Cultural competency training to view these activities
advertisement
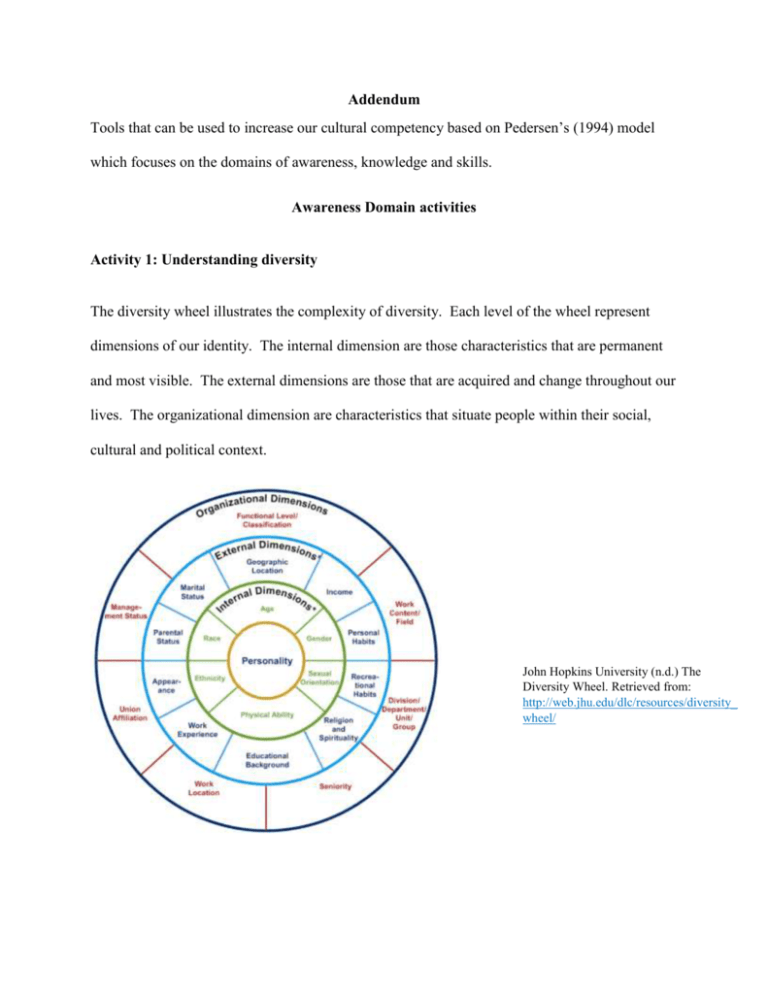
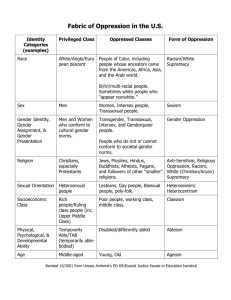
Addendum Tools that can be used to increase our cultural competency based on Pedersen’s (1994) model which focuses on the domains of awareness, knowledge and skills. Awareness Domain activities Activity 1: Understanding diversity The diversity wheel illustrates the complexity of diversity. Each level of the wheel represent dimensions of our identity. The internal dimension are those characteristics that are permanent and most visible. The external dimensions are those that are acquired and change throughout our lives. The organizational dimension are characteristics that situate people within their social, cultural and political context. John Hopkins University (n.d.) The Diversity Wheel. Retrieved from: http://web.jhu.edu/dlc/resources/diversity_ wheel/ Exercise: 1. Take a moment to complete the diversity wheel with information about yourself. 2. Take a moment to think about how your identity has shaped your values, beliefs, behaviours, experiences and expectations? How does your identity make you unique? 3. Share your diversity wheel with the group and your thoughts on how your identify impacts you (depending on your comfort level). 4. Recognize and discuss with the group the similarities and differences between people’s world views. How do these similarities and difference impact our ability to work together? How does it impact our ability to work with clients? Activity 2: Understanding power and privilege Exercise: 1. Read the following article individually and check off the ones that you believe describe your position McIntosh, P. (1989, July/August). White privilege: Unpacking the invisible knapsack. Peace and Freedom,10-12. 2. In small groups discuss your thoughts on this article. What feelings does it bring up? 3. How does privilege impact your relationships with clients? Knowledge domain activities Activity 1: Expanding knowledge of cultural groups Exercise: 1. Identify marginalized groups that are represented within the staff and clients of the organization 2. Divide into groups and answer the following questions about one marginalized group using the resources provided a. Describe their cultural history. b. What are their unique cultural values and beliefs? c. What are their unique cultural behaviours? d. What is unique to their communication style? e. How would these characteristics impact the way in which you work with this cultural group? Activity 2: Understanding the complexity of oppression Oppression occurs when an individual’s access to services, benefits, privileges and society is influences by their membership in a particular group (Adams, et al, 2013). All forms of oppression are interconnected and therefore cannot be fully understood in isolation (Adams et al, 2013). Exercise: 1. Divide into groups and discuss a story that demonstrates the complexity of oppression Examples of stories: Neysmith, S., (2005). Policing motherhood: The gender and racial effects of poverty. In K. Bezanson ,S. Neysmith, & A. O’Connell (Eds.). Telling tales – Living the effects of public policy. (pp. 74-95). Fernwood Publishing Company: Halifax 2. Answer the following discussion questions a. What type of oppression is the individual experiencing? b. How are their experiences of oppression connected? c. How has oppression affected their access to services or resources? Skills domain Activities Exercise: Put the group into partners and have then sit back to back. Give one partner a simple drawing the other partner a blank piece of paper and pencil. The partner with the drawing must get their partner to copy their drawing without telling the partner what the drawing is and without showing the drawing to their partner. Questions: 1. What worked and did not work in communicating with your partner? 2. How does this exercise relate to cross cultural communication? 3. What lessons did you learn that you can utilize in cross cultural communication?