jan. 89
235
562
1024
Oct. 90
Oct. 91
Oct. 92
1,961
5,089
33,000
Oct. 94
Oct. 95
Jul. 96
No. of hosts
80,000
313,000
617,000
1,136,000
2,056,000
3,864,000
12,881,000
What is Happening on the Web
Sending packets of information (like sending a letter)
Delivery address: The location of the internet provider.
Return address: The location of your home.
Internet Domain Names and Addresses
o o
Domain name : A name that identifies one or more IP
Addresses, they are used in URLs to identify particular
Web pages.
Example1 : umd.edu represents about a dozen IP addresses.
Example 2: in URL https://mail.umd.edu/ mail.umd.edu is the domain name.
Internet is based on IP addresses, not domain names, every web server requires Domain Name System (DNS) server to translate domain names into IP addresses.
Email addresses
Email addresses follow a three-part format:
Person’s UserID@ domain name of the computer.
Parastoo@umd.edu
Parastoo@gmail.com
Top Level Domains( TLD)
Every domain name has a suffix that indicates which top level domain (TLD) it belongs to. There are only a limited number of such domains.
gov - Government agencies edu - Educational institutions org - Organizations (nonprofit) mil – Military com - commercial business net - Network organizations ca – Canada th - Thailand
Domain Names and Address Resolution
Internet Services
Basic Services the World Wide Web is providing:
E-mail: Sending and receiving Electronic messages
Telnet: The Telecommunication Network allows user to remotely login to computers over the network.
File Transfer: The File Transfer Protocol enables copying files from one computer to another computer in the network.
Examples of the Internet Services
http:// www.ence.umd.edu/welcome.html
Connects to an HTTP server and retrieves an HTML file.
ftp://rtfm.mit.edu/pub/usenet
Opens an FTP connection to the usenet frequently asked questions stored at rtfm.mit.edu
Hypertext and Hypermedia
Hypertext: The same as regular text - it can be stored, read, searched, or edited - with an important exception: hypertext is text with pointers to other text.
Hypermedia: is a superset of hypertext. Hypermedia documents contain links not only to other pieces of text, but also to other forms of media - sounds, images, and movies.
Uniform Resource Locators
The Web employs called Uniform Resource Locators( URLs) to represent hypertext, hypermedia links to network services within Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) documents.
URL format:
First part: The method of accessing (http is the most common one)
Second part: is the address of the computer where the data or service is located.
Further parts: Specify the names of files, the port to connect, or the text to search for in a database.
http://www.ence.umd.edu/welcome.html
Web Search Engines
A web search engine is simply a computer program that allows users to make queries for information residing in a database.
The URLs for some of the good search engines are as follows:
Search Engine
Yahoo
Alta Vista google
Uniform Resource Locator http://m.www.yahoo.com/ http://www.altavista.digital.com
http://www.google.com/