Native Americans
advertisement

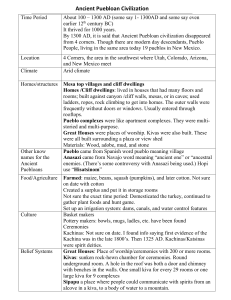
Early Americans Beringia land bridge: possible migration route Glaciers Thick sheets of ice Bering Strait Bering evolution Native Americans Descendents of the first people to reach America Artifacts- tools, baskets, weapons- objects made by people Archaeology- (2)study of evidence left by early people Study artifacts, technology, and carbon dating Culture- way of life that people develop (homes, arts, gov) pass from generation to generation Great Serpent Mound in Ohio Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site, Illinois Pueblo Bonito in New Mexico Pueblo Indians Hohokams (3) Farming society, S. Arizona Dug large irrigation systems- bring water to dry land Anasazi Also farming- irrigation Adobe- walls of stone and sun dried brick Pueblos- villages- hundreds of families Cliff Dwellings- protect from warlike neighbors Built along cliffs- toeholds to climb On top crops Abandoned- drought- long dry spell Anasazi cliff dwellers Cliff dwellers People of North America Culture area- region where people share same way of life Tribe- group of villages, share common customs, rituals, language 10 major culture areas- Arctic, Subarctic, Great Basin, Plateau, California, Great Plains, Southeast, Eastern Woodlands, Northwest Coast, Middle America Eskimo (Inuit- people of the Arctic) Igloo- houses of snow & ice- seal oil heat Subarctic- moved due to limited resources- fur traders Northwest Coast- dentalia shells= money Permanent villages- potlatch big dinner demonstrate how much you have = power gave everyone presents Great Basin- dry climate, little watermoved a lot Plateau- fresh rivers California- many dif climates resources Southwest pueblos- Spanish name for people of the SWmade up of sev groups- descendents of Anasazi-- kiva- underground religious chamber Kachinas- masked spirit dancers (see back board) rain dance- fam line traced through momswomen politically strong Apaches & Navajo- sometimes raided pueblos for food Navajos- Hogans- homes made of mud plaster over wooden poles Apaches- moved around following herds Great Plains homes- sod & thickly matted grass Travois- sled pulled by dogs to carry their goods Village ruling class by best hunters 1700’s change- caught and tamed wild horses (brought from Spain 200 years ago) Less farming more hunting- could travel far- built tepees- cone shaped tents made of buffalo hides Southeast home to more NA than any other region Men & women different roles- religious ceremonies linked to farming Natchez- 13 month calendar named for food or animal grown or hunted Religious beliefs- worshipped sun- leader “The Great Sun” worshipped as a godfamily=Little Suns >nobles>honored people>Stinkards (majority) Marriage- helped change class Nobles had to marry Stinkards (why?) People of the Eastern Woodland Iroquois (NY most powerful) Built long houses- wood poles with bark 150 ft long x 20 ft wide Women- owned all household property (like Pueblos) marry live w/ wife family- chose clan leaders=political power Clan- group of 2 or more related families Iroquois- 5 nations= Mohawk, Seneca, Oneida, Cayuga, Onandaga Hiawatha- formed league to end fighting League of the Iroquois- governing alliance Sachem- chose tribal leaders- met once year vote discuss issues All nations must agree to do anything Strong defensive alliance against enemies Iroquois longhouse Iroquois people Native Americans Comprehension 1.Native American Cultures adapted to their environment: Great Plains- tepees & travois- winter travel after buffalo, summer fish or plant near water- horses Navajo & Apache- hogans- hunters or raid Pueblos 2. Farming Hunting Stay in one place nomadwander after food 3. Pueblo, Long House Tepee Critical Thinking Religion major role- worshiped according to harvest, hunting, etc Ex. Natchez calendar, Kiva- rain dance for harvest Iroquois League compared to today United Nations US Government Founding fathers looked to Iroquois for advice while creating new nation