Network Reference Model
advertisement

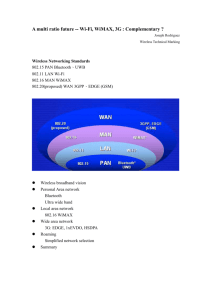
WiMAX core Network Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements 簡介 WiMAX 全名Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access,中文譯名為「微波存取 全球互通」。 具有遠距離、傳輸量大,使用IEEE 802.16的 協定,其傳輸速度最高可達70Mbps,傳輸範 圍最廣可達30英哩,對個人、家庭與企業的行 動化將有很大助益為新一代的無線網路標準。 名詞解釋 BS(Base Station,基地臺),指訊號發射端。 SS(Subscriber Station,接收端),有室內、戶外型,必須轉接 才能連到一般設備。 CPE(Customer Premise Equipment,客戶端接收器),內建在 設備上,不用像SS還要轉接裝置。 RS(Rely Station,中繼器),在802.16j(Mobile Multi-hop Relay )制定,能延伸BS訊號,能智慧型轉發訊號。 PTP(Point to Point,點對點模式),1臺BS對應1臺SS。 PMP(Point to Multiple,點對多點模式),1臺BS可對應多臺SS 。 License Band及Un-License Band(License-Exempt),前者為特 許營運頻帶,必須有營運執照才能使用,例如2.5GHz及3.5GHz, 後者為非特許營運頻帶,不需執照,一般皆可使用,例如5.8GHz 。 LOS(Line-of-sight)及NLOS(Non-Line-of-sight),前者是指設 備間沒有任何障礙物,視為直視距離,後者則是兩端間有障礙物 ,視為非直視距離。 WiMAX特色 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 包含非直視性(Non-Line-of-Sight,NLOS)及 直視性(Line-of-Sight,LOS)技術、傳輸 距離長、網路涵蓋範圍廣。 高頻譜效率、高傳輸速率。 具彈性的系統容量。 支援語音、影像等服務之服務品質(QoS) 需求。 支援多種工作頻段,可配合不同國家之頻譜 指配。 LOS模式與NLOS模式 NLOS(Non Line of Sight)模式 速度較慢,穿透力較高,適用於都會環境 使用2-11GHz頻段,最大傳輸距離為10公里 當通道頻寬為20MHz時,最高速度約75Mbps LOS(Line of Sight)模式 速度較高,穿透力差,適用於空曠的環境 使用10-66GHz頻段,最大傳輸距離為5公里 當頻寬為28MHz時,速度最高為134Mbps 應用情境 固接式WiMAX IEEE 802.16 工作小組,最初是將寬頻點發展 為多點 (PMP) 標準,以作為有線網路基礎架 構的無線擴充。而第一個獲認可的空中介面, 即是建立在分時多工存取 (TMDA) 通訊協定上 。 此一介面支援分時雙工 (TDD) 與分頻雙工 (FDD)。 移動式WiMAX 主要以2.5G頻譜為主,具有行動上網的優勢, 未來汽車也將全面配備WiMAX連網設備,以 便行駛間能接收網路訊息。 協定演進 Uplink nad Downlink Uplink From SS to BS Downlink From BS to SS TDD and FDD Frequency Frequency-Division Duplex (FDD) DL & UL on separate RF channels Time Time-Division Duplex (TDD) DL & UL time-share the same RF channel SS does not transmit/receive simultaneously Time Time-Division Duplex (TDD) 實體層定義 WiMAX系統為了因應各種不同使用場景,訂定 了兩個使用頻段:10~66GHz與2~11GHz,及4 種不同的實體層介面規範:WirelessMAN-SC、 WirelessMAN-SCa、WirelessMAN-OFDM及 WirelessMAN-OFDMA,其中WirelessMAN-SC屬 於10~66GHz頻段,而其餘三者屬於2~11GHz 頻段 使用環境 WirelessMAN-SC及WirelessMAN-SCa適用於 直視路線(Line of Sight, LOS)環境,而 WirelessMAN-OFDM及WirelessMANOFDMA適用於非直視路線(Non-Line of Sight, NLOS)環境 效能提升方法 WirelessMAN-SCa、WirelessMAN-OFDM及 WirelessMAN-OFDMA均可採用「適應性天線 系統」(Adaptive Antenna System, AAS)技術 提升效能;其中Wireless MAN-Sca基本上採 用的是「智慧型天線」波束形成技術,而 WirelessMAN-OFDM及Wireless MANOFDMA則採用MIMO技術 實體層規格 ‧WirelessMAN-OFDM 本規範主要訴求在藉由OFDM有效對抗通道多 重路徑效應與提高資料傳輸率。OFDM調變共 有256個次載波,可支援包括QPSK、16-QAM 和64-QAM的適應性調變(adaptive modulation),根據各個次載波通道狀況決定其 調變位階。多重接取採用的是分時的TDMA。 為因應多路徑環境之特性, WirelessMAN-OFDMA 本規範主要訴求在提供移動式應用。調變方式 與WirelessMAN-OFDM相同,但多重接取採 用的是分頻的FDMA,並支援可變(scalable)頻 寬的機制,其功能為根據通道狀況改變系統頻 寬與次載波數 WirelessMAN-OFDMA (cont.) OFDMA的運作原則是將所有次載波分割成若 干群組,稱為次通道(subchannel),分配給不 同用戶使用,並根據傳輸環境狀況決定各個次 通道的次載波數。 WirelessMAN-OFDMA (end) MIMO 多輸入多輸出(Multiple Inputs, Multiple Outputs, MIMO) MIMO的核心概念為利用多根發射天線與多根 接收天線所提供之空間自由度提升傳輸速率與 改善通訊品質。 MIMO功能形式 空間多樣(spatial diversity) 利用發射或接收端的多根天線所提供的多重傳輸途 徑來對抗通道衰落(fading)的影響 空間多工(spatial multiplexing) 在發射端利用多根天線傳送不同資料序列,並在接 收端利用多根天線的空間自由度將該組資料序列分 別解出 MIMO優點 系統涵蓋範圍 提升鏈路品質 提高系統容量及頻譜效率 與提高資料傳輸率 Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements Introduction QoS supporting is a fundamental part of the WiMAX MAC-layer design. How does WiMAX support for QoS? Connections A connection-oriented MAC architecture all downlink and uplink connections are controlled by the serving BS Each connection is identified by a connection identifier (CID) Service flows A service flow is a unidirectional flow of packets with a particular set of QoS parameters is identified by a service flow identifier (SFID) The service flow characteristics of the connection provide the QoS for that packet Service Flow Creation Service Flow Management Dynamic Service Change (DSC) Dynamic Service Delete (DSD) Dynamic Service Activate (DSA) DSD DSC NULL DSA OPERATIONAL Classifier A classifier is a set of matching criteria applied to each