MAX232
advertisement

ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CONTENTS
Chapter-1
2-6
Project Title
Introduction
Components List
Circuit Diagram
Chapter-2
7-10
Functional block diagram
Internal Working Of The Circuit
Project Working
Chapter-3
11-35
Introduction to microcontrollers
Description of components
Explanation
Block Diagram and
Features Of IC’s used in the circuit
Chapter-4
35-41
Software Description
Chapter-5
42-43
Result
Conclusion
Appendix:
Advantages
Disadvantages
Future-Scope
Bibliography
Data sheets
44-48
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
1
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER-1
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE
USING
GSM TECHNOLOGY
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
2
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
ABSTRACT
India is world’s largest democracy. Fundamental right to vote or simply
voting in elections forms the basis of Indian democracy. In India all earlier
elections a voter used to cast his vote by using ballot paper. This is a long,
time-consuming process and very much prone to errors.
This situation continued till election scene was completely changed by
electronic voting machine. No more ballot paper, ballot boxes, stamping,
etc. all this condensed into a simple box called ballot unit of the electronic
voting machine.
The aim of the project is to implement an Voting machine using GSM
technology. GSM (Global system Mobile Communication)based voting
machine provides more reliability and restricts the unauthorized person
who is trying to miss use his vote. Today GSM fitted Banks, cars;
ambulances, fleets and police vehicles are common sights on the roads of
developed countries.
Cell phone based voting machine is capable of saving considerable printing
stationery and transport of large volumes of electoral material. It is easy
to transport, store, and maintain. It completely rules out the chance of
invalid votes. Its use results in reduction of polling time, resulting in fewer
problems in electoral preparations, law and order, candidates' expenditure,
etc. and easy and accurate counting without any mischief at the counting
centre.
Artificial voting machine is simple and costs less. This system is
implemented using an embedded micro controller.
The GSM module is connected with the 8051 microcontroller through serial
port. Using ‘AT’ commands the SMS is transferred to the GSM module. The
GSM module converts the digital information into airborne signals.
The GSM module consist of Wireless CPU, SIM card holder and power LED.
It helps transmit and receive the SMS with UART. Liquid crystal display is a
thin, flat display device made up of any number of color or mono- chrome
pixels arrayed in front of a light source or reflector.
This project is based on assembly language programming. The software
platform used in this project are Keil uVision3
COMPONENTS LIST:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
3
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Semiconductors:
IC-1
: 8051 micro controller
IC-2
: Max 232
IC-3
: 7805
IC-4
: 7809
Resistors:
R1
: 1,10 K ohms
Capacitors:
C1 , C2
: 100microfarad
C4, C3
: 33pf
C5
: 10 microfarad
C9, C6, C7, C8
: 1micro farad/10 micro farad
Miscellaneous:
XTAL
: 11.590592 MHz.
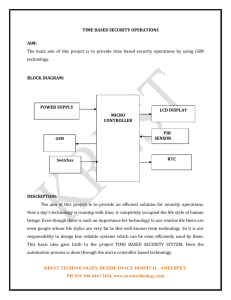
POWER SUPPLY
: 9V, 500mA
Push buttons
LCD DISPLAY
GSM Modem
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
4
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
5
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
6
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER – 2
Block diagram
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
7
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Internal Working of the Circuit
The circuit mainly consists of three IC’s 8051, Max232 and an LCD and
GSM Modem and a power supply.
The Max232 IC is used as a voltage convertor it converts the voltage
between the modem and the microcontroller 8051. The pins 11,12
connected to 8051 port-3 pins p-10 and p-11 respectively.
The LCD display is used to display the particular message. The pins of
port2 of the microcontroller 8051 are connected to the LCD display.
Port – 1 pins p1.1,p1.2,p1.3,p1.4 are used to check the result or status
of the votes. These are connected to ground through a push back
switch.
A crystal oscillator of 11.0592MHZ is connected in between the pins 10
and 11 of the 8051 which gives continuous pulses to the micro
controller.
13,14 pins of the max 232 IC is connected to serial port where the GSM
module is interfaced. The GSM module is connected with the 8051
microcontroller through serial port. Using ‘AT’ commands the SMS is
transferred to the GSM module. The GSM module converts the digital
information into airborne signals.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
8
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Contrast of the testing :
Step – 1
Registration:
WE HAVE TO INITIALLY REGISTER YOUR MOBILE NUMBER ALONG
WITH THE AADHAR CARD TO YOUR SERVICE PROVIDER.YOUR MOBILE
NUMBER WILL BE SAVED WITH YOUR AADHAR ID i.e., the provider will
save the details in the data base.
Step - 2
CHECK VALIDATION OF REGISTRATION
AFTER REGISTRATION YOUR NUMBER WILL BE SAVED IN THE
MICROCONTROLLER ALONG WITH YOUR AADHAR CARD.
HOW TO CHECK VALIDATION
BY SENDING AN SMS TO THE VOTING MACHINE AS < AADHAR ID > IT
WILL CHECK YOUR NUMBER VALIDATION WETHER IT IS CONFIRM OR
NOT.IF THE NUMBER IS VALID AND REGISTERED ONE THE MC WILL
SEND YOU BACK THE MESSAGE THAT YOUR REGISTRATION IS
SUCCESSFUL .EVEN IT IS NOT REGISTERED IT WILL SEND BACK
MESSAGE THAT YOUR NUMBER IS NOT REGISTERED.
