File learner profile card presentation
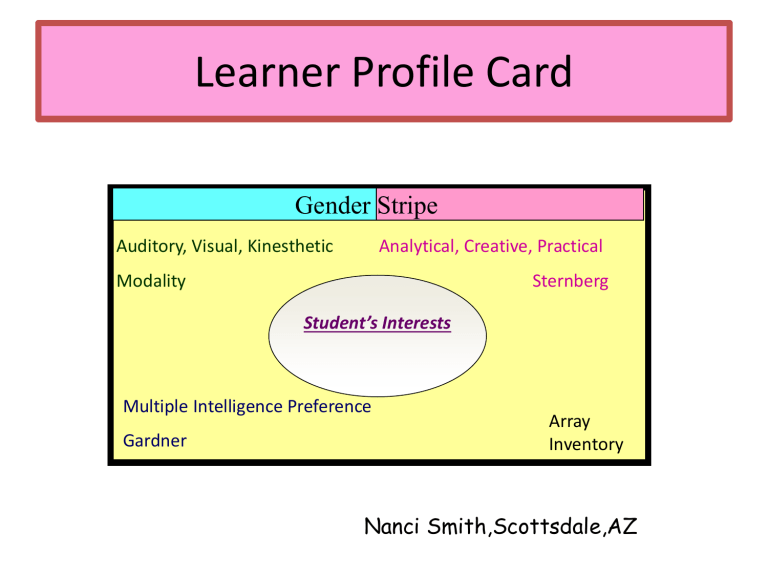
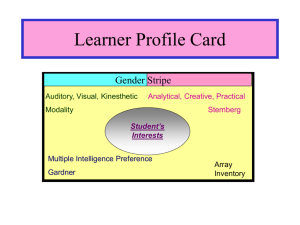
Learner Profile Card
Gender Stripe
Auditory, Visual, Kinesthetic
Modality
Analytical, Creative, Practical
Sternberg
Student’s Interests
Multiple Intelligence Preference
Gardner
Array
Inventory
Nanci Smith,Scottsdale,AZ
13.
14.
15.
16.
9.
10.
11.
12.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
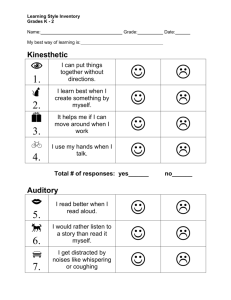
7.
8.
5.
6.
3.
4.
1.
2.
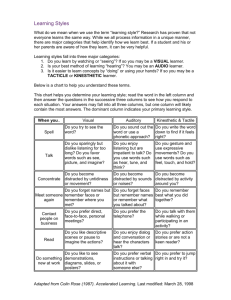
– The Modality Preferences Instrument (HBL, p. 23)
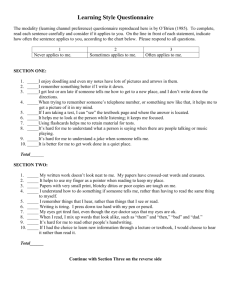
Follow the directions below to get a score that will indicate your own modality (sense) preference(s). This instrument, keep in mind that sensory preferences are usually evident only during prolonged and complex learning tasks.
Identifying Sensory Preferences
Directions: For each item, circle “A” if you agree that the statement describes you most of the time. Circle “D” if you disagree that the statement describes you most of the time.
I Prefer reading a story rather than listening to someone tell it.
I would rather watch television than listen to the radio.
I remember faces better than names.
I like classrooms with lots of posters and pictures around the room.
The appearance of my handwriting is important to me.
I think more often in pictures.
I am distracted by visual disorder or movement.
I have difficulty remembering directions that were told to me.
I would rather watch athletic events than participate in them.
I tend to organize my thoughts by writing them down.
My facial expression is a good indicator of my emotions.
I tend to remember names better than faces.
I would enjoy taking part in dramatic events like plays.
I tend to sub vocalize and think in sounds.
I am easily distracted by sounds.
I easily forget what I read unless I talk about it.
I would rather listen to the radio than watch TV.
My handwriting is not very good.
When faced with a problem , I tend to talk it through.
I express my emotions verbally.
I would rather be in a group discussion then read about a topic.
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
22.
I prefer talking on the phone rather than writing a letter to someone.
23.
I would rather participate in athletic events than watch them.
24.
I prefer going to museums where I can touch the exhibits.
25.
