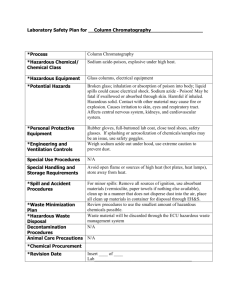
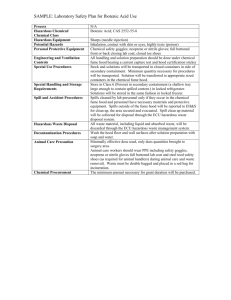
Outline of Right to Know Chemical
advertisement

Outline of Right to Know Chemical-Specific Training • • • • • • • • Right to Know -- the law MSDS Labeling Personal Protective Equipment Emergencies Chemicals Gas Cylinders Hazardous Waste Right to Know Overview • Advise of operations where hazardous materials are present • Right to Know about hazardous chemicals in your workplace • Make aware and provide proper training in the hazards associated with chemicals • Can not be fired, discriminated against, or disciplined for exercising your Right to Know • Train personnel maintenance and use of PPE • Grievance procedure may be filed Training Requirements • Basic Training All state employees (10 min. video viewed at T&D) • Chemical-Specific Training Employees who work with hazardous chemicals • Annual Refresher Training Employees who work with hazardous chemicals Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) CLICK ON OUR MSDSONLINE MSDS • • • • • • • • Chemical identity and components Manufacturer - address/phone number Physical & chemical characteristics Fire & explosion hazard information Personal protective equipment Chemical exposure information Spill information Disposal information Labeling • Original Containers • Secondary Containers SIGNAL WORDS DANGER immediate threat of serious injury or death WARNING potential threat of serious injury or death CAUTION potential threat of moderate injury NFPA Diamond FIRE HAZARD Flash Points HEALTH HAZARDS 4 3 2 1 0 Deadly Extreme Danger Hazardous Slightly Hazardous Normal Material 4 Below 73° F 3 Below 100° F 2 Above 100° F, Not Exceeding 200° F 1 Above 200° F 0 Will Not Burn SPECIFIC HAZARD Oxidizer Acid Alkali Corrosive Use NO WATER Radioactive OX ACID ALK COR W Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) HEALTH FLAMMABILITY REACTIVITY PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT Secondary Container Labeling • Chemical Name • Hazard Warning CHEMICAL OW NER Lab Safety Supply Inc. HEALTH DATE Reorder No. 706 CRS # 848525 FLAMMABILITY REACTIVITY Chloroform toxin 2/4/99 PPE CRS # 848510, 848512 Methanol flammable 2/4/99 Hydrochloric Acid corrosive 2/4/99 Sodium Nitrate oxidizer 2/4/99 Acetic Acid Acetonitrile Benzene Carbon Tetrachloride Chloroform Ethanol Hydrogen Peroxide Sulfuric Acid Hydrochloric Acid Hydrofluoric Acid Nitric Acid Potassium Chloride Potassium Nitrate Potassium Hydroxide Methylene Chloride Methanol Sodium Chloride Sodium Chlorate Sodium Nitrite Sodium Nitrate Sodium Hydroxide Trichloroethylene Tetrahydrofuran C2H4O2 or AA ACN C6H6 CCl4 CHCl3 EtOH H2O2 H2SO4 HCL HF HNO3 KCl KNO3 KOH CH2Cl2 MeOH NaCl NaClO3 NaNO2 NaNO3 NaOH TCE THF Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Routes of Exposure • Absorption • Ingestion • Inhalation • Injection Skin Protection • Proper Attire • Lab Coats or Aprons • Proper Gloves • Face Shields Eye Protection • • • • Safety Glasses Goggles Face Shield UV Protection Ingestion Protection • • • • NO FOOD Removal of Gloves Personal Hygiene Face Shield Respiratory Protection • Fume Hoods • Dusk Masks • Respirators Fume Hoods Work with the sash at 10-12 inches Work 6 inches inside the face of the hood Prevent excessive movement near the hood Raise any equipment 1-2 inches off the flat surface of the hood Keep 1-2 inches of space in front of the hood baffle Fume hoods are tested annually by ESD Average face velocities should range between 100-120 feet per minute (fpm) Do not use power strips inside the hood Keep doors and windows closed Do not clutter hood with chemical storage and equipment Fume Hoods Respirator Program • Engineering controls • Respirator use and maintenance • Fit Testing • Record-Keeping RESPIRATOR FIT TESTING Emergency Procedures Fire Extinguisher Emergency Procedures FIRE ALARM Emergency Procedures PULL IN CASE OF FIRE Keep Fire Doors Closed Fire Door Fire Alarm Pull Stations DO NOT BLOCK In Case of a Fire Keep Exits Clear Types of Fire Extinguishers Fire Classification Class A - Wood/Paper Class B - Oil/Grease