Electron Microscopes
advertisement

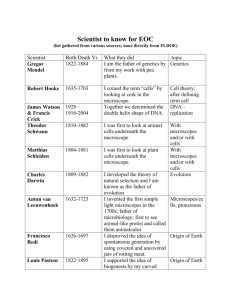
MICROSCOPES “illumination” Light (visible) Fluorescent U-V Electron Resolving Power N.A. affects Wavelength affects MICROSCOPES eyepieces Monocular Binocular specimen background Bright field Dark field 1 PARTS & TERMS Lenses (ocular, objective) Total Magnification • ocular mag. X objective mag. Condenser Diaphram MICROSCOPES 2 PARTS & TERMS Numerical Aperture (N.A.) optical characteristic of a lens N.A. = i sinq N.A. increases with magnification MICROSCOPES 3 PARTS & TERMS Resolving Power (R.P.) • size of the smallest discernable detail • minimum distance between objects so that they are able to be distinguished as separate R.P. = wavelength of illumination (2)N.A. MICROSCOPES [ RP of human eye ~ 0.2mm = ______m ] 4 Resolving Power (R.P.) l = 650nm, NA = 0.25 1300 1.3 m R.P. = l/2NA = _____nm = _____ l = 650nm, NA = 1.25 260 0.260 m R.P. = l/2NA = _____nm = _____ l = 450nm, NA = 1.25 180 0.180 m R.P. = l/2NA = _____nm = _____ MICROSCOPES 5 Resolving Power (R.P.) R.P. = l/2NA Larger or Smaller R.P. = BETTER ? R.P. improves as N.A. increases or decreases? R.P. improves as l increases or decreases? MICROSCOPES 6 Types of Scopes MICROSCOPES 7 Types of Scopes MICROSCOPES 8 Types of Scopes Compound Light • Bright or Dark field • Use blue light or blue filter for shorter l • R.P. ~ 0.2m MICROSCOPES 9 Types of Scopes Fluorescent • Dark field compound light microscope • Uses U-V for side illumination of specimen, fluorescent parts or dyes give off visible light that is viewed • R.P. ~ 0.2m MICROSCOPES 11 Types of Scopes UltraViolet (U-V) • Uses U-V as illumination (shorter l) • Image recorded then viewed… still or video camera image (should NOT look directly at U-V!) • Special lens material (quartz), glass absorbs U-V • R.P. ~ 0.15m MICROSCOPES 12 Types of Scopes Electron Microscopes Use electron beam for illumination, magnets for “lenses”, video to view Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) • beam passes thru, view internal structure Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) • beam reflects, see external structure, texture MICROSCOPES 13 Types of Scopes Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) MICROSCOPES 15 Types of Scopes Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) • Special specimen preparation (vacuum) • Working magnification: whole bacteria….. thin section, viruses…. 8,000x - 10,000x 30,000x - 40,000x • Maximum magnification ~100,000x • R.P. ~0.001m = ______nm MICROSCOPES 16 rickettsia herpes simplex Types of Scopes Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) MICROSCOPES 18 Types of Scopes Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) • Special specimen preparation (vacuum & conductor) • Working magnification: 14,000x - 50,000x • Maximum magnification ~130,000x • R.P. ~0.01m = ______nm MICROSCOPES 19 Q fever (rickettsia) Image enhancement