Male and Female Reproductive Organs Male Reproductive System
advertisement

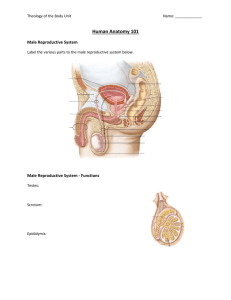
Male and Female Reproductive Organs Male Reproductive System Sperm-sex cells that are produced by the testes and is needed to fertilize an egg. Testes(testicles)-make sperm and testosterone The testes start producing sperm at puberty and the duration of a male’s livelihood. The testes produce several hundred million sperm each day. Male Reproductive System Testosterone- major sex horomone. At puberty it causes facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and also influences sperm production. Male Reproductive System Scrotum- this is where the two testes rest. There are small muscles in the scrotum that move the testes closer or further from the body. This movement keeps the sperm cooler because sperm cannot develop properly at the higher inner body temp. Male Reproductive System Penis-male reproductive organ that removes urine from the body and that can deliver sperm to the vagina. Made of soft tissue and blood vessels During sexual activity the penis becomes erect. Also known as an erection. Male Reproductive System The erection occurs because the blood vessels in the penis fill with blood. Once the penis is erect, ejaculation can take place Ejaculation-when sperm is released from the penis. Male Reproductive System Sometimes males ejaculate when they sleep; this is normal. This is called nocturnal emissions or “wet dreams.” The tip of the penis is covered by foreskin but is sometimes removed after birth in a procedure called a circumcision. Male Reproductive System The mixture of sperm and other secretions from the male reproductive organs is a fluid known as semen. The path of the sperm goes as followed: testes-epididymis-van deferens-seminal vesicles-prostate gland-bulbourethral glands Problems Jock Itch-fungal infection Cystits-inflammation of urinary bladder due to bacterial infection. Prostatitis-bacterial infection of prostate Hernia-bulging portion in abdomen,groin,or scrotum Problems Testicular torsion-twisting of testis on the nerves and blood vessels attached to it Undescended testes-faliure of one or both testes to move from the abdomen to the scrotum. Prostate and Testicular cancer. Performing Testicular Check-Up Perform self-exam during or after a warm bath or shower. Examine each testicle seperately. Roll each testicle gently between fingers. Look and feel for any lumps or any change in size, shape, or consistency of testicle Contact doctor if any trouble. Female Reproductive System The function of the system is to make eggs and to provide a place to support and nourish a developing human. Breasts are considered secondary reproductive organs. Female Reproductive System Two Ovaries. Ovaries-produce eggs and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Eggs are fertilized by sperm All the eggs that a female will ever have are in her two ovaries when she is born. Female Reproductive Organ Estrogen-causes reproductive organs to mature, pubic and underarm hair to grow, and helps strengthens bones. Estrogen and Progesterone regulate the monthly release of an egg and prepare the body for pregnancy. Female Reproductive System Vagina-connects the outside of the body to the uterus and receives sperm. Also allows menstrual flow to exit the body and is part of the birth canal where the baby is delivered. Female Reproductive System Above the vagina is the urethra, where urine is dispensed. Fallopian Tubes-transport the eggs from the ovary to the uterus. Uterus-place to support a developing human. Cervix-uterus meets the vagina Female Reproductive system Menstrual Cycle-monthly series of hormone controlled changes that prepare the uterine lining for pregnancy. Ovulation-release of an egg Before ovulation estrogen levels rise and causes the uterine lining to thicken. Female Reproductive System If the egg does not become fertile then estrogen and progesterone levels drop, thus causing menstruation to take place. Menstruation typically lasts 3-7 days. During this time females use tampons or sanitary pads. Problems Cystitis-inflammation of urinary bladder Vaginitis-vaginal infection by fungus or bacteria. Delayed Puberty-anorexia,excessive weight loss and/or overexercise Menstrual Cramps Problems PMS-mental and physical changes related to menstrual cycle. Toxic Shock Syndrome-poisoning of body from bacterial toxins; related to tampons Endometriosis-growth of tissue from uterine lining outside the uterus Problem Ovarian Cyst-failure of follicle in ovary to rupture and release an egg Cervical Cancer-abnormal division of cells in the cervix. Annual Pelvic Exam Doctor should exam the breast and genital area and a pap smear. Pap Smear-examines the cells of the cervix. This exam is important for detecting and preventing cervical cancer. Breast Self-Exam Perform during or after a warm bath or shower. Place one hand over your head and use the other hand to examine the breast. Squeeze the nipple and look for unusual discharge. Breast Self-Exam Check breast for swelling, dimpling, or scaliness Feel each breast for unusual lumps or thickening under the skin. Check under the armpits and b/t armpits and breasts.