My handwriting deteriorates when the space becomes smaller.
26.
My mental pictures are usually accompanied by movement.
27.
I like being outdoors and doing things like biking, camping, swimming, hiking etc.
28.
I remember best what was done rather then what was seen or talked about. A D
29.
When faced with a problem, I often select the solution involving the greatest activity. A D
30.
I like to make models or other hand crafted items.
31.
I would rather do experiments rather then read about them.
32.
My body language is a good indicator of my emotions.
33.
I have difficulty remembering verbal directions if I have not done the activity before.
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
A D
Total the number of “A” responses in items 1-11
This is your visual score
Total the number of “A” responses in items 12-22
This is your auditory score
Total the number of “A” responses in items 23-33
This is you tactile/kinesthetic score
Interpreting the Instrument’s Score
_____
_____
_____
If you scored a lot higher in any one area: This indicates that this modality is very probably your preference during a protracted and complex learning situation.
If you scored a lot lower in any one area: This indicates that this modality is not likely to be your preference(s) in a learning situation.
If you got similar scores in all three areas: This indicates that you can learn things in almost any way they are presented.
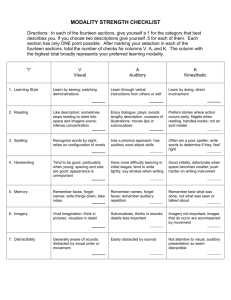
Visual
•
Take numerous detailed notes
•
Tend to sit in the front
•
Are usually neat and clean
•
Often close their eyes to visualize or remember something
•
Find something to watch if they are bored
•
Like to see what they are learning
•
Benefit from illustrations and presentations that use color
•
Are attracted to written or spoken language rich in imagery
•
Prefer stimuli to be isolated from auditory and kinesthetic distraction
http://www.usd.edu/trio/tut/ts/styleres.html
Auditory
•
Sit where they can hear but needn't pay attention to what is happening in front
•
May not coordinate colors or clothes, but can explain why they are wearing what they are wearing
•
Hum or talk to themselves or others when bored
•
Acquire knowledge by reading aloud
•
Remember by verbalizing lessons to themselves
(if they don't they have difficulty reading maps or diagrams or handling conceptual assignments like mathematics).
http://www.usd.edu/trio/tut/ts/styleres.html
Kinesthetic
• Need to be active and take frequent breaks
• Speak with their hands and with gestures
• Remember what was done, but have difficulty recalling what was said or seen
• Find reasons to tinker or move when bored
• Rely on what they can directly experience or perform
• Activities such as cooking, construction, engineering and art help them perceive and learn
• Enjoy field trips and tasks that involve manipulating materials
• Sit near the door or someplace else where they can easily get up and move around
• Are uncomfortable in classrooms where they lack opportunities for hands-on experience
• Communicate by touching and appreciate physically expressed encouragement, such as a pat on the back http://www.usd.edu/trio/tut/ts/styleres.html
Possible Formats to use to Differentiate by Learning Modality
Written
•diary entry
•bulleted list
•obituary
•invitation
•product guide
•game rules
•recipe
•movie critic
•FreqAskQues
•editorial
•character monologue
•job application
•gossip column
•mag. article
Visual
•cartoon/comic
•crossword puzzle
•map
•scale plan or drawing
•graphic org.
•concept web
•illustration
•print ad
•photograph
•powerpoint
•‘how to’ diagram
•fashion design
Auditory
•song
•set of discussion ?s
•conversation
•monologue
•sermon
•radiocast
•museum guide
•commercial
•reader’s theater
•interview
•tasting
•political speech
•puppet show
•storytell
Kinesthetic
•model
•cheer
•mime
•reenactment
•wax museum
•demonstration
•sales pitch with demo elements
•physical analogies
•taste tests
•‘how to’ video
•game
•sew, cook, build
•design a ....