Class C - Electrical Class D - Metal Carbon Dioxide Dry Chemical for Class B & C for Class A,B, & C ACCIDENTS & INJURIES • Keep Eyewash Stations and Safety Showers unobstructed and functional • Make sure First Aid Kits are present and properly stocked • Fill out an Incident and Accident Report and a First Report of Injury form • SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION CHEMICAL SPILLS Contact ESS in the event of ANY spill 478-7161 OR UPD@ 85234 DO NOT clean up spill if: • • • • appropriate materials are not available chemical or level of hazard is unknown PPE is not available proper training has not been received CHEMICAL SPILLS Identify chemical Look for injuries Alert others Seal off area Get help Initiate area notification procedures CHEMICAL SPILL KIT Build One: Large tub Plastic dust pan and brush Safety goggles and gloves Disposal bags Absorbent material (kitty litter Neutralizers pH Paper Dilute bleach solution CRS : Spill Attack Pac / Catalog No. 931770 pg 133 / approximately $40.00 CHEMICALS Chemical Storage Codes General Guidelines for Chemical Storage •Store hazardous materials below shoulder height •Store by hazard classification [color codes] •Shelving: well anchored/chemical resistant SOLVENTS • Solvents include variety of chemicals -- hazards: Toxins Flammables Non-Hazardous • Most solvents handled in research laboratories are flammable liquids FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS • Use approved flammable storage cabinets • 20 gallons per 100 sq.ft. - fire separation • 10 gallons outside of approved cabinets or safety cans • 120 gallons maximum storage for any lab • Approved refrigerators/freezers only The Fire Triangle FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS Flashpoint: min. temp. at which a liquid gives off enough vapor to ignite Vapor Density: ratio of vapor vs. density of air Air = 1 <1 = lighter than air >1 = heavier than air FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS Explosive limit of gasoline Too Lean 0 1.3 Too Rich 100 7.6 LEL: min. % of vapor in air which can explode upon ignition UEL: max. % of vapor in air which can explode upon ignition Substance Hydrogen Acetylene Toluene LEL % 4.0 2.5 1.2 UEL % 75.0 80.0 7.1 CORROSIVES • Use Chemical-Resistant Secondary Containment • Separate Acids and Bases • Separate Inorganic/Organic Acids • Store in Lower Shelves or in Corrosives Cabinet CORROSIVES Corrosive material destroys living tissue CORROSIVES 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10,000,000 X 1,000,000 X 100,000 X 10,000 X 1,000 X 100 X 10 X neutral 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 CORROSIVES Spill of Sulfuric Acid Neutralizing Media Needed 1 gallon (~4L) 2 gallons 3 gallons 4 gallons 5 gallons 10 gallons 50 gallons 55 gallons 16 lbs. 32 lbs. 48 lbs. 64 lbs. 80 lbs. 160 lbs. 800 lbs. 880 lbs. CORROSIVES Be Careful when Mixing Acid and Water AAA Always Add Acid to water TOXINS • Store according to the nature of the chemical • Appropriate security may be necessary for some toxins • OXIDIZERS:(nitric acid) Store away from flammables, combustibles, reducers • WATER-REACTIVES:(sodium) Store in cool dry place Do not store under sinks, above water baths… Class D fire extinguishers • PEROXIDE-FORMERS:(THF, ethyl ether) Store in airtight containers in cool, dry place receipt and on opening Date upon Common oxidizers: • • • • • • • Nitrates Nitrites Chromates Permangantes Perchloric Acid Nitric Acid Persulfates Methanol: Chloroform & Sodium Hydroxide (explosive reaction) Calcium Carbide (violent reaction) Magnesium (violent reaction) Cyanuric Chloride (violent reaction) Berylium Hydride (intense reaction @ 200C) Bromine (intense exothermic reaction) Chromic Anhydride (possible explosive reaction) Nickel (possible ignition in the presence of catalytic amounts) GAS CYLINDERS Secured in upright position Replace stem caps when not in use Label Status - Full/Empty Turn off at main valve stem Transport with proper dolly HAZARDOUS WASTE Hazardous Waste Training: Call ESS @478-7161 Become Registered User for Waste Pick Up