Earthquakes
advertisement

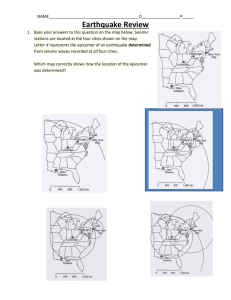
Earthquakes And Earth’s Structure Earth’s Structure Origin of the Earth • Meteors and Asteroids bombarded the Earth • Gravitational compression • Density Stratified planet Earth’s Interior • Core – – – – dense Iron and Nickel Inner Core - solid Outer Core - liquid • Mantle – – – – Less dense than core Iron and Magnesium silicates Mostly solid Upper mantle is partially molten • Crust – Outermost layer – Very thin and rigid – Continental – granite – Density = 2.8 g/cm3 – Oceanic – basalt – Density = 3.0 g/cm3 Evidence of Internal Structure • Density – calculate density of Earth – Speculate on probable compositions • Meteorites – Use composition and age to determine composition and age of Earth • Seismic waves – Travel times and direction give indication of internal structure of Earth Granite Basalt Types of Seismic Waves • P waves – Primary waves – Push and pull movement – Travel fastest (~ 6 km/sec) – Travel thru solids and liquids • S waves – Secondary waves – Move side-to-side – Slower (~ 4 km/sec) – Travel thru solids only Seismic Waves Through Earth What is an Earthquake? • The vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Elastic Rebound Theory • The crust will first bend • When the stress exceeds strength of the rock, it will “snap” into a new position • In the process of breaking, “seismic waves are released Parts of an Earthquake • Focus –place within earth where EQ originate • Epicenter – Location on surface directly above the focus • Energy released radiates in all directions from the focus • Energy is in the form of waves – “seismic waves” How Do We Locate an Epicenter? Seismograph • Instruments around the world record EQ • Record Earth movements by stationary mass on rotating drum • Use seismogram to: – Locate an epicenter – Determine magnitude Seismogram • Help determine the epicenter • Measure the distance between P- and S-waves – This is the time difference in arrival times Locating the Epicenter • Plot the time difference on y-axis (time interval) • Trace plot to blue line to determine distance to epicenter Locating an Epicenter Triangulation • Measure that distance around the seismic station • The epicenter may be located anywhere on that line • A minimum of 3 seismic stations are needed to determine the epicenter Determining Magnitude • Measure the amplitude of the strongest wave • The amplitude is the height on paper • Plot distance between pand s-wave • Plot amplitude • Connect plots to determine magnitude You are now a Seismologist!! Virtual Earthquake Introduction: http://vcourseware5.calstatela.edu/Vir tualEarthquake/VQuakeExecute/htm Virtual Earthquake: http://sciencecourseware.org