Astronomy - Final – Review Sheet NAME: PD: ______ Sun – Inner
advertisement
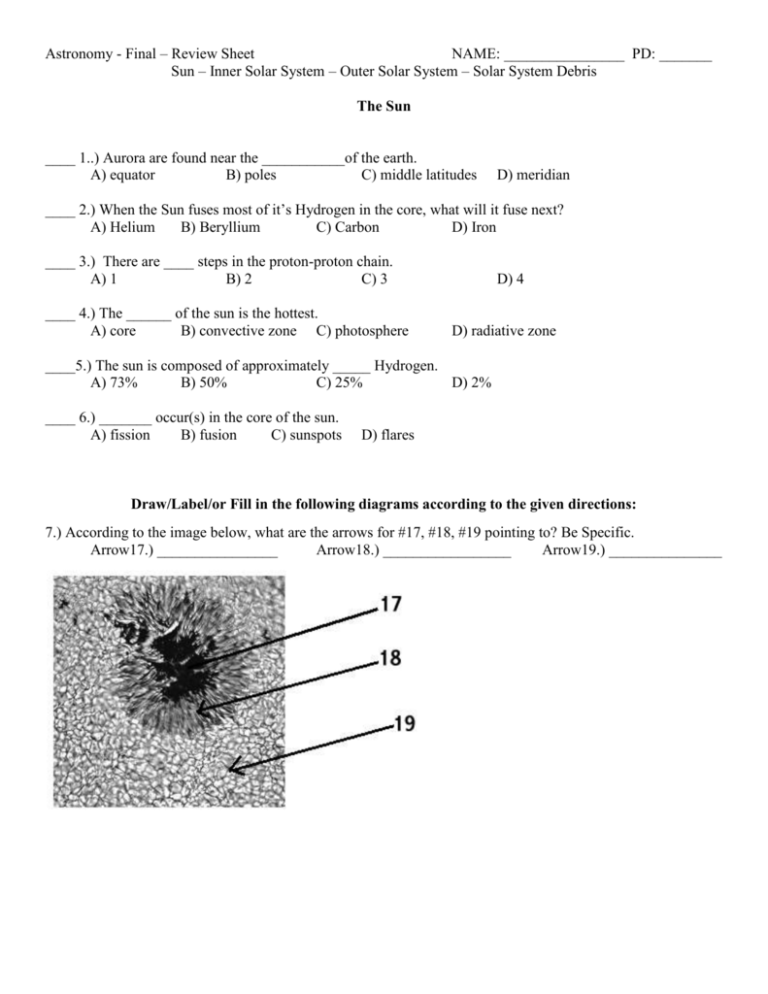
Astronomy - Final – Review Sheet NAME: ________________ PD: _______ Sun – Inner Solar System – Outer Solar System – Solar System Debris The Sun ____ 1..) Aurora are found near the ___________of the earth. A) equator B) poles C) middle latitudes D) meridian ____ 2.) When the Sun fuses most of it’s Hydrogen in the core, what will it fuse next? A) Helium B) Beryllium C) Carbon D) Iron ____ 3.) There are ____ steps in the proton-proton chain. A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 ____ 4.) The ______ of the sun is the hottest. A) core B) convective zone C) photosphere D) 4 D) radiative zone ____5.) The sun is composed of approximately _____ Hydrogen. A) 73% B) 50% C) 25% D) 2% ____ 6.) _______ occur(s) in the core of the sun. A) fission B) fusion C) sunspots D) flares Draw/Label/or Fill in the following diagrams according to the given directions: 7.) According to the image below, what are the arrows for #17, #18, #19 pointing to? Be Specific. Arrow17.) ________________ Arrow18.) _________________ Arrow19.) _______________ Inner Solar System: Match the following description to the planet. Write (ME) for Mercury , (V) for Venus, (E) for Earth, and (MA) for Mars. ___ 8.) Largest terrestrial planet ___ 9.) Has the largest volcano ___ 10.) Has the thickest atmosphere. ___ 11.) Has a disproportionately large iron core. ___ 12.) Has captured 2 asteroids that are now orbiting it ___ 13.) Contains an ozone layer ___ 14.) Contains lobate scarps ___ 15.) Rotates backwards 16) What is the name of the biggest volcano in the Solar system? What is the name of the largest canyon in the solar system? 17) What are the two main features of Mercury that make it unique from any other planet or moon? 18) The two exploration rovers on Mars found proof of past water on mars. What mineral did they find? Why is does this mineral show there was liquid water on Mars? Outer Solar System: (C) Callisto Match the corresponding satellite to the information given below: (E) Europa (G) Ganymede (I) Io (T) Titan (Tr) Triton ____ 19.) Has a thick atmosphere. ____ 20.) This satellites interior is mostly molten magma. ____ 21.) This moon has a large ocean under the ice. ____ 22.) Resembles an early earth, before life appeared. ____ 23.) The farthest Galilean moon from Jupiter. ____ 24.) Undergoes the most tidal heating and has the youngest surface of any moon. ____ 25.) The most volcanically active object in the solar system. ____ 26.) Has geysers of Nitrogen shooting from its surface. ____ 27.) The largest Galilean moon. 28) This is a schematic of the interior of Juptier. Label what the different layers in this planet are composed of. _______A. __________B. _______________________D. _______________________________C. 29) In the above diagram, which layer is Neptune and Uranus missing? Why? 30) Name 2 ways in which shepherd moons help sustain a ring system. 31) Most astronomers believe a moon in the solar system is the best place to search for life. Identify this moon, and explain why they think it’s the best place to search for life. 32) Explain why the earth does not have belt-zone circulation, and storms that last large amounts of time. 33.) Explain what the Roche limit is. What happens to large objects inside the limit? Solar System Debris: Match the asteroid to the descriptions below. You can use each asteroid more than once. (C) C-type (S) S-type (M) M-type ___34.) This type is always differentiated ___35.) Usually composed of Iron ___36.) The least common type of asteroid ___37.) This type is very dark in color ___38.) This type often contains complex organic molecules. ____39.) Chondrules are not found on _______ meteorites. A) Stony B) Stony-Iron C) Iron D) C-type ___40.) ______ are the most rare types of meteorites. A) M-type B) Stone C) Stony-Iron D) Iron ___41.) ______ are the most common type of meteorite found. A) M-type B) Stone C) Stony-Iron D) Iron ___42.) Almost all meteors seen during a meteor shower come from dust of a(n) ______. A) asteroid B) planet C) comet D) NEA ___43.) Pluto has the same composition, orbit, and a has similar size as a(n) ____________. A) Planet B) Oort cloud comet C) Asteroid D) Kuiper belt comet ___44.) _______ are small glassy teardrop-shaped minerals found in the ejecta blanket of craters. A) Chondrules B) Tektites C) Shocked Minerals D) Blanket materials ___45.) A comet with an orbital period of a few thousand years most likely originated from the __________. A) Asteroid Belt B) Trojan Belt C) Kuiper Belt D) Oort Cloud 46.) Why is Pluto not considered a planet anymore? 47.) What is the largest Kuiper Belt object named?