packet It consists of some protocol-specific packet matching criteria (destination IP address, for example) a classifier priority a reference to a CID. Classifiers can be added by dynamic signaling Scheduler Scheduler Service Classifier flows QoS logical connections MS1 MAC Service flow over QoS connections BS MAC Priority queues MS2 MAC Associate packets into service flow Define QoS parameter for each service flow Dynamically establishing QoS-enabled service flows Associate QoS service flow with logical connections Quality of Service Support Scheduling services Four services are supported in 802.16 802.16-2004 Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS), Real-time Polling Service (rtPS), Non-real-time Polling Service (nrtPS), and Best Effort (BE). Five services are supported in 802.16e 802.16e2005 UGS (Unsolicited Grant Service) RT-VR (Real-Time -Variable Rate Service) NRT-VR (Non-Real Time -Variable Rate service) BE (Best Efforts) ERT-VR (Extended Real-Time Variable Rate) Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) support real-time data streams consisting of fixed-size data packets issued at periodic intervals Such as T1/E1 and Voice over IP without silence suppression INTERNET VoIP Real-time Polling Service (rtPS) support real-time data streams consisting of variable-sized data packets that are issued at periodic intervals Such as moving pictures experts group (MPEG) video. Non-real-time Polling Service (nrtPS) support delay-tolerant data streams consisting of variable-sized data packets for which a minimum data rate is required such as FTP Best Effort (BE) support data streams for which no minimum service level is required and therefore may be handled on a space-available basis. Extended Real-Time Variable Rate (ERT-VR) service support real-time applications with variable data-rates, which require guaranteed data and delay, for example VoIP with silence suppression. Handover An mobile station (MS) migrates from the airinterface provided by one BS to the air interface provided by another BS Handover in WiMAX Hard Handover Fast Base Station Switching (FBSS) Active Set (Diversity set) Anchor BS MS Anchor BS Macro Diversity Handover (MDHO) Active Set (Diversity set) Anchor BS MS all BSs in an active set Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements WiMAX Forum The WiMAX Forum is a nonprofit organization formed in 2001 to enhance the compatibility and interoperability of equipment based on the IEEE 802.16 family of standards WiMAX Forum_Network Working Group (NWG) define Stage 1: use case scenarios and service requirements and defined along with Service Provider Working Group Stage 2: Architecture Tenets, Reference Model and Reference Points Stage 3: Detailed Protocols and Procedures WiMAX Working Group ‧Application Working Group (AWG) ‧Certification Working Group (CWG) ‧Evolutionary Technical Working Group (ETWG) ‧Global Roaming Working Group (GRWG) ‧Marketing Working Group (MWG) WiMAX Working Group ‧Network Working Group (NWG) ‧Regulatory Working Group (RWG) ‧Service Provider Working Group (SPWG) ‧Technical Working Group (TWG) Relationship between the scopes of WiMAX NWG and 802.16 From IEEE 802.16 to WiMAX NWG build an interoperable broadband wireless network. Interoperable networks involve end-to-end service such as IP connectivity and session management, security, QoS, and mobility. Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements WiMAX Network Reference Model(1/2) Decomposed ASN into BS and ASN GW entities Entities of the WiMAX Network Reference Model (1/2) ASN: Access Serving Network Logical representation of the functions of a NAP, e.g. 802.16 interface network entry and handover Radio Resource Management & Admission ctrl. L2 Session/mobility management QoS and Policy Enforcement Foreign Agent (FA) Forwarding to selected CSN Entities of the WiMAX Network Reference Model (2/2) CSN: Connectivity Serving Network Logical representation of the functions of a NSP, e.g. Connectivity to the Internet, ASPs Authentication, authorization and accounting IP address management L3 Mobility and roaming between ASNs Policy & QoS management based on a SLA Network Reference point (1/2) R1: R2: Reference point between MS and ASN-GW or CSN: logical interface used for authentication, authorization, IP host configuration and mobility management. R3: Reference point between MS and BS: implements IEEE 802.16e-2005. Reference point between ASN and CSN: supports AAA, policy enforcement, and mobility –management capabilities. Implements tunnel between ASN and CSN. R4: Reference point between ASN and ASN: used for MS mobility across ASNs. Reference point (2/2) R5: R6: Reference point between BS and ASN: implements intraASN tunnels and used for control plane signaling. R7: Reference point between CSN and CSN: used for internetworking between home and visited network. Reference point between data and control plane in ASNGW: used for coordination between data and control plane in ASN-GW. R8: Reference point between BS and BS: used for fast and seamless handover. WiMAX Network Reference Model(2/2) Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements ASN Network & GW ASN-GW Reference model Internetworking with 3GPP Scope WiMAX-3GPP Interworking refers to the integration of a WiMAX Access Network to an existing 3GPP core network. Internet Billing Server PDG Home Agent WAG Home AAA 3GPP Core Network GCSN WiMAX Network Service Provider Local AAA SGSN RNC 3GPP Access Network Loosely-Coupled Internetworking WiMAX ASN WiMAX Base Stations 3GPP Card WiMAX Card UE Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements 802.16e network entry In a WiMAX network, a full network entry includes four steps: a. Network Discovery and Selection b. Access Authentication c. Connection Setup d. Data Transfer 802.16 TDD Frame Structure Time Slot Downlink Subframe Uplink Subframe Frame Control Contention Request Bandwidth Request DATA Contention Slot UCD DCD DATA UL-MAP DL-MAP TDD Frame Structure Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements Network entry A WiMAX subscriber station has to complete the network entry process , in order to communicate on the network. Steps: Scan for DL channel and establish synchronization with the BS Obtain transmit parameters (form UCD message) Perform initial ranging Negotiate basic capabilities Authorize MS and perform key exchange Establish IP connectivity Establish time of day Transfer operational parameters optional Set up connections Network entry a)Downlink Channel Synchronization: When an SS wants to communicate on a WiMAX network, it first scans for available channels in the defined frequency list. On finding a DL channel, it tries to synchronize at the PHY level using the periodic frame preamble. Information on modulation and other DL and UL parameters is obtained by observing the DL Channel Descriptor (DCD) and the UL channel descriptor (UCD) of the DL channel. Ranging(1/2) b) Initial Ranging: An SS starts an Initial ranging process by sending a ranging request MAC message using the minimum transmission power. If no response is received from the BS, the SS resends the message on a subsequent frame using a higher transmission power. The response either indicates power and timing corrections that the SS must make or indicates success. Purpose: The process by which the SS and BS maintain the quality of RF communication link between them. Ranging(2/2) Periodic ranging Allows SS to adjust transmission parameters and maintain uplink communication with the BS. Network entry c) Exchanging Capabilities: After successful completion of the initial ranging step, the SS sends capability