Sandra Page bookpage@nc.rr.com 2008
Visual
Pictures
Graphic Organizers
Modality Task Prompts
Auditory Kinesthetic
Speeches Matching games
Discussions Modeling
Color coding
Posters
Charts / Graphs
Videos
Infomercials or PSAs “Becoming” the task
Creating Question Lists Hands-on tasks / touching
Read Alouds
Books / Instructions on tape
“Peg Board” yarn game
Gestures and Motions
Detailed Notes
Visualizing
Making Books
To Do Lists
Self Talk (Whispies)
Tape Recording
Answers
Interviews
Lectures / Tone &
Inflection
Motion
Drama / Skits
Charades
Manipulatives
Written Directions Spoken Directions Modeled Directions
Partial List of Learning Modality Tasks/Skills
Kinesthetic
•model •demonstrate •build
•act out •use tools to.. •dance
•produce •simulate •craft
•transform •show in lab •make
Visual
•diagram •overlay •map
•chart •timeline •web
•illustrate •cartoon •model
•graph •video •pop-up
Oral
•recite •broadcast •speech
•discuss •question •interview
•debate •cook/taste •sing
•argue •converse •perform
Auditory
•radiocast •soundscape •music
•preach •commercial •chant
•persuade •ad/jingle
•compose •speech
•rhythm
•phone
Self Assessment: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences
12.
13.
14.
9.
10.
11.
6.
7.
8.
2.
3.
4.
5.
18.
19.
20.
21.
15.
16.
17.
25.
26.
27.
22.
23.
24.
28.
29.
30.
1.
Where does your true intelligence (processing ability) lie? This quiz can help you determine where you stand. Read each statement. If it expresses some characteristic of yours and sounds true for the most part jot down a “T”. If it doesn’t mark and “F”. If the statement is sometimes true, sometimes false, leave it blank.
_____ I’d rather draw a map than give someone verbal directions.
_____ I can play (or used to play) a musical instrument.
_____ I can associate music with my moods.
_____ I can add or multiply quickly in my head.
_____ I like to work with calculators and computers.
_____ I pick up new dance steps quickly.
_____ It’s easy for me to say what I think in an argument or debate.
_____ I enjoy a good lecture, speech, or sermon.
_____ I always know north from south no matter where I am.
_____ Life seems empty without music.
_____ I always understand the directions that comes with new gadgets or appliances.
_____ I like to work puzzles and play games.
_____ Learning to ride a bike (or skate) was easy.
_____ I am irritated when I hear an argument or statement that sounds illogical.
_____ My sense of balance and coordination is good.
_____ I often see patterns and relationships between numbers faster and easier than others.
_____ I enjoy building models (or sculpting).
_____ I am good at finding the the fine points of word meanings.
_____ I can look at an object one way and see it turned sideways or backwards just as easily.
_____ I often connect a piece of music with some event in my life.
_____ I like to work with numbers and figures.
_____ Just looking at shapes of buildings and structures is pleasurable to me.
_____ I like to hum, whistle, and sing in the shower or when I am alone.
_____ I’m good at athletics.
_____ I’d like to study the structure and logic or languages.
_____ I’m usually aware of the expressions on my face.
_____ I’m sensitive to the expressions on other people’s faces.
_____ I stay in touch with my moods. I have no trouble identifying them.
_____I am sensitive to the moods of others.
_____ I have a good sense of what others think of me.
Scoring Sheet
Place a checkmark by each item, which you marked as "True." Add your totals. A total of
(four in any of the categories A through E indicates strong ability. In categories F through G a score of one or more means you have abilities in these areas as well.
A
Linguistic
7 ____
8 ____
14 ___
18 ___
25 ___
B
Logical/Math.
4 ____
5 ____
12 ___
16 ___
21 ___
C
Musical
2 ____
3 ____
10 ___
20 ___
23 ___
D
Spatial
1 ____
9 ____
11 ___
19 ___
22 ___
E
Body/Kinesthetic
6 ____
13 ___
15 ___
17 ___
24 ___
F
Intrapersonal
26 ___
28 ___
G
Interpersonal
27 ___
29 ___
30 __
TYPE
LINGUISTIC
LEARNER
“ The Word Player”
EIGHT STYLES OF LEARNING
CHARACTERISTICS LIKES TO IS GOOD AT LEARNS BEST BY
Learns through the manipulation of words. Loves to read and write in order to explain themselves. They also tend to enjoy talking
Read
Write
Tell stories
Memorizing names, places, dates and trivia
Saying, hearing and seeing words
LOGICAL/
Mathematical
Learner
“The Questioner”
SPATIAL
LEARNER
“The Visualizer”
Looks for patterns when solving problems. Creates a set of standards and follows them when researching in a sequential manner.
Learns through pictures, charts, graphs, diagrams, and art.
