Power Point
advertisement

Providing Specially Designed
Instruction in Inclusive Settings
“If you don’t know where you are headed, you’ll probably end up
someplace else.”
-Douglas J. Eder, Ph.D
Hmmmm!!!!!
Begin with the End in mind
•
Administer assessment linked to CCSS
•
Analyze test data
Reading Skills (learning HOW to read)
vs.
Comprehension (reading for meaning)
Vocabulary
•
Determine focus for intervention
Curriculum analysis
Point of entry into curriculum
Degree of accommodations/
modifications
Assessment tied to CCSS
Begin with the End in mind
Analyze curriculum (CCSS)
Anchor Reading Standards (RI):
Key Ideas and details (RI.1,2,3)
Craft and Structure (RI.4, {L.4,5,6} 5,6)
Integration of Knowledge and ideas (RI.7,8,9)
Range of Reading and Level of Text complexity
(RI.10)
Anchor Reading Standards (RL):
Key Ideas and details (RL.1,2,3)
Craft and Structure (RL.4, {L.4,5,6} 5,6)
Integration of Knowledge and ideas
(RL.7, NO 8, 9)
Range of Reading and Level of Text
complexity (RL.10)
CCSS - Vocabulary
• Reading Areas in CCSS:
– Reading for Literacy – 9 standards
– Reading for Informational Text – 10
standards
• R.L.4 and R.I.4 – Vocabulary
– Add Language Standards 4, 5 and 6
• Standards in each reading area
minimally
– 4 of the 12 (33%) in the area of
Vocabulary
• CCSS Vocabulary – 3 tiers
Vocabulary in context of ELA standards:
“vocabulary instruction has been neither
frequent nor systematic in most schools”
National Governor’s Association Center for Best Practices
Council of Chief State School Officers [NGAC/CCSSO}, 2010, p. 32
“vocabulary has been empirically
connected to reading
comprehension since at least
1925 and had its importance to
comprehension confirmed in
recent years”
(Whipple, 1925)
(NGAC/CCSSO. 2010, p.32)
Strategies That Most Impact Achievement
Rank
1
Strategy
Extending
Thinking Skills
Percentile
Gain
45
(compare/contrast; cause/effect; classifying;
analogies/metaphors
2
Summarizing
34
3
Vocabulary In Context
33
4
Advance
Organizers
28
5
Non-Verbal
Representations
Visible Learning ES = 0.67
25
3 Tiered System for Selecting Target Words
Beck & McKeown (1985)
400,000 words
7,000 words
5,500 words
Word Types
Tier 1: Basic
Tier 2: Academic
Tier 3: Content Specific
home
dog
happy
see
come
again
find
go
look
boy
analyze
approach
role
consist
major
require
significant
vary
interpret
consequence
volcano
lava
pumice
glaciated
abdominal
peninsula
molt
phonological
diphthong
quadrilateral
Beck et al. (2002)
Criteria for selecting words to teach
• Have poor or no context clues in the text being read
• Are critical to understanding academic texts, both
literary and informational
• Appear in all sorts of texts and are highly generalizable
• Require deliberate effort to learn, unlike Tier 1 words
• Are far more likely to appear in written
texts than in speech.
• Often represent subtle or precise ways
to say otherwise relatively simple things
• Are seldom heavily scaffold by authors or
teachers, unlike Tier 3 words
Beck, et al
Choosing words
• Jose avoided playing the ukulele.
• Which word would you choose to
pre-teach?
Which word?
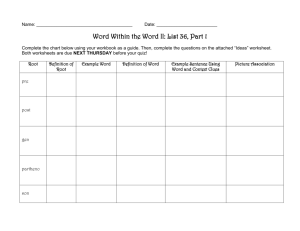
Find this handout
In early times, no one knew how volcanoes
formed or why they spouted red-hot molten rock. In
modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes.
They still don’t know all the answers, but they know
much about how a volcano works.
Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The
top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep
beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is so
hot that some rock melts. The melted, or
molten, rock is called magma.
Volcanoes are formed when magma
pushes its way up through the crack in the
Earth’s crust. This is called a volcanic
eruption. When magma pours forth on the
surface, it is called lava.
In early times, no one knew how volcanoes
formed or why they spouted red-hot molten rock. In
modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes.