request message indicating the supported modulation level, coding scheme and rates and duplexing methods. Network entry d) Authentication: After capability negotiation, the BS authenticates the SS, determines the ciphering algorithm to be used, and sends an authentication response to the SS. e) Registration: After authentication, the SS sends a registration request message to the BS and the BS sends a registration response. Network entry f) IP Connectivity: After registration, the SS gets the IP address via DHCP. The SS also downloads other operational parameters using TFTP. g) Connection Creation: After completing the IP connectivity step, transport connections are created. For preprovisioned service flows, the BS sends a dynamic service flow addition request message to the SS and SS confirms the creation of connection. For non-preprovisioned service flows, connection creation is initiated by the SS by sending a dynamic service flow addition request message to the BS. The BS responds with the confirmation. Network Discovery and Selection NAP discovery NSP discovery NSP Enumeration and selection ASN attachment based on NSP Selection NSP Discovery ASN Attachment based on NSP Selection Connection setup The ASN setup Access Authentication Binding of MS flow to intra-ASN DATA PATH MIP req / resp PMIP4 / CMIP4 / CMIP6 MIP tunnel Connection setup procedure ( DHCP proxy ) Connection setup procedure ( CMIPv4 ) Connection Setup Procedure (CMIP6 ) Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements Mobility management The WiMAX mobility solution consists of two mobility levels Intra-ASN mobility ASN Anchored Mobility inter-ASN mobility ASN-anchor (based on profile A & C) CSN Anchored Mobility ASN Anchored Mobility Management(1/4) ASN Anchored Mobility Management is defined as mobility of an MS not involving a CoA update (MIP re-registration) ASN anchor Mobility (2/4) ASN anchored mobility (3/4) CSN Anchor mobility ( R3-mobility ) Re-anchoring of the current FA to a new FA and the consequent binding updates to update the upstream and downstream data forwarding paths. Authentication, Authorization and Accounting The WiMAX AAA framework is based on IETF specifications. The term AAA is used to refer to the AAA protocols, Radius or Diameter. The AAA framework provides the following services to WiMAX: Authentication Services Authorization Services These include MS, user, or combined MS and user authentication. These include the delivery of information to configure the session for access, mobility, QoS and other applications. Accounting Services These include the delivery of information for the purpose of billing (both prepaid and post paid billing) and information that can be used to audit session activity by both the home NSP and visited NSP. Accounting Architecture Outline WiMAX introduction WiMAXQoS & Flow Network Working Group (NWG) Network Reference Model WiMAX Inter Networking Key hierarchy Network Entry Mobility management Network QoS Functional Elements QOS IEEE 802.16 MAC is connection oriented. Each connection, upon establishment, subscribes to one of the scheduled services Resource allocation, admission, and scheduling is controlled the base station QoS Functional Elements Service Flow Management (SFM) Service Flow Authorization (SFA) e.g., SIP Proxy PF: Policy Function Evaluate any service request against user QoS profile. AF: Application Function responsible for the creation, admission, activation, modification and deletion of 802.16 service flows. Maintained information includes HNSP's general policy rules LPF: Local Policy Function enforce admission control based on available resources Reference Wimax forum WiMAX End-to-End Network Systems Architecture (Stage 3: Detailed Protocols and Procedures) Wimax forum WiMAX End-to-End Network Systems Architecture (Stage 2)