Do experiments
Figure things out
Work with numbers
Ask questions
Explore patterns and relationships
Draw, build, design and create things
Daydream
Look at pictures/slides
Watch movies
Play with machines
Math
Reasoning
Logic
Problem solving
Imagining things
Sensing changes
Mazes/puzzles
Reading maps, charts
Categorizing
Classifying
Working with abstract patterns/relationships
Visualizing
Dreaming
Using the mind’s eye
Working with colors/pictures
MUSICAL
LEARNER
“The Music
Lover”
Learning is often easier for these students when set to music or rhythm
Sing, hum tunes
Listen to music
Play an instrument
Respond to music
Picking up sounds
Remembering melodies
Noticing pitches/ rhythms
Keeping time
Rhythm
Melody
Music
TYPE
BODILY/
Kinesthetic
Learner
“ The Mover”
INTERpersonal
Learner
“The Socializer”
INTRApersonal
Learner
“The Individual”
NATURALIST
“The Nature
Lover”
EIGHT STYLES OF LEARNING,
Cont’d
CHARACTERISTICS
Eager to solve problems physically. Often doesn’t read directions but just starts on a project
Likes group work and working cooperatively to solve problems. Has an interest in their community.
Enjoys the opportunity to reflect and work independently. Often quiet and would rather work on his/her own than in a group.
LIKES TO
Move around
Touch and talk
Use body language
Have lots of friends
Talk to people
Join groups
Work alone
Pursue own interests
Enjoys relating things to their environment. Have a strong connection to nature.
Physically experience nature
Do observations
Responds to patterning nature
IS GOOD AT
Physical activities
(Sports/dance/ acting) crafts
Understanding people
Leading others
Organizing
Communicating
Manipulating
Mediating conflicts
Understanding self
Focusing inward on feelings/dreams
Pursuing interests/ goals
Being original
Exploring natural phenomenon
Seeing connections
Seeing patterns
Reflective Thinking
LEARNS BEST BY
Touching
Moving
Interacting with space
Processing knowledge through bodily sensations
Sharing
Comparing
Relating
Cooperating interviewing
Working along
Individualized projects
Self-paced instruction
Having own space
Doing observations
Recording events in Nature
Working in pairs
Doing long term projects
Triarchic Theory of Intelligences
Robert Sternberg
Mark each sentence T if you like to do the activity and F if you do not like to do the activity.
1.
Analyzing characters when I’m reading or listening to a story ___
2.
Designing new things ___
3.
Taking things apart and fixing them ___
4.
Comparing and contrasting points of view
5.
Coming up with ideas
___
___
6.
Learning through hands-on activities
7.
Criticizing my own and other kids’ work
8.
Using my imagination
9.
Putting into practice things I learned
10.
Thinking clearly and analytically
11.
Thinking of alternative solutions
12.
Working with people in teams or groups
13.
Solving logical problems
14.
Noticing things others often ignore
15.
Resolving conflicts
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
Triarchic Theory of Intelligences
Robert Sternberg
Mark each sentence T if you like to do the activity and F if you do not like to do the activity.
16.
Evaluating my own and other’s points of view
17.
Thinking in pictures and images
18.
Advising friends on their problems
19.
Explaining difficult ideas or problems to others
20.
Supposing things were different
21.
Convincing someone to do something
22.
Making inferences and deriving conclusions
23.
Drawing
24.
Learning by interacting with others
25.
Sorting and classifying
26.
Inventing new words, games, approaches
___
___
___
27.
Applying my knowledge ___
28.
Using graphic organizers or images to organize your thoughts ___
29.
Composing
30.
Adapting to new situations
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
___
Triarchic Theory of Intelligences – Key
Robert Sternberg
Transfer your answers from the survey to the key. The column with the most True responses is your dominant intelligence.
Analytical
1. ___
4. ___
7. ___
10. ___
13. ___
16. ___
19. ___
22. ___
25. ___
28. ___
Total Number of True:
Analytical ____
Creative
2. ___
5. ___
8. ___
11. ___
14. ___
17. ___
20. ___
23. ___
26. ___
29. ___
Creative _____
Practical
3. ___
6. ___
9. ___
12. ___
15. ___
18. ___
21. ___
24. ___
27. ___
30. ___
Practical _____
Thinking About the Sternberg Intelligences
ANALYTICAL
Linear – Schoolhouse Smart - Sequential
Show the parts of _________ and how they work.
Explain why _______ works the way it does.
Diagram how __________ affects __________________.
Identify the key parts of _____________________.
Present a step-by-step approach to _________________.
