module specification template
advertisement

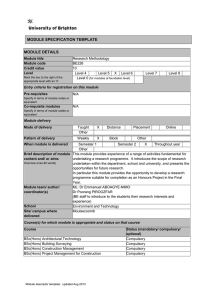
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Mathematics 1 CN118 10 Level 4 x Level 5 Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other Pattern of delivery Weekly x Distance Placement Block Other Online When module is delivered Semester 1 x Semester 2 Throughout year Other Brief description of module This module covers the review of elementary functions and trigonometry, content and/ or aims vectors, matrix analysis, the solution of a set of linear equations and Overview (max 80 words) introduction to differentiation and its applications required to provide a foundation for the study of civil and environmental engineering. Module team/ author/ ML: Dr Ourania Tsioulou coordinator(s) Dr Paul Harris School School of Environment and Technology Site/ campus where Moulsecoomb Campus delivered Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course BEng(Hons) / MEng Civil Engineering BEng(Hons) / MEng Civil with Environmental Engineering BEng(Hons) / MEng Civil Engineering with Construction Management Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Compulsory Compulsory Compulsory MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims To develop competence in basic analytic and numerical techniques in mathematics relevant to Civil Engineering Learning outcomes By the end of this module the student should be able to: 1. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 understand the meaning of vectors and vector operations 2. 3. 4. Content solve sets of linear simultaneous equations; perform matrix operations; apply concepts of differentiation. Elementary Functions Review of elementary functions (such as polynomial up to the 3rd order, trigonometric and exponential functions) and their graphs. Review of basic trigonometry and logarithm. Geometry Graphical Vector operations (sum, components of a vector). Resolving vector into components. Scalar and vector products. Definition of moment of a force respect to a point and to a line. Equation of the line passing through two points. Collinear and non collinear points. Distance of a point from a line. Intersection of two lines. Simultaneous Linear Equations Gauss elimination. Planes, equation of a plane. Quadratic forms, paraboloid. Matrix Algebra Definition and properties of Matrices. Determinants and Matrices Definition and properties of Determinants (Sarrus and Laplace rules for the calculation of determinants). Test for consistency of linear simultaneous equations. Cramer’s rule for solution of systems of up to 3 linear equations. Inverse matrices by Gauss-Jordan method. Transformations of coordinates in 2D (translations and rotations) Analytical determination of eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Introduction to differentiation Slopes, basic differentiation, differentiation of products and quotients. Maximum and minimum points – finding and classifying Plot of a function. Zeros, Maxima and minima, concavity. computation of asymptotes for a function Learning support Recommended Reading List : Engineering Mathematics (7th Ed.) by K A Stroud MacMillan 2013 Mathematical Formulae by J O Bird and A J C May Longman 1999 Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Lectures and tutorials. Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, and external visits. 40 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 60 Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University. It includes work-based learning and study that occurs overseas. TOTAL STUDY HOURS Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module 100% Examination (LO1-LO3) The assessment task consists of two linked compulsory tests (LO1, 2, 3) (2 hours each) all under exam conditions. Class Test 1 (25% of the final mark) Exam (75% of the final mark) Deferred/ referred assessment consists of a single 2 hour exam. Types of assessment task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Class test 1 (under exam condition) 2 hour exam 25% 75% COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Built Environment & Civil Engineering Area Examination Board Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Dr Alessandro Palmeri Senior Lecturer in Structural Engineering Oct 2013 Sept 2017 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval 1999 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision July 2014 Only complete where this is not the first version 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Date of approval for this version October 2015 Version number 3 Modules replaced Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2012 Yes No x