They still don’t know all the answers, but they know
much about how a volcano works.
Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The
top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep
beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is
so hot that some rock melts. The melted,
or molten, rock is called magma.
Volcanoes are formed when magma
pushes its way up through the crack in the
Earth’s crust. This is called a volcanic
eruption. When magma pours forth on the
surface, it is called lava.
Red Words are Tier 2
Green Words are Tier 3
How Many Words?
• In school settings, students can be explicitly
taught a deep understanding of about 300 words
each year.
• Divided by the range of content students need to
know (e.g., math, science, history, literature), of
these 300–350 words, roughly 60 words
can be taught within one subject area
each year.
• It is reasonable to teach thoroughly
about five to ten words per week.
(Marzano, Beck, and Chall )
Vocabulary Casserole
Ingredients Needed:
20 words no one has ever heard before in his life
1 dictionary with very confusing definitions
1 matching test to be distributed by Friday
1 teacher who wants students to be quiet on Mondays copying
words
Put 20 words on chalkboard.
• Have students copy then look up in dictionary.
• Make students write all the definitions.
• For a little spice, require that students write words
in sentences.
• Leave alone all week.
• Top with a boring test on Friday.
Perishable. This casserole will be forgotten by
Saturday afternoon.
Serves: No one.
Adapted from When Kids Can’t Read,
What Teachers Can Do by Kylene Beers
Vocabulary Treat
Ingredients Needed:
5-10 great words that you really could use
1 thesaurus
Markers and chart paper
1 game like Jeopardy or BINGO
1 teacher who thinks learning is supposed to be fun
Mix 5 to 10 words into the classroom.
• Have students test each word for flavor.
• Toss with a thesaurus to find other words that
mean the same.
• Write definitions on chart paper and let us draw
pictures of words to remind us what they mean.
• Stir all week by a teacher who thinks learning is
supposed to be fun.
• Top with a cool game on Fridays like jeopardy or
BINGO to see who remembers the most.
Serves: Many
Adapted from When Kids Can’t Read,
What Teachers Can Do by Kylene Beers
R.I. 3.4
R.I. 3.4, L.4.4, 4.5
R.I. 2.4, L.3.4
4th grader with overall 2nd
grade vocabulary skills
POE: Point of Entry into Curriculum
Grade: Fourth – Checklist of CCSS Essential Skills
Anchor 4: Interpret words and phrases as they RL.4.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Use context clues to help determine the
are used in a text, including determining
meaning of unknown words or phrases in text
technical, connotative, and figurative
Use definitions, examples, or restatements to
meanings, and analyze how specific word
help figure out the meaning of unknown words
choices shape meaning or tone.
or phrases in text
Reading Standard for Literature: RL.4.4
Determine the meaning of words and phrases
as they are used in a text, including those that
allude to significant character found in
mythology (e.g., Herculean). (see Language
Standards 4-6 for additional expectations)
Reading Standard for Informational Text:
RI.4.4
Determine the meaning of general academic
and domain-specific words or phrases in a text
relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area.
(See grade 4 Language Standards 4-6 for
additional expectations.)
Use strategies such as: using a glossary,
footnote, or digital media, to determine the
meaning of an unknown word or phrase
Identify major mythological characters and their
traits
RI.4.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Know how to use a dictionary to determine the
meaning of unknown words
X Understand that words may have multiple
meanings
X Use root words, Latin and Greek suffixes and
prefixes to determine the meaning of academic
words used in science, history/social studies
X Use antonyms and synonyms as clues to find the
meaning of grade level words
Understand that words may be used as figurative
Language
Recognize when words are used as a common
idiomatic expression
Grade: Fourth – Checklist of CCSS Essential Skills
Language Standard: L.4.4
L.4.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Determine or clarify the meaning of
Have strategies for solving unknown
unknown and multiple-meaning words and
words
phrases based on grade 4 reading and
Understand that the context may
content, choosing flexibly from a range of
provide clues to help determine the
strategies.