STEP-3
VOTING
ON THE DAY OF ELECTIONS YOU WANT TO DO IS NOTHING JUST SEND
A SINGLE SMS TO THE VOTING MACHINE TO WHICH PARTY YOU
WANTS TO VOTE
HOW TO SEND SMS
SIMPLY TYPE <PARTY ID> OF THE PARTY YOU WANT TO VOTE AND
SEND IT TO THE VOTING MACHINE.
IF THE PARTY ID IS A VALID ID THEN YOU WILL GET A CONFIRMATION
MESSAGE
“VOTE IS SUCCEESFULL TO PART ID”
IF IT IS NOT A VALID PARTY ID THEN YOU GET
“VOTE UNSUCCESSFULL PLEASE ENTER VALID ID AND RETRY”
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
9
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
NOTE: ONLY ONE AADHAR ID CAN VOTE TO ONLY ONE PARTY
ACCODING TO THE PROGRAM WRITTEN IN THE VOTING MACHINE THE
MESSAGES OF DECODED AND RESPOND TO ITS ACTION.
EVEN IF YOU WANT TO KNOW HOW MANY VOTES THAT EACH PARTY GETS
AND THE TOTAL NUMBER OF VOTES WE CAN GET IT BY SIMPLY SENDING A
SMS TO VOTING MACHINE
HOW TO SEND
TYPE < TOTAL > TO THE VOTING MACHINE
THE VOTING MACHINE DECODES THE MESSAGE AND SEND RESPECTIVE
RESULT BACK TO US.
THE VOTING MACHINE CONTAINS A GSM MODEM WITH A NUMBER.BY
SENDING SMS TO GSM MODEM WHICH IS INTERFACED TO
MICROCONTROLLER WE CAN GET THE DETAILS AND USE THE PROJECT
IN THIS CIRCUIT WE ARRAGE 4 PUSH ON RESET BUTTONS AT PORT-1 TO
PINS P1.0,P1.1,P1.2,P1.3 RESPECTIVELY TO GROUND WICH ARE USED TO
KNOW THE RESULT OF HOW MANY VOTES BY RESPECTIVE PARTY’S AND
TOTAL NUMBER OF VOTES.HERE WE TAKE 3 PARTIES.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
10
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER-3
INTRODUCTION TO MICROCONTROLLER:
Introduction:
A Micro controller consists of a powerful CPU tightly coupled with
memory, various I/O interfaces such as serial port, parallel port timer or
counter, interrupt controller, data acquisition interfaces-Analog to Digital
converter, Digital to Analog converter, integrated on to a single silicon chip.
If a system is developed with a microprocessor, the designer has to go
for external memory such as RAM, ROM, EPROM and peripherals. But
controller is provided all these facilities on a single chip. Development of a
Micro controller reduces PCB size and cost of design.
One of the major differences between a Microprocessor and a Micro
controller is that a controller often deals with bits not bytes as in the real
world application. Intel has introduced a family of Micro controllers called the
MCS-51.
Figure: micro controller
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
11
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Pin Configuration:-
Pin Description:VCC - Supply voltage.
GND - Ground.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
12
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Port 0 –
Port 0 is an 8-bit open drain bi-directional I/O port. As an output port, each
pin can sink eight TTL inputs. When 1s are written to port 0 pins, the pins can
be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 can also be configured to be the
multiplexed low-order address/data bus during accesses to external program
and data memory. In this mode, P0 has internal pull-ups. Port 0 also receives
the code bytes during Flash programming and outputs the code bytes during
program
verification.
External
pull-ups
are
required
during
program
verification.
Port 1
Port 1 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. The Port 1
output buffers can sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 1
pins, they are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs.
As inputs, Port 1 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current
(IIL) because of the internal pull-ups. Port 1 also receives the low-order
address bytes during Flash programming and verification.
Port 2
Port 2 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. The Port 2
output buffers can sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 2
pins, they are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs.
As inputs, Port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current
(IIL) because of the internal pull-ups. Port 2 emits the high-order address
byte during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to
external data memory that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @ DPTR). In this
application, Port 2 uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. During
accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit addresses (MOVX @ RI),
Port 2 emits the contents of the P2 Special Function Register. Port 2 also
receives the high-order address bits and some control signals during Flash
programming and verification.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
13
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Port 3
Port 3 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. The Port 3
output buffers can sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 3
pins, they are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs.
As inputs, Port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current
because of the pull-ups. Port 3 receives some control signals for Flash
programming and verification. Port 3 also serves the functions of various
special features of the 8051
P3.0-RxD:
It is an Input signal. Through this I/P signal microcontroller receives serial
data of serial communication circuit.
P3.1-TxD:
It is O/P signal of serial port. Through this signal data is transmitted.
P3.2- (INT0):
It is external hardware interrupt I/P signal. Through this user, programmer or
peripheral interrupts to microcontroller.
P3.3-(INT1):
It is external hardware interrupt I/P signal. Through this user, programmer or
peripheral interrupts to microcontroller.
P3.4- T0:
It is I/P signal to internal timer-0 circuit. External clock pulses can connects
to timer-0 through this I/P signal.
P3.5-T1:
It is I/P signal to internal timer-1 circuit. External clock pulses can connects
to timer-1 through this I/P signal.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
14
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
P3.6-[WR(bar)]:
It is active low write O/P control signal. During External RAM (Data memory)
access it is generated by microcontroller. when [WR(bar)]=0, then performs
write operation.
P3.7-[RD(bar)]:
It is active low read O/P control signal. During External RAM (Data memory)
access it is generated by microcontroller. when [RD(bar)]=0, then performs
read operation from external RAM.
