Java
advertisement

Concurrent & Distributed Computing
PRACTICAL 2 – More Features of Java
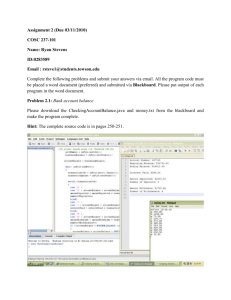
You can now use the NETBEANS Development Environment for editing/compiling/running your
programs (You may need to refer to an online NetBeans Tutorial for further information, or you
may wish to download NetBeans from the link https://netbeans.org/downloads/index.html
(download the JavaEE version with Glassfish and Tomcat).
Question 1 - Introduction to NETBEANS
Open the NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
To start development:
Click > File > New Project to display the dialog box below:
Select Java and Application in the Projects section and click Next to display the New Java
Application dialog box, as shown below.
Complete the details regarding the Project Name, Project Location, Create Main Class
(called Project) and click Finish.
The new project is then displayed in the IDE as follows:
As show below, the default creation has produced a MageeProject file with a package called
mageeproject and the specified class called MyHelloClass as shown below.
Develop the “MyHelloClass.java” file as follows:
package mageeproject;
public class MyHelloClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello From Magee!");
}
}
Build and Run the program
The results should be as follows:
The results are displayed in the lower right window.
Note. You can also Build/Run by right-clicking on the project and selecting from the context
menu.
Congratulations you have run a Java program in NetBeans.
Question 2 – Scanner class
In “MageeProject” create a package called “pract1Q2” and create a class called “TestScanner”
in the “pract1Q2” package and test the program below:
import java.util.Scanner; // Note Using Scanner class
public class TestScanner
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print( "Type two integers: " );
int i1 = scan.nextInt(); //reads an integer
int i2 = scan.nextInt(); // reads an integer
System.out.println( "They were " + i1 + " and " + i2 );
System.out.print( "Type two words: " );
String firstWord = scan.next(); //reads a string
String secondWord = scan.next(); // reads a string
System.out.println( "They were " + firstWord + " and " + secondWord );
} // end main
} // end TestScanner
Question 3 – Exception Handling with Input
Create a new project to test the following program:
import java.io.*;
public class Testio {
// method to convert a string representation to equivalent integer value
public static int stringToInt(String s) {
Integer idValue = null;
try {
idValue = new Integer(s);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Exception caught from toInt() : " + e.getMessage());
} // end catch
return idValue;
} // end method stringtoInt
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
// maps the default System.in stream to BufferedReader so readLine is available
BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Type two integers with a <return> after each: ");
System.out.flush();
int i1 = stringToInt(cin.readLine());
int i2 = stringToInt(cin.readLine());
System.out.println("The integers were " + i1 + " and " + i2);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Type two words with a <return> after each: ");
System.out.flush();
String firstWord = cin.readLine();
String secondWord = cin.readLine();
System.out.println("The words were " + firstWord + " and " + secondWord);
} // end main
}
Question 4 – Reading Console Input
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 5 – Reading Strings from the Console
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 6 – InputStream and OutputStream
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 7–Java Exceptions
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 8 –Java Interfaces
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 9 –Using Packages
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 10– Enumeration Interface
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 11 – Vector
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 12 – Lists
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 13– ArrayList
Determine the output from the following program:
Question 14– Generics
Determine the output from the following program:
Note. If you do not fully understand the notation or activity in any of the programs you
should reference a Java textbook or an online Java tutorial to get a better
understanding.
Installation of JavaBeans EE
(Make sure to select the EE version – when installing to can opt to install the Glassfish
and/or Tomcat web servers.)
END