Recover
advertisement

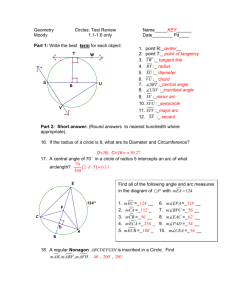
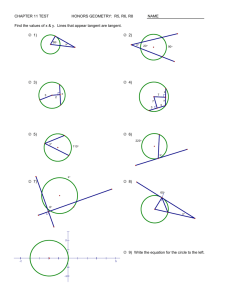
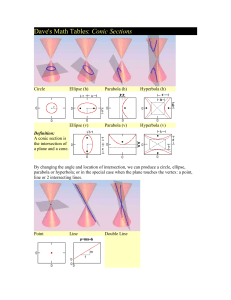
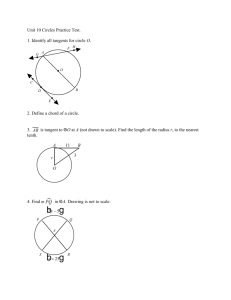
1. 2. 3. 4. symphony instrument cd movie 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 R Angle Parallel Triangle Perpendicular Radius Square Diameter Centerline CL 1. 2. With a compass With a triangle 50% 1 50% 2 Given line AB With points A & B as centers and any radius greater than ½ of AB, draw arcs to intersect, creating points C & D Draw line EF through points C and D Given line AB H F D Draw line CD from endpoint A Draw line EF from endpoint B E B C A Draw line GH through intersection G Given arc AB With points A & B as centers and any radius greater than ½ of AB, draw arcs to intersect, creating points C & D Draw line EF through points C and D Given angle AOB With point O as the center and any convenient radius R, draw an arc to intersect AO and OB to located points C and D With C and D as centers and any radius R2 greater than ½ the radius of arc CD, draw two arcs to intersect, locating point E Draw a line through points O and E to bisect angle AOB 1. 2. True False 50% 1 50% 2 A Given lines AB and CD Construct parallel lines at distance R B O Construct the perpendiculars to locate points of tangency With O as the point, construct the tangent arc using distance R C D Given lines AB and CD Construct parallel lines at distance R A Construct the perpendiculars to locate O points of tangency With O as the point, construct the tangent arc using distance R B C D Given angle ABC With B as the point, strike arc R1 equal to given radius With D and E as the points, strike arcs R2 equal to given radius With O as the point, strike arc R equal to given radius A O D B E C Given line AB and arc CD Strike arcs R1 (given radius) Draw construction arc parallel to given arc, with center O Draw construction line parallel to given line AB From intersection E, draw EO to get tangent point T1, and drop perpendicular to given line to get point of tangency T2 Draw tangent arc R from T1 to T2 with center E O C E T1 R1 A B D T2 Given arc AB with center O and arc CD with center S Strike arcs R1 = radius R A Draw construction arcs O parallel to given arcs, using centers O and S Join E to O and E to S to get tangent points T Draw tangent arc R from T to T, with center E E T BC S T D Prism ◦ Right Rectangular ◦ Right Triangular Cylinder Cone Sphere Pyramid Torus 1. 2. 3. 4. Torus Sphere Cylinder Pyramid 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 An alternative postion for the side view is rotated and aligned with the top view. Third angle projection is used in the U.S., and Canada 1. 2. 3. First Angle projection Second Angle projection Third Angle Projection 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 The six standard views are often thought of as produced from an unfolded glass box. Distances can be transferred or projected from one view to another. Only the views necessary to fully describe the object should be drawn. Review 1. 2. 3. 4. RIFG UZDP IFBH EBHB 73% 18% 9% 0% 1 2 3 4 1. 2. 3. 4. peach fig apricot prune 64% 18% 18% 2 3 0% 1 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Carthage Rome Jerusalem Babylon 38% 31% 23% 8% 1 2 3 4 The advantage of oblique pictorials like these over isometric pictorials is that circular shapes parallel to the view are shown true shape, making them easy to sketch. Oblique pictorials are not as realistic as isometric views because the depth can appear very distorted. 1. 2. 3. 30/30/120 60/60/40 90/60/30 36% 57% 7% 1 2 3 Oblique drawings of objects having a lot of depth can appear very unnatural due to the lack of foreshortening. Perspective drawings produce the view that is most realistic. A perspective drawing shows a view like a picture taken with a camera There are three main types of perspective drawings depending on how many vanishing points are used. These are called one-point, two-point, and three-point perspectives. Orient the object so that a principal face is parallel to the viewing plane (or in the picture plane.) The other principal face is perpendicular to the viewing plane and its lines converge to a single vanishing point. 1. 2. 3. Where all the lines converge together. Where the earth ends. Where the view point comes together. 