meaning of a word or phrase
a. Use context (e.g., definitions,
X Identify the most common Greek and
examples, or restatements in text) as a
Latin affixes and roots
clue to the meaning of a word or
Use common Greek and Latin affixes
phrase
and roots to solve unknown words
b. Use common, grade-appropriate Greek
Use a pronunciation guide in a
and Latin affixes and roots as clues to
dictionary to help read unknown
the meaning of a word (e.g.,
words
telegraph, photograph, autograph)
Know how to use a textbook glossary
c. Consult reference materials (e.g.,
Access reference materials, including
dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses),
digital, to help determine the precise
both print and digital, to find the
meaning of key words
pronunciation and determine or clarify
Use a print or digital dictionary to
the precise meaning of key words and
locate definitions of key words and
phrases and to identify alternate word
phrases
choices in all content areas
Identify alternate word choices using
print or digital thesauruses or
Grade: Fourth – Checklist of CCSS Essential Skills
L.4.6 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Language Standard: L.4.6
Develop a corpus of
Acquire and use accurately
grade level academic
grade-appropriate general
words and phrases
academic and domain-specific
X Determine which word
words and phrases, including
best describes an
those that signal precise
action, emotion or state
actions, emotions, or states of
of being
being (e.g., quizzed, whined,
Understand that words
stammered) and that are
have nuances and
basic to a particular topic
various shades of
(e.g., wildlife, conservation,
meaning
and endangered when
Acquire and use words
discussing animal
that are basic to underpreservation).
standing a concept
Anchor: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical,
connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone .
R.L.2.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
R.L.3.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Distinguish between words and phrases
Distinguish between words, phrases, and
Distinguish the “cadence” of spoken
sentences
Determine word
language
Determine
wordand
andphrase
phrasemeaning
meaning
through context
context
Ability to hear same and/or differing sounds
through
in words
Distinguish between literal and non-literal
Ability to see and hear the pattern of the
language
spoken language
Know that alliteration means words start
with the same or similar sounds
Know that often authors repeat the same
lines for emphasis or effect
R.L.4.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
R.L.5.4 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Usecontext
context
clues to help determine the
Usecontext
contextclues
clues to help determine the
Use
clues
Use
meaning of unknown words or phrases in
meaning of unknown words or phrases in
text
text
Use definitions, examples, or restatements
Use definitions, examples, or restatements
to help figure out the meaning of unknown
to help figure out the meaning of unknown
words or phrases in text
words or phrases in text
Use strategies such as: using a glossary,
Understand that words and phrases often
footnote, or digital media, to determine the
have literal and figurative meanings
meaning of an unknown word or phrase
Know that similes and metaphors are words
Identify major mythological characters and
used to compare two objects
their traits
Use glossary, footnotes, or digital sources to
determine the meaning of an unknown word
or phrase
Vocabulary objective
In Reading assessment
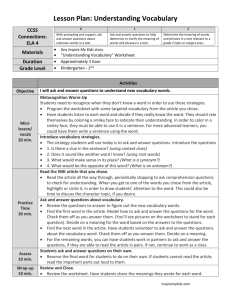
Creating a Tiered Lesson
Anchor 1:
Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to
make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence
when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from
the text.
Grade Level Standard: (4th grade) CCSS RL.4.1/RI.4.1:
Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what
the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from
the text.
Preassessment:
Evidence the students can answer who, what, when, why,
and where questions and refer to the text for the answers.
Informal checkup (thumbs up/down) by asking: “Do
authors always say exactly what they mean?”
Vocabulary quiz: 10 Tier 2 words relating to reading selection
Grade: Ninth and Tenth
Grade: Eleventh and Twelfth
Reading Standard for Literature: RL.9-10.1/RI.9-10.1) Reading Standard for Literature:
Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support
RL.11-12.1/RI.11-12.1
analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as
Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support
inferences drawn from the text.
analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as
inferences drawn from the text, including
determining where the text leaves matters uncertain.
RL.9-10.1 Essential Skills and Concepts:
RL.11-12.1 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Analyze the text
Analyze the text (RI.11-12.1)
Identify explicit textual evidence
Identify explicit textual evidence (RI.11-12.1)
Cite evidence
Cite evidence
Draw inferences
Draw inferences
Support inference using several pieces from
Support inference using textual evidence
the text
Determine matters of uncertainties (RI.11Provide varying degrees of support (evidence)
12.1)
RI.9-10.1 Essential Skills and Concepts:
RI.11-12.1 Essential Skills and Concepts:
Identify what is explicitly stated in the text
Infer additional information from a text
Identify inference that can be drawn from the
Distinguish between inferences and explicit
text
ideas
Provide support for analysis of the text
Determine uncertainties in the text
Identify hierarchy of evidence to support
analysis
Tier 1
Tier 2
• Can the student apply • How can the author’s meaning be
Critical
knowledge of an
determined if it is not explicit in the
Questions
author’s use of
text?
inferences to own
• What clues (details) in the text can
writing of paragraphs,
be used to infer meaning?
poems, or songs?