RST
Reset input. A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is
running resets the device. This pin drives High for 98 oscillator periods after
the Watchdog times out. The DISRTO bit in SFR AUXR (address 8EH) can be
used to disable this feature. In the default state of bit DISRTO, the RESET
HIGH out feature is enabled.
ALE/PROG
Address Latch Enable (ALE) is an output pulse for latching the low byte of the
address during accesses to external memory. This pin is also the program
pulse input (PROG) during Flash programming. in normal operation, ALE is
emitted at a constant rate of 1/6 the oscillator frequency and may be used for
external timing or clocking purposes. Note, however, that one ALE pulse is
skipped during each access to external data memory. If desired, ALE
operation can be disabled by setting bit 0 of SFR location 8EH. With the bit
set, ALE is active only during a MOVX or MOVC instruction. Otherwise, the pin
is weakly pulled high. Setting the ALE-disable bit has no effect if the
microcontroller is in external execution mode.
PSEN
Program Store Enable (PSEN) is the read strobe to external program
memory. When the 8051 is executing code from external program memory,
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
15
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
PSEN is activated twice each machine cycle, except that two PSEN activations
are skipped during each access to external data memory.
EA/VPP
External Access Enable. EA must be strapped to GND in order to enable the
device to fetch code from external program memory locations starting at
0000H up to FFFFH. Note, however, that if lock bit 1 is programmed, EA will
be internally latched on reset. Port Pin Alternate Functions
8051 EA should be strapped to VCC for internal program executions.
This pin also receives the 12-volt programming enable voltage (VPP) during
Flash programming.
XTAL1
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock
operating circuit.
XTAL2
Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier
Architecture of 8051 Microcontroller:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
16
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Special Function Registers
A map of the on-chip memory area called the Special Function Register (SFR)
space is shown in Note that not all of the addresses are occupied, and
unoccupied addresses may not be implemented on the chip. Read accesses to
these addresses will in general return random data, and write accesses will
have an indeterminate effect.
Data Memory
The 8051 implements 128 bytes of on-chip RAM. The 128 bytes are
accessible via direct and indirect addressing modes. Stack operations are
examples of indirect addressing, so the 128 bytes of data RAM are available
as stack space.
Interrupts
The AT8051 has a total of five interrupt vectors: two external interrupts
(INT0 and INT1), two timer interrupts (Timers 0 and 1), and the serial port
interrupt. These interrupts are all shown in Each of these interrupt sources
can be individually enabled or disabled by setting or clearing a bit in Special
Function Register IE. IE also contains a global disable bit, EA, which disables
all interrupts at once.bit positions IE.6 and IE.5 are unimplemented. User
software should not write 1s to these bit positions, since they may be used in
future AT89 products. The Timer 0 and Timer 1 flags, TF0 and TF1, are set at
S5P2 of the cycle in which the timers overflow. The values are then polled by
the circuitry in the next cycle.
ACCUMULATOR (ACC):
Accumulator is a general-purpose register, which s t o r e s r u n t i m e
results. Before performing any operation upon an operand ,
operand has to be stored in the accumulator. Results of arithmetical
operations are also stored in the accumulator. When transferring
data from one register to another, it has to go through the accumulator.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
17
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
B REGISTER:
This B register provides temporary storage space for the result of
multiplication & division operation. Instructions of multiplication and
division can be applied only to operands located in registers A and B. Other
instructions can use this register as a secondary accumulator (A).
Data Pointer (DPTR) :
The Data pointer register is made up of two 8 bit
registers, named DPH (Data Pointer High) and DPL (Data Pointer Low).
These r e g i s t e r s a r e u s e d t o g i v e a d d r e s s e s o f t h e i n t e r n a l
o r e x t e r n a l m e m o r y . T h e DPTR is under the control of program.
DPTR is also manipulated as one 16 bit register; DPH & DPL are each
assigned an address. The 8051 microcontroller has additional DPTR. There
are two 16-bitDPTR registers that address the external memory,
and a single bit called DPS (bit0 in AUXR1) that allows the program
code to switch between them.
Serial Port:
Serial port is used to provide communication among two
devices.
S e r i a l
d a t a
c o m m u n i c a t i o n
h a s
b e e n
w i d e l y
u s e d
f o r
l o n g
d i s t a n c e
communication because of the ease and the economy of using
only one wire to t r a n s m i t d a t a .
Serial port is also referred as RS232 port.
RS232
is
an
asynchronous way of communication.
Asynchronous transmission allows data t o b e t r a n s m i t t e d
without the sender having to send a clock signal to
t h e receiver. Instead, the sender and receiver must agree on
timing parameters in advance and special bits are added to each
word, which are used to synchronize the sending and receiving units.
When a word is given to the UART for Asynchronous transmissions, a bit
called the “Start Bit “ I s a d d e d t o t h e b e g i n n i n g o f e a c h
word that is to be transmitted. The Start Bit is used to
a l e r t t h e r e c e i v e r t h a t a w o r d o f d a t a i s about to be sent, and
to force the clock in the receiver into synchronization with the clock in
the transmitter.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
18
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Stack Pointer (SP) :
The stack refers to an area of internal RAM that is used in conjunction with
certain opposes to store and retrieve data quickly. The register used to
access the stack is called Stack Pointer. The 8 bit stack pointer register is
used by the 8051 to hold an internal RAM address that is called then top
of the stack.
