The Work of Streams
advertisement

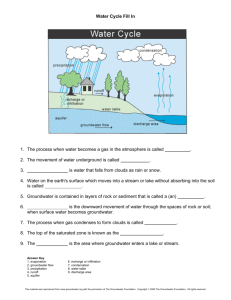
The Work of Streams Erosion Usually happen by streams flowing through their channels and lifting loose particles by abrasion, grinding, and by dissolving soluble material. Ex. Like how sandpaper grinds down wood. Sediment Transport Three ways: 1.) In Solution: dissolve load 2.) In Suspension: suspended load Enters through the groundwater Carry the largest part of their load this way 3.) Scooting/rolling across the bottom: bed load Solid material to large to be carried in suspension Competence and Capacity Measures the largest part of the materials that a stream can transport. Steam Discharge: Estimate of how much water can flow through in one second. The maximum load that the stream can carry The greater the volume of water in the stream, the greater its capacity for carrying sediment. Deposition Occurs when sediments in a stream start to deposit because the stream slows down. Two types: 1.) Delta: an accumulation of sediment formed where a stream enters a lake or ocean. When a stream/river enters a lake/ocean 2.) Natural Levees: a landform that parallels some streams. Happens when a stream overflows its banks. Narrow Valley vs. Wide Valley A stream’s primary work has been to down cut to the base level. More commonly known as a floodplain. Flood Control Caused by rapid spring melts or snow storms. Three types to control floods: 1.) Artificial Levees: Earth mounds on top of the banks of rivers. 2.) Flood – Control Dam 3.) Limiting Development Drainage Basin The land area that contributes water to a stream/river. Water Beneath the Surface Distribution and Movement Soaks into the ground but does not travel far. Seeps until it goes to the water table. Moves through the pores of the groundwater. Porosity – percentage of rocks and soil that have pores. Springs Where ever the water reaches the surface of the Earth. Spring – a naturally flow of groundwater. Hot Springs vs. Geysers Warmer than the air temperature around it. Intermittent hot spring – its on a timer. Wells A hole that is bored into the zone of saturation (water table). Artesian Well: any formation in which groundwater rises on its own under pressure. Environmental Problems Overuse and contamination 1.) Treating groundwater like it is a nonrenewable resource 2.) Groundwater Contamination (pollution) Caverns vs. Sink holes A naturally formed underground chamber caused by erosion from streams. A region where groundwater has removed the rock.