• How is inferring a problem-solving
strategy?
Resources Literature book
Literature Book
Smart Board
Inference chart
Day 1
Writing Journal
Learning Centers:
Day 1:
Student selected and lead
Group leader/partner at
1. Inferring Meaning from Pictures
learning centers
2. Inference Riddle Game
Day 2:
3. Who’s Talking?
Must complete centers 4. Inferring Meaning from Poems
Day 2
Focus group for sharing
Learning Centers:
writing
1. Reading story and Infer (teacherlead)
2. Create Your Own Inferences
3. Test Prep Story (teacher-lead)
Graphic organizer: Inference Chart
Center Checklists for
Center Checklists for teacher-led
Means of
centers
Assessment teacher-led centers
Rubric for writing activity Homework
Homework
Where Next Quote from text using
author’s name and
Citing specific example and details to
support inferences
Tier 3
• What does infer mean?
• How can context clues help in the
process of inferring?
• What clues besides words can help infer
author meaning?
Parallel and Station Teaching Co-Teaching
Models
Vocabulary development (Base on PreAssess)
Word Questioning Strategy
Marzano’s Six Step Process for Learning
Vocabulary
Cooperative Group Learning Activity to
discover meaning of infer:
Detectives and clues
Story on CD
Context Clues: Silly Word Game
Teacher selected centers based on individual
abilities and needs
All written work adjusted to student
independent reading level
Rubric for cooperative group learning activity
for roles assigned
Center Checklist for teacher-led centers
Homework to focus on Context Clues with
adjusted reading level
Draw inferences
Your Turn
1. Find the handouts entitled
“Creating a Tiered Lesson” (one
elementary science and one secondary
math)
2. Choose the one appropriate for the
level you prefer
3. Tier 2 has been completed as the
lesson for that grade level
4. Modify the topics on the lesson
plan for Tiers 1 and 3
Tiered Lesson: 2nd Grade Science
Unit, Chapter, or Big Idea: Animals, like humans, change as they grow. What are the similarities and differences between
humans and animals?
Grade Level Standard: (2nd grade) Relate observations of an animal’s (ex. butterfly) life cycle to students’ growth and
changes.
Preassessment: Have students studied life cycles of other animals before? What do they know already about changes and
growth?
Tier 1
Tier 2
Tier 3
Critical
Compare your life cycle to that of How is your life cycle similar to
How are you like a butterfly?
Questions
animals other than butterflies.
and different from that of a
How are you different from a
How is it similar or different?
butterfly? Compare and contrast. butterfly?
Butterfly kit
Resources
Butterfly kit
Butterfly kit
Domain-specific Vocabulary
Observation forms, and journals, Observation forms and
Modified observation forms
Graphic organizer (can also create Journals
(simplified terms) and journals
own if desired)
Graphic organizer
(can, cut and paste)
KWL (can research independently KWL
Modified graphic organizer (Cloze)
for “what I want to know”)
Word Wall
Word Wall (only required to do
Word Wall
some based on voc. assessment)
Means of
Cooperative groups create
Cooperative groups create
Cooperative groups create
Assessment
slideshow of animal life cycle and slideshow of animal life cycle and slideshow of animal life cycle and
model of butterfly’s life; all
model of butterfly’s life; all
model of butterfly’s life; all
students participate and have
students participate and have
students participate and have
active roles (roles will be
active roles; Rubric
active roles (roles will match
sufficiently challenging); modified
readiness level); modified rubric
rubric
Where Next
Begin to observe other animals
Begin to observe other animals
Begin to observe other animals
and discuss habitats as they relate and discuss habitats as they relate and discuss habitats as they relate
Unit, Chapter, or Big Idea: Solving with variables
Secondary Work Task
Grade Level Standard: CCSS HSA REI.C.6 (Algebra 1 Reasoning, Equations & Inequalities) Solve
multistep linear equations in multiple variable and apply skills toward solving practical problems
Preassessment: Do students know what variables are? Can they solve single-step linear equations using
variables?