The stack pointer increments before storing the data on the stack. As
retrieved from the stack the SP is decremented by one. The
number in Stack Pointer points to the location of the last "valid" address
within the Stack. With the beginning of every new routine, Stack
Pointer increases by 1; upon return from routine, SP decreases by 1.
Upon reset (or turning the power on), the stack pointer contains the value
07h..
Program Status Word (PSW):
The Program Status Word (PSW) register is an8 bit register. It is also
referred to as the flag register. It contains the math flags, user program
flag F0, and the register select bits that identify which of the four general
purpose register banks is currently in use by the program.
Program Counter (PC):
U s e d t o a c c e s s c o d e m e m o r y . P r o g r a m c o u n t e r always
points to the address of the next instruction in memory to be
executed. Upon reset (or turning the power on), the program
counter resets to the starting location of the program
Timers/Counters:
•
Timers
are
usually
the
most
complicated
p a r t s o f m icrocontroller. Physically, timer is a register
w h o s e v a l u e i s c o n t i n u a l l y i n c r e a s i n g . The 8051 MCU
clock employs a quartz c r y s t a l . A s t h i s f r e q u e n c y i s h i g h l y
stable and accurate, it is ideal for time measuring.
•
Since one instruction takes 12 oscillator cycles to
c o m p l e t e , t h e Math is easy. 8051 has three Timers/Counters
marked as T0, T1 & T2. Their purpose is to measure time and count
external occurrences, but can also be used as clock in serial
communication purpose called as, Baud Rate.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
19
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Oscillator Characteristics:
XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respectively, of an inverting
amplifier which can be configured for use as an on-chip oscillator, as shown in
Figs 6.2.3. Either a quartz crystal or ceramic resonator may be used. To drive
the device from an external clock source, XTAL2 should be left unconnected
while XTAL1 is driven as shown in Figure 6.2.4.There are no requirements on
the duty cycle of the external clock signal, since the input to the internal
clocking circuitry is through a divide-by-two flip-flop, but minimum and
maximum voltage high and low time specifications must be observed.
Fig 6.2.3 Oscillator Connections
Fig 6.2.4 External Clock Drive
Description Of components:
GSM Module:
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
20
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
EXPLANATION:
GSM has been the backbone of the phenomenal success in mobile telecom
over the last decade. GSM is an open, non- proprietary system that is
constantly evolving. One of its great strengths is the international roaming
capability.
This gives consumers seamless and same standardized same number
contact ability in more than 212 countries. This has been a vital driver in
growth, with around 300 million GSM subscribers currently in Europe and
Asia.
Voice is digitally encoded via a unique encoder, which emulates the
characteristics of human speech.
In the Americas, today's 7 million subscribers reset to grow rapidly, with
market potential of 500 million in population, due to the introduction of
GSM 800, which allows operators using the 800 MHz band to have access
to GSM technology too.
This method of transmission permits a very efficient data rate/information
content ratio. Cellular mobile communication is based on the concept of
frequency reuse.
The propagation environment determines the interference received from
neighboring co-channel cells, which in turn governs the reuse distance,
that is, the distance allowed between co-channel cells (cells using the
same set of frequency channels). The cell size determination is usually
based on the local traffic distribution and demand in the area. The smaller
the cell has to be sized in order to avail the frequency set to a smaller
number of roaming subscribers and thus limit the call blocking probability
within the cell.
The smaller the cell is sized, the more equipment will be needed in the
system as each cell requires the necessary transceiver and switching
equipment, known as the base station subsystem(BSS), through which the
mobile users access the network over radio links.
Since digital modulation systems can operate with a smaller signal to noise
(i.e., signal to interference) ratio for the same service quality, they, in one
respect, would allow smaller reuse distance and thus provide higher
spectrum efficiency. This is one advantage the digital cellular provides over
the older analogue cellular radio communication systems.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
21
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
GSM NETWORK
A GSM network is composed of several functional entities, whose functions
and interfaces are specified. The GSM network can be divided into three
broad parts. The Mobile Station is carried by the subscriber
GSM SPECIFICATION
Device Name: Wave com ROM (Flash): 16MbRAM: 2MbOperating Voltage:
3.1 – 4.5 V Receiving Frequency: 925 – 960 MHz
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF 8051:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
22
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
EXPLANATION :
Microcontroller (MC) may be called computer on chip since it has basic
features of microprocessor with internal ROM, RAM, Parallel and serial
ports within single chip. Or we can say microprocessor with memory and
ports is called as microcontroller. This is widely used in washing machines,
vcd player, microwave oven, robotics or in industries.
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems
Microcontroller can be classified on the basis of their bits processed like
8bit MC, 16bit MC.
8 bit microcontroller, means it can read, write and process 8 bit data. Ex.
8051 microcontroller. Basically 8 bit specifies the size of data bus. 8 bit
microcontroller means 8 bit data can travel on the data bus or we can
read, write process 8 bit data.
Features of 8051:
8051 Central Processing Unit:
On-chip Flash Program Memory with In-System Programming (ISP) and
In-Application Programming (IAP) capability.
Boot
ROM
contains
low
level
Flash
p r o g r a m m i n g r o u t i n e s f o r downloading via the UART.
Supports 6-clock/12-clock mode via parallel programmer (default
clock mode after Chip Erase is 12-clock).
6-clock/12-clock mode Flash bit erasable and programmable via ISP.
6-clock/12-clock mode programmable “on-the-fly” by SFR bit.
Peripherals (PCA, timers, UART) may use either 6 -clock or
1 2 - c l o c k mode while the CPU is in 6-clock mode.