60% 40% 0% 1 2 3 A review of some ideas, That are both relevant to calculus and drafting. The physical tools for drawing the figures are: ◦ The unmarked ruler (i.e., a ‘straightedge’) ◦ The compass (used for drawing of circles) Given any two distinct points, we can use our straightedge to draw a unique straight line that passes through both of the points Given any fixed point in the plane, and any fixed distance, we can use our compass to draw a unique circle having the point as its center and the distance as its radius Given any two points P and Q, we can draw a line through the midpoint M that makes a right-angle with segment PQ P M Q Given a circle, and any point on it, we can draw a straight line through the point that will be tangent to this circle Step 1: Draw the line through C and T C T Step 2: Draw a circle about T that passes through C, and let D denote the other end of that circle’s diameter C T D Step 3: Construct the straight line which is the perpendicular bisector of segment CD tangent-line C T D Any other point S on the dotted line will be too far from C to lie on the shaded circle (because CS is the hypotenuse of ΔCTS) S C T D Given an ellipse, and any point on it, we can draw a straight line through the point that will be tangent to this ellipse F1 F2 Step 1: Draw a line through the point T and through one of the two foci, say F1 T F1 F2 Step 2: Draw a circle about T that passes through F2, and let D denote the other end of that circle’s diameter T F1 F2 D Step 3: Locate the midpoint M of the linesegment joining F2 and D T M F1 F2 D Step 4: Construct the line through M and T (it will be the ellipse’s tangent-line at T, even if it doesn’t look like it in this picture) T D M F1 F2 tangent-line Observe that line MT is the perpendicular bisector of segment DF2 (because ΔTDF2 will be an isosceles triangle) T D M F1 F2 tangent-line So every other point S that lies on the line through points M and T will not obey the ellipse requirement for sum-of-distances S T D M F1 F2 tangent-line SF1 + SF2 > TF1 + TF2 (because SF2 = SD and TF2 = TD When we encounter some other methods that purport to produce tangent-lines to these curves, we will now have a reliable way to check that they really do work! 1. 2. Yes No 100% 0% 1 2 A cone is generated by a straight line moving in contact with a curved line and passing through a fixed point, the vertex of the cone. This line is called the generatrix. Each position of the generatrix is called element The axis is the center line from the center of the base to the vertex Conic sections are curves produced by planes intersecting a right circular cone. 4-types of curves are produced: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. A circle is generated by a plane perpendicular to the axis of the cone. A parabola is generated by a plane parallel to the elements of the cone. An ellipse is generated by planes between those perpendicular to the axis of the cone and those parallel to the element of the cone. A hyperbola is generated by a planes between those parallel to the element of the cone and those parallel to the axis of the cone. 1. 2. 3. 4. Circle Ellipse Parabola Hyperbola 86% 7% 7% 0% 1 2 3 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Circle Ellipse Parabola Hyperbola 92% 8% 0% 1 0% 2 3 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 3 4 5 71% 29% 0% 1 0% 2 3 4 If a circle is viewed at an angle, it will appear as an ellipse. This is the basis for the concentric circles method for drawing an ellipse. Draw two circles with the major and minor axes as diameters. Draw any diagonal XX to the large circle through the center O, and find its intersections HH with the small circle. From the point X, draw line XZ parallel to the minor axis, and from the point H, draw the line HE, parallel to the major axis. Point E is a point on the ellipse. Repeat for another diagonal line XX to obtain a smooth and symmetrical ellipse. Along the straight edge of a strip of paper or cardboard, locate the points O, C, and A so that the distance OA is equal to one-half the length of the major axis, and the distance OC is equal to one-half the length of the minor axis. Place the marked edge across the axes so that point A is on the minor axis and point C is on the major axis. Point O will fall on the circumference of the ellipse. Move the strip, keeping A on the minor axis and C on the major axis, and mark at least five other positions of O on the ellipse in each quadrant. Using a French curve, complete the ellipse by drawing a smooth curve through the points. 1. 2. 3. Splitting a line in 3rd’s Splitting a line in 4ths Splitting a line in Half 100% 0% 1 0% 2 3 1. 2. Trammel Concentric Circles 54% 46% 1 2 1. 2. Yes No 69% 31% 1 2