Tier 1
Tier 2
Tier 3
Critical
Given a multistep linear
Given a single-step linear
Given a multistep linear
Questions
equation in multiple variables, equation in one variable, can equation in one variable, can
you apply skills toward solving you apply skills toward solving
can you apply skills toward
a practical problem?
a practical problem?
solving a practical problem?
Textbook
Resources
Textbook
Textbook
Domain-specific Vocabulary
Worksheet (with more
Worksheet
Adapted worksheets (with
complex problems)
single-step equations)
Reader for problems
Manipulatives, Examples
Means of
Compete adapted worksheet Complete worksheet
Compete adapted worksheet
Assessment Homework 1-5 (application
Homework 1-30 (process and Homework (modified 1-5)
questions)
calculation)
Can talk out problems with
teachers
Where Next Analyzing complex linear
Solving multistep linear
Solving multistep equations
equations with variables and OR solving single-step
equations and interpreting
interpreting results on number equations with variables and
results on number line;
interpreting results on simple
demonstrating application of line
number line
number line results
Functional Skills
Objectives:
1. Student will identify areas of responsibility in personal
appearance.
2. Students will identify appropriate and inappropriate dress,
appearance.
3. Student is expected to choose appropriate garments for
various social situations.
4. Student will be able to observe his or her own appearance
and determine if acceptable.
5. Student will be able to observe the appearance of others
to determine if acceptable.
6. Student is expected to choose and identify from pictures
which examples of appearance are socially acceptable.
C Layer
Key daily topics use prompts as needed, augmentative communication devices, one to one
training and small group strategy teaching. Daily one to one training [or small group training
with higher level]
Assignment Choices: [some students require physical assistance here]
Each day present 2 activities to student for choice. Keep a checklist record of choice
activities for each child and rotate activities so by Friday each student has done most activities.
1. Watch videotaped illustrations of presentable appearance, and unacceptable appearance.
[These can be commercial or your taped videos of different people.]
2. Students create clothing 'ensembles' to dress paper dolls -student chooses articles of
clothing to dress appropriately dressing paper dolls as examples and next communicates
with teacher as to where their dolls might be going when dressed this way.
3. Language Master: students choose what to wear to one of these social events; a party,
going to church, baseball game, school, add your own ideas. [ tape the clothing words on
cards and attach pictures to language master cards.]
4. Match picture and words cards with set of Barbie/Ken dolls dressed for various occasions.
5. Choose and listen to a tape recorded story of dressing up for specific occasions, birthdays,
church, dances, the movies, working on the farm, etc. [have 4 or 5 on tape.]
6. Match pictures of clothes to picture illustrations of categories, slouchy, dress up, everyday.
7. Sort clothes for washing, into whites, and colors piles, or into tops and bottoms piles, and
name them as you sort.
8. Name label each article of clothing in the clothes basket with a name card, or picture.
B Layer
Note: Use prompting only if needed.
The way others dress
1. Teacher dresses differently each day, depicting different social and work
situations. Students guess/decide what activity the teacher is dressed for,
where she is going, what she will do there.
2. Students go throughout the school building and take pictures of others
students and adults. Then back in class print out or use on computer and
critique dress of others and record if they were appropriately attired for
school and work or their outfit was not appropriate for school or work. [Be
sure to get PE coach and café workers]
3. Selecting clothes for another person. Students select an appropriate outfit
for someone else, from a clothes basket collection, of like or similar colors,
complementary colors, and colors they would like that other person to wear,
to complete an outfit suitable to wear out to a social event. [Name/ID, colors
and pieces of clothing]
4. The chosen partner student dresses up using clothes outfit chosen, then
asks another persons opinion, Am I dressed appropriately, what do you
think?
A Layer
Choose and modify according to student
Teacher: Use a digital camera to record student dress everyday for the
previous week.
The way I dress.
1. Ask the student to look at what he or she is currently wearing.[today]
Are you dressed well today?
Tell/show me two places it would be appropriate to wear this outfit.
[some students will use pictures to communicate answers here.]
Where else could you wear this outfit?
2. Go to computer and show student their dress from the pictures you
took everyday last week. Evaluate appropriateness
Grade scale:
Introduce, [teaching],
In progress [learning] ,
Mastery [performance criteria met],
Maintain. [skill maintenance]
Questioning Strategies-Study Skills
C Layer: Maximum 65 points in this section.