Speed up to 20 MHz with 6-clock cycles per machine cycle
( 4 0 M H z equivalent performance); up to 33 MHz with 12 clocks per
machine cycle.
Fully static operation RAM expandable externally to 64 kilo bytes.
Four interrupt priority levels.
Seven interrupt sources.
Four 8-bit I/O ports.
Full-duplex enhanced UART.
Automatic address recognition
Power control modes
Clock can be stopped and resumed
Idle mode
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
23
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Power down mode
Programmable clock-out pin Second DPTR register Asynchronous port
reset Low EMI (inhibit ALE)Programmable Counter Array (PCA)
PWM Capture/compare
MAX232:
The MAX232 IC is used to convert the TTL/CMOS logic levels to RS232 logic
levels during serial communication of microcontrollers with PC. The controller
operates at TTL logic level (0-5V) whereas the serial communication in PC
works on RS232 standards (-25 V to + 25V). This makes it difficult to
establish a direct link between them to communicate with each other.
The intermediate link is provided through MAX232. It is a dual driver/receiver
that includes a capacitive voltage generator to supply RS232 voltage levels
from a single 5V supply. Each receiver converts RS232 inputs to 5V
TTL/CMOS levels. These receivers (R1 & R2) can accept ±30V inputs. The
drivers (T1 & T2), also called transmitters, convert the TTL/CMOS input level
into RS232 level.
The transmitters take input from controller’s serial transmission pin and send
the output to RS232’s receiver. The receivers, on the other hand, take input
from transmission pin of RS232 serial port and give serial output to
microcontroller’s receiver pin. MAX232 needs four external capacitors whose
value ranges from 1µF to 22µF.
Pin Diagram:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
24
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Pin Description:
Pin
No
1
Function
Name
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Capacitor connection pins
Output pin; outputs the serially transmitted data at
RS232 logic level; connected to receiver pin of PC
serial port
Input pin; receives serially transmitted data at RS 232
logic level; connected to transmitter pin of PC serial
port
Output pin; outputs the serially transmitted data at
TTL logic level; connected to receiver pin of controller.
Input pins; receive the serial data at TTL logic level;
connected to serial transmitter pin of controller.
Output pin; outputs the serially transmitted data at
TTL logic level; connected to receiver pin of controller.
Input pin; receives serially transmitted data at RS 232
logic level; connected to transmitter pin of PC serial
port
Output pin; outputs the serially transmitted data at
RS232 logic level; connected to receiver pin of PC
serial port
Ground (0V)
Supply voltage; 5V (4.5V – 5.5V)
Capacitor
1
+
Capacitor
3
+
Capacitor 1 Capacitor
2
+
Capacitor 2 Capacitor 4 T2 Out
R2 In
R2 Out
T2 In
T1 In
R1 Out
R1 In
T1 Out
Ground
Vcc
The MAX232 datasheet specifies that the IC is a dual driver/receiver that
includes a capacitive voltage generator to supply TIA/EIA-232-F voltage
levels from a single 5-V supply. Each receiver converts TIA/EIA-232-F
inputs to 5-V TTL/CMOS levels. These receivers have a typical threshold
of 1.3 V, a typical hysteresis of 0.5 V, and can accept ±30-V inputs. Each
driver converts TTL/CMOS input levels into TIA/EIA-232-F levels.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
25
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
FEATURES OF MAX232 IC:
Low power consumption, the typical supply current of 5Ma.
The internal integration of two RS-232C driver
The internal integration of the two RS-232C receivers
Only requires a single 5V power supply
Chip charge pump with a boost, voltage, polarity reversal ability to
generate 10V and-10V voltage V
PUSH TO ON SWITCH:
A push-button (also spelled pushbutton) or simply button is a simple switch
mechanism for controlling some aspect of a machine or aprocess. Buttons are
typically made out of hard material, usually plastic or metal. The surface is
usually flat or shaped to accommodate the human finger or hand, so as to be
easily depressed or pushed. Buttons are most often biased switches, though
even many un-biased buttons (due to their physical nature) require a spring
to return to their un-pushed state. Different people use different terms for
the "pushing" of the button, such as press, depress, mash, and punch. In this
circuit it is used to see the total count of each party and total votes in LCD
Presets:
These are miniature versions of the standard variable resistor. They are
designed to be mounted directly onto the circuit board and adjusted only
when the circuit is built. For example to set the frequency of an alarm tone
or the sensitivity of a light-sensitive circuit. A small screwdriver or similar
tool is required to adjust presets. Presets are much cheaper than standard
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
26
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
variable resistors so they are sometimes used in projects where a standard
variable resistor would normally be used.
Preset symbol
Multitier presets are used where very precise adjustments must be made.
The screw must be turned many times (10+) to move the slider from one end
of the track to the other, giving very fine control.
Power Supply:
The power supplies are designed to convert high voltage AC mains
electricity to a suitable low voltage supply for electronic circuits and other
devices. A power supply can by broken down into a series of blocks, each
of which performs a particular function. A d.c power supply which
maintains the output voltage constant irrespective of a.c mains
fluctuations or load variations is known as “Regulated D.C Power Supply”
For example a 5V regulated power supply system as shown below:
Transformer:
A transformer is an electrical device which is used to convert electrical
power from one Electrical circuit to another without change in frequency.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
27
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Transformers convert AC electricity from one voltage to another with little
loss of power. Transformers work only with AC and this is one of the
reasons why mains electricity is AC. Step-up transformers increase in
output voltage, step-down transformers decrease in output voltage.