PRACTICAL Streetsmart – Contextual – Focus on Use
Demonstrate how someone uses ________ in their life or work.
Show how we could apply _____ to solve this real life problem ____.
Based on your own experience, explain how _____ can be used.
Here’s a problem at school, ________. Using your knowledge of
______________, develop a plan to address the problem.
CREATIVE Innovator – Outside the Box – What If - Improver
Find a new way to show _____________.
Use unusual materials to explain ________________.
Use humor to show ____________________.
Explain (show) a new and better way to ____________.
Make connections between _____ and _____ to help us understand ____________.
Become a ____ and use your “new” perspectives to help us think about
____________.
Array Interaction Inventory
Directions:
• Rank order the responses in rows below on a scale from 1 to 4 with 1 being “least like me” to 4 being “most like me”.
• After you have ranked each row, add down each column.
• The column(s) with the highest score(s) shows your primary Personal Objective(s) in your personality.
In your normal day-to-day life, you tend to be:
Nurturing
Sensitive
Caring
Logical
Systematic
Organized
Spontaneous creative
Playful
Quiet
Insightful reflective
In your normal day-to-day life, you tend to value:
Harmony
Relationships are important
Work
Time schedules are important
In most settings, you are usually:
Authentic
Compassionate
Harmonious
Traditional
Responsible
Parental
In most situations, you could be described as:
Empathetic
Communicative
Devoted
Practical
Competitive
Loyal
Stimulation
Having fun is important
Active
Opportunistic
Spontaneous
Impetuous
Impactful
Daring
Reflection
Having some time alone is important
Inventive
Competent
Seeking
Conceptual
Knowledgeable
Composed
Array Interaction Inventory, cont’d
You approach most tasks in a(n) _________ manner:
Affectionate
Inspirational
Vivacious
Conventional
Orderly
Concerned
Courageous
Adventurous
Impulsive
Rational
Philosophical
Complex
When things start to “not go your way” and you are tired and worn down, what might your responses be?
Say “I’m sorry”
Make mistakes
Feel badly
Over-control
Become critical
Take charge
“It’s not my fault”
Manipulate
Act out
When you’ve “had a bad day” and you become frustrated, how might you respond?
Over-please
Cry
Feel depressed
Be perfectionistic
Verbally attack
Overwork
Become physical
Be irresponsible
Demand attention
Withdraw
Don’t talk
Become indecisive
Disengage
Delay
Daydream
Add score:
Harmony Production Connection Status Quo
Personal Objectives/Personality Components
Teacher and student personalities are a critical element in the classroom dynamic. The Array Model
(Knaupp, 1995) identifies four personality components; however, one or two components(s) tend to greatly influence the way a person sees the world and responds to it. A person whose primary Personal Objective of
Production is organized, logical and thinking-oriented. A person whose primary Personal Objective is
Connection is enthusiastic, spontaneous and action-oriented. A person whose primary Personal Objective is
Status Quo is insightful, reflective and observant. Figure 3.1 presents the Array model descriptors and offers specific Cooperative and Reluctant behaviors from each personal objective.
COOPERATIVE
(Positive Behavior)
RELUCTANT
(Negative Behavior)
HARMONY
Caring
Sensitive
Nurturing
Harmonizing
Feeling-oriented
Overadaptive
Overpleasing
Makes mistakes
Cries or giggles
Self-defeating
Friendships
Sensory experience
PSYCHOLOGICAL
NEEDS
WAYS TO MEET
NEEDS
Value their feelings
Comfortable work place
Pleasing learning environment
Work with a friend sharing times
Personal Objectives/Personality Component
PRODUCTION
Logical
Structured
Organized
Systematic
Thinking-oriented
Overcritical
Overworks
Perfectionist
Verbally attacks
Demanding
Task completion
Time schedule
CONNECTION
Spontaneous
Creative
Playful
Enthusiastic
Action-oriented
Disruptive
Blames
Irresponsible
Demands attention
Defiant
Contact with people
Fun activities
Value their ideas
Incentives
Rewards
Leadership positions
Schedules
To-do lists
Value their activity
Hands-on activities
Group interaction
Games
Change in routine
STATUS QUO
Quiet
Imaginative
Insightful
Reflective
Inaction-oriented
Disengaging
Withdrawn
Delays
Despondent
Daydreams
Alone time
Stability
Value their privacy
Alone time
Independent activities
Specific directions
Computer activities
Routine tasks