1. Take notes on questioning strategies.
5 points
2. Complete EASY strategy worksheet.
15 points
3. Complete FIST strategy worksheet.
15 points
4. Complete PARS strategy worksheet.
15 points
5. Complete RARE strategy worksheet.
15 points
6. Complete ReQuest strategy worksheet.
15 points
7. Complete QAR strategy worksheet.
15 points
8. Complete I-CHART strategy worksheet.
15 points
9. Complete QUESTION THE AUTHOR strategy worksheet.
15 points
10. Write 3-5 open-ended questions related to a topic/concept.
15 points
11. Write 3-5 closed-ended questions related to a topic/concept. 15 points
12. Pair with another student to design a questioning worksheet. 15 points
13. Exchange questioning worksheet with another pair and complete it.
B Layer: Choose one. Maximum 20
points in this section.
1. Apply a questioning strategy using
expository text.
2. Apply a questioning strategy using
narrative text.
3. Apply a questioning strategy on a
test.
4. Read a passage and design
questions for another student.
5. Document usage of strategy in
another class or subject.
6. Design a structured interview.
Grade Scale:
A Layer: Choose one. Maximum 20
points in this section.
1. Document and discuss the
academic and social benefits of
questioning.
2. Use a questioning strategy to
analyze a real world problem,
issue or event.
3. Demonstrate how your favorite
questioning strategy has improved
your grades.
0-40 = F
41-55 = D
56-70 = C
71-85 = B
86-100 = A
Layered Curriculum for Nonfiction Unit
Each student must complete the needed number of points at each level. These projects
must be kept together, but they can be reviewed separately at anytime.
C level activities: Must have at least 40 points
1. Oral read a nonfiction book to a friend. – 10 points
2. Listen and take notes of one of Mr./Ms _______ ‘s lectures – 10 points
3. Find a Nonfiction book and explain to friend the visual clues that tell you it is a nonfiction book –
5 points
4. Make a book list or chart of books that fit into the different nonfiction categories: Description,
Temporal Sequence, Compare and Contrast, Cause and Effect, and Problem and
Solution. There should be five books in each category. A book might be present in multiple
categories - 20 points
5. Make flash cards defining the meaning of the nonfiction visual clues and different nonfiction
categories – index, caption, glossary, table of contents, title page, Description, Temporal
Sequence, Compare and Contrast, Cause and Effect, and Problem and Solution. – 15 points
6. Make a poster – reporting some of the interesting facts you learned from a nonfiction book. –
5 points
7. Write a page, every-line letter to your friends about the book, sharing your thoughts. Read the
letter to the class. - 10 points.
8. Write a rhyme or poem to help you remember the visual clues of a nonfiction book. – 5 points
9. Think of a topic - Find as many nonfiction books about that topic as you can. Use my library
and the school library. Write the topic and all the titles on a piece of paper – 5 points
B level activities - 20 points
1. Find two books about the same topic
Create a Venn Diagram showing the
similarities and differences between
the two books – 10 points
2. Read and orally present a book to the
class or a small group. Tell us what it
is about. Why you liked or disliked
it. Tell us any interesting facts you
found. This should be short – 5
minutes of talk time. You need to be
able to field questions about your
book. - 10 points
3. Read a nonfiction book and create 10
questions you could ask to test the
comprehension of another student
who read the book. 10 points
4. Make flash cards of at least ten new
words you encountered in the book.
Put the word on one side, the
definition and the word used in context
on the other side. 10 points
A level activities: 20 points needed
1. Write an Essay explaining to me
your three favorite reference
books and why – 20 points
2. Read a nonfiction book - Write an
essay explaining three reasons
you liked or disliked the book. –
20 points
3. You are an author, and you are
writing a nonfiction book. Write a
letter to a publisher giving her
three reasons why the company
should print your nonfiction book.
20 points
What does it take to meet the needs of
100% of the students 100% of the time?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Use assessment to drive instruction
Know curriculum
Use data to make decisions
Monitor student progress to inform
instruction
Use a problem solving approach to
make decisions
Intervene early
Use a collaborative model of service
delivery (shared responsibility)
Use research-based instruction
John Dewey