Most power supplies use a step-down transformer to reduce the
dangerously high mains voltage to a safer low voltage. The input coil is
called the primary and the output coil is called the secondary.
There is no electrical connection between the two coils; instead they are
linked by an alternating magnetic field created in the soft-iron core of the
transformer. The two lines in the middle of the circuit symbol represent
the core.
Transformers waste very little power so the power out is (almost) equal to
the power in. Note that as voltage is stepped down current is stepped up.
The ratio of the number of turns on each coil, called the turn’s ratio,
determines the ratio of the voltages. A step-down transformer has a large
number of turns on its primary (input) coil which is connected to the high
voltage mains supply, and a small number of turns on its secondary
(output) coil to give a low output voltage.
Turns ratio = Vp/ VS = Np/NS
Power Out= Power In
VS X IS=VP X IP
VP = primary (input) voltage
NP = number of turns on
primary coil
Ip = primary (input) current
RECTIFIER:
A circuit which is used to convert ac to dc is known as RECTIFIER. The
process of conversion ac to dc is called “rectification”.
TYPES OF RECTIFIERS:
1. Half wave Rectifier
2. Full wave rectifier
Centre tap full wave rectifier.
Bridge type full bridge rectifier.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
28
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
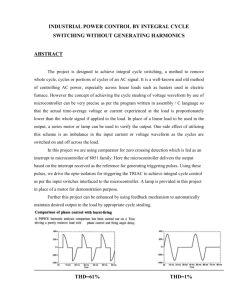
Comparison of rectifier circuits:
Parameter
Type of Rectifier
Half wave
Number of
Full wave
Bridge
diodes
1
2
4
Vm
2Vm
Vm
2Vm/
2Vm/
0.318Vm
0.636Vm
0.636Vm
1.21
0.482
0.482
f
2f
2f
0.406
0.812
0.812
0.287
0.693
0.812
Vim/2
Vim/√2
Vim/√2
PIV of diodes
D.C output voltage
Vdc,at
Vm/
no-load
Ripple factor
Ripple
Frequency
Rectification
Efficiency
Transformer
Utilization
Factor(TUF)
RMS voltage V m
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
29
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Full-wave Rectifier:
From the above comparison we came to know that full wave bridge
rectifier as more advantages than the other two rectifiers. So, in our
project we are using full wave bridge rectifier circuit.
Bridge Rectifier:
A bridge rectifier makes use of four diodes in a bridge arrangement to
achieve full-wave rectification. This is a widely used configuration, both
with individual diodes wired as shown and with single component bridges
where the diode bridge is wired internally.
A bridge rectifier makes use of four diodes in a bridge arrangement as
shown in fig(a) to achieve full-wave rectification. This is a widely used
configuration, both with individual diodes wired as shown and with single
component bridges where the diode bridge is wired internally.
Fig (A)
Operation:
During positive half cycle of secondary, the diodes D2 and D3 are in
forward biased while D1 and D4 are in reverse biased as shown in the
fig(b). The current flow direction is shown in the fig (b) with dotted
arrows.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
30
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
During negative half cycle of secondary voltage, the diodes D1 and D4 are
in forward biased while D2 and D3 are in reverse biased as shown in the
fig(c). The current flow direction is shown in the fig (c) with dotted arrows.
Regulator:
Voltage regulator ICs is available with fixed (typically 5, 12 and 15V)
variable output voltages. The maximum current they can pass also rates
them. Negative voltage regulators are available, mainly for use in dual
supplies. Most regulators include some automatic protection from
excessive current ('overload protection') and overheating ('thermal
protection').
Many of the fixed voltage regulator ICs has 3 leads and look like power
transistors, such as the 7805 +5V 1A regulator shown on the right. The
LM7805 is simple to use. You simply connect the positive lead of your
unregulated DC power supply (anything from 9VDC to 24VDC) to the Input
pin, connect the negative lead to the Common pin and then when you turn
on the power, you get a 5 volt supply from the output pin.
A Three Terminal Voltage Regulator
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
31
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
78XX:
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
EXPLANATION:
The Bay Linear LM78XX is integrated linear positive regulator with three
terminals. The LM78XX offer several fixed output voltages making them
useful in wide range of applications. When used as a zener diode/resistor
combination replacement, the LM78XX usually results in an effective
output impedance improvement of two orders of magnitude, lower
quiescent current. The LM78XX is available in the TO-252, TO-220 & TO263packages,
FEATURES OF 78XX IC:
• Output Current of 1.5A
• Output Voltage Tolerance of 5%
• Internal thermal overload protection
• Internal Short-Circuit Limited
• No External Component
• Output Voltage 5.0V, 6V, 8V, 9V, 10V, 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V
• Offer in plastic TO-252, TO-220 & TO-263
• Direct Replacement for LM78XX
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
32
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
LCD DISPLAY:
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen is an electronic display module and
find a wide range of applications. A 16x2 LCD display is very basic module
and is very commonly used in various devices and circuits. These modules
are preferred over seven segments and other multi segment LEDs.
The reasons being: LCDs are economical; easily programmable; have no
limitation of displaying special & even custom characters (unlike in seven
segments), animations and so on.
A 16x2 LCD means it can display 16 characters per line and there are 2
such lines. In this LCD each character is displayed in 5x7 pixel matrix. This
LCD has two registers, namely, Command and Data.
The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD.
A command is an instruction given to LCD to do a predefined task like
initializing it, clearing its screen, setting the cursor position, controlling
display etc. The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD.
The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD.
Liquid crystal display is a thin, flat display device made up of any number
of color or mono- chrome pixels arrayed in front of a light source
or reflector.
This is used to display functioning mode of the microcontroller.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
33
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Pin description:
Pin.
No
Function
1
Ground (0V)
2
Supply voltage; 5V (4.7V – 5.3V)
Vcc
3
Contrast adjustment; through a variable resistor
VEE
4
Selects command register when low; and data Register
register when high
Select
5
Low to write to the register; High to read from the Read/write
register
6
Sends data to data pins when a high to low pulse Enable
is given
Name
Ground
7
DB0
8
DB1
9
DB2
10
11
8-bit data pins
DB3
DB4
12
DB5
13
DB6
14
DB7
15
Backlight VCC (5V)
Led+
16
Backlight Ground (0V)
Led-
1. Command/Instruction Register- stores the command instructions given to
the LCD. A command is an instruction given to LCD to do a predefined task
like initializing, clearing the screen, setting the cursor position, controlling
display etc.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
34
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
2. Data Register- stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the
ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD.
Programming the LCD:
1. Data pin8 (DB7) of the LCD is busy flag and is read when R/W = 1 & RS =
0. When busy flag=1, it means that LCD is not ready to accept data since it is
busy with the internal operations. Therefore before passing any data to LCD,
its command register should be read and busy flag should be checked.
2.
To send data on the LCD, data is first written to the data pins with R/W
= 0 (to specify the write operation) and RS = 1 (to select the data register).
A high to low pulse is given at EN pin when data is sent. Each write operation
is performed on the positive edge of the Enable signal.
3.
To send a command on the LCD, a particular command is first specified
to the data pins with R/W = 0 (to specify the write operation) and RS = 0 (to
select the command register). A high to low pulse is given at EN pin when
data is sent.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
35
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER - 4
SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION:
KEIL COMPILER
INTRODUCTION:
The Real View Microcontroller Development Kit is the complete software
development environment for all ARM7, ARM9, Cortex -M1, and Cortex-M3
processor based devices. It combines the industry leading Real View
compilation tools (by ARM) with the µVision IDE/Debugger, providing
developers with an easy to use, feature-rich environment optimized for ARM
Powered devices. The Real View Microcontroller Development Kit (MDK)
provides an easy-to-use development interface, with many unique features
designed to help you develop your project quickly and easily. Save time by
using the Device Database to automatically configure device and project
parameters. Benefit from better verification by using the integrated Device
Simulator which accurately models more than 260 ARM Powered devices
including the ARM instruction set and on-chip peripherals. The Real View MDK
is based on the ARM Real View compilation tools, recognized as delivering the
tightest, highest performing code for all ARM-Powered devices. In addition,
further code size savings can be gained by selecting the new Micro Lib, which
has been specifically developed and optimized for embedded systems [9].
DEBUGGER AND DEVICE SIMULATOR:
The µVision Debugger supports complex breakpoints (with conditional or
logical expressions) and memory access breakpoints (with read/write
access from an address or range).The debugger also displays code
coverage and execution profiling information in the editor windows.
Additionally, the µVision Debugger simulates a complete ARM Powered
microcontroller including the instruction set and on-chip peripherals. These
powerful simulation capabilities provide serious benefits and promote
rapid, reliable embedded software development and verification.
Simulation allows software testing with no hardware.
Improve overall reliability with early software debugging.
Simulation allows breakpoints that are not possible with hardware
debuggers.
Simulation allows for optimal input signals (hardware debuggers add extra
noise).
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
36
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Signal functions are easily programmed to reproduce complex, real-world
input signals.
Single-step through signal processing algorithms.
Test failure scenarios that would destroy real hardware.
MAIN WINDOW OF KEIL COMPILER
PROJECT CONFIGURATION:
The µVision IDE incorporates a Device Database of supported ARM
Powered microcontrollers. In µVision projects, required options are set
automatically when you select the device from the Device Database.
µVision displays only those options that are relevant to the selected device
and prevents you from selecting incompatible directives. Only a few
dialogs are required to completely configure all the tools (assembler,
compiler, linker, debugger, and flash download utilities) and memory map
for the application.
EDITOR AND SOURCE BROWSER:
The µVision Editor includes all the standard features you expect in a
professional editor. Workflow is optimized with intuitive toolbars providing
quick access to editor functions, most of which are also available while
debugging for easy source code changes. The integrated µVision Source
Browser quickly displays information about symbols and variables in your
program using the F12 key and the Source Browser Window.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
37
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
GETTING STAR
The µVision IDE is the easiest way for most developers to create
embedded applications using the Kiel development tools. To launch
µVision, click on the icon on your desktop or select Kiel µVision3 from the
Start Menu.
CREATIG A PROJECT
In the Project Menu:
New Creates a new project.
Open Opens an existing project.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT:
File Groups allow you to group associated files together. They may be
used to separate files into functional blocks or to identify engineers in your
software team.
Project Targets allow you to create several programs from a single
project. You may require one target for testing and another target for a
release version of your application. Each target allows individual tool
settings within the same project file.
A Project is the collection of all the source files as well as the compiler,
assembler, and linker settings required to compile and link a program.
µVision includes several robust features that make project management
easy.
DEVICE SUPPORT:
One of the hardest parts of starting a new project is selecting the right mix
of compiler, assembler, and linker options for the particular chip you use.
µVision provides the Device Database which makes this tedious task easy.
When you create a new project, you select the chip you will use and
µVision sets all the necessary assembler, compiler, and linker options
automatically.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
38
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
TARTUP CODE:
Configuring startup code can be one of the most frustrating aspects of
embedded software development. The µVision IDE automatically includes
the appropriate startup code (based on the device you select) and
provides a known foundation from which to start. The Configuration
Wizard helps you set startup options for your target hardware using
familiar dialog controls.
OPTION SETTINGS:
µVision lets you set the options for all files in a target, a group, or even a
single source file. Click the Options for Target button on the toolbar to
change the project options for the currently selected target. In the Project
Workspace, you may right-click the target, group, or source file to open
the options dialog specific to that item.
The Options Dialog offers several Tabs where you specify option settings:
The Device tab allows you to select the device for this target.
The Target tab allows you to specify the memory model and memory
parameters. You may enter the external (or off-chip) memory address
ranges under External Memory. When you start a new project, you
typically only need to setup the options on this tab.
The Output tab allows you to specify the contents of the output files
generated by the assembler, compiler, and linker.
The Listing tab allows you to configure the contents of the listing files.
The C/C++, Asm, and Linker tabs allow you to enter tool-specific options
and display the current tool settings.
The Debug tab configures the µVision Debugger.
The Utilities tab configures Flash memory programming for your target
system.
TARGETS & GROUPS:
µVision projects are composed of one or more targets, one or more file
groups, and source files.
A target is a collection of all files groups and the development tool
options. While most projects require only one target, you may create as
many targets as you like. Each target generates a different target file with
different options.
These two targets, Simulator-Real View and Simulator-CARM, create
distinct binary files. The Simulator-Real view target uses the Real View
compilation tools for ARM while the Simulator-CARM target uses the Kiel
compilation tools for ARM.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
39
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
Each target has its own tool configuration settings. Files and groups may
be included or excluded as needed for startup or other target-specific
source code[9].
Click the Setup Editor Button to manage the targets maintained in your
project. In the Project Components tab, you may configure the Project
Targets, Groups, and Files in your project.
Each Target has its own option settings and output file name that you may
define. You may create one Target for testing with the simulator and
another Target for a release version of your application that will be
programmed into Flash ROM.
Within Targets, you may have one or more file Groups which allow you to
associate source files together. Groups are useful for grouping files into
functional blocks or for identifying engineers in a software team.
Files are simply the source files within a group.
SOURCE FILES:
The source files in your µVision project display in a Project Workspace.
Each Project can be configured to generate one or more Targets. Each
Target has its own option settings and output file name that you may
define. You may create one Target for testing with the simulator and
another Target for a release version of your application that will be
programmed into Flash ROM. Within a Target, you may have one of more
file Groups which allow you to associate source files together. Groups are
useful for grouping files into functional blocks or for identifying engineers
in a software team.
The Project menu provides access to all dialogs for project management
including...
New Project... which creates a new project.
Targets, Groups, Files... which add components to a project. The Local
menu in the Project window allows you to add files to the project.
Open Project... which opens an existing project.
BUILDING PROJECTS:
µVision includes an integrated make facility that compiles, assembles, and
links your program. Click the Build Target button on the toolbar to
compile and assemble the source files in your project and link them
together into an absolute, executable program.
The assembler and compiler automatically generate file dependencies and
add them to the project. File dependency information is used during the
make process to build only those files that have changed or that include
other files that have changed. As µVision compiles and assembles your
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
40
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
source files, status information as well as errors and warnings appear in
the Output Window[9].
You may double-click on an error or warning to immediately begin editing the
file with the problem--even while µVision continues compiling your source
files in the background. The line numbers for errors and warnings are
synchronized even after you make changes to the source file(s). To get more
information about a particular error message, select the message and press
F1 for full help text. If you enable global optimizations, µVision re-compiles
your source files to achieve the most optimal global use of registers.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
41
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
CHAPTER – 5
Result :
Conclusion :
Number of candidates could be increased by using other microcontroller.
It could be interfaced with printer to get the hard copy of the result almost
instantly from the machine itself.
It could also be interfaced with the personal computer and result could be
stored in the central server and its backup could be taken on the other
backend servers.
Again, once the result is on the server it could be relayed on the network
to various offices of the election conducting authority. Thus our project
could make the result available any corner of the world in a matter of
seconds.
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
42
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
AREA OF APPLICATIONS
Fast track voting which could be used in small scale elections, like
resident welfare association, “panchayat” level election and other
society level elections.
It could also be used to conduct opinion polls during annual share
holders meeting.
It could also be used to conduct general assembly elections where
number of candidates are less than or equal to eight in the current
situation.
It is used in various TV serials as for public opinion.
REFRENCES
Muhammad Ali Mazidi , Janice Gillispie Mazidi, Rolin D. Mckinlay.
Second edition, “THE 8051 MICROCONTROLLER AND EMBEDDED
SYSTEM”
K. J. Ayala. Third edition, “The 8051 MICROCONTROLLER”
Tutorial on microcontroller:
www.8051projects.net/microcontroller_tutorials/
Tutorial on LCD:
www.8051projects.net/lcd-interfacing/
WEBSITES
www.atmel.com
www.seimens.com
www.howstuffworks.com
www.alldatasheets.com
www.efyprojects.com
www.google.com
www.eci.gov.in/Audio_VideoClips/presentation/EVM.ppt
www.rajasthan.net/election/guide/evm.htm
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
43
ARTIFICIAL VOTING MACHINE USING GSM TECHNOLOGY
APPENDIX:
Data sheet:
P.B.SIDDHARTHA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE |
44