Students With Special Needs - Sir Wilfrid Laurier School Board
advertisement

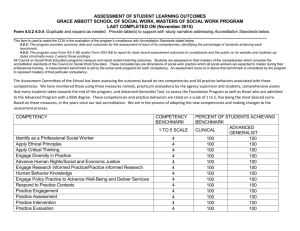
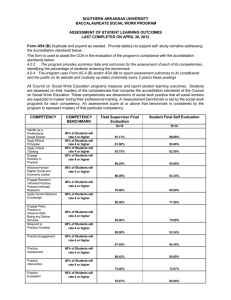
Secondary Cycle I Report Card School Team Workshop Questions and Answers from June 21, 2006 Development of the Secondary Cycle I Report Card Current version of the report card was developed by the Report Card Committee (04-05) with more recent input from the Secondary Principals. The current version respects the requirements of the Basic School Regulations. Question and Answer Format What are your questions with respect to the new Report Card? Questions were divided into five categories: Legends and Scales Subject Competencies Cross-Curricular Competencies Special Needs Students, and Other Questions LEGENDS & SCALES Legends and Scales Why are there two letters representing failure (e.g. D & E) and why are the ranges so large? Generally, we build rubrics with 4 levels, however the MELS requires 5 levels. The levels and ranges used in this report card will be familiar to English teachers as the same as those used to mark the Sec. V MELS English exam. Levels D & E allow a child who is struggling but still progressing to show improvement. Legends and Scales Why is 85% considered to be an “A” or highly satisfactory? MELS designates the ranges Generally speaking parents will understand an “A” to be 85% and above. This is the same as an “A” at McGill, for example. Legends and Scales How can 71%(only 11% points above passing) be considered “very satisfactory”? “Very This satisfactory” applies to a range of marks range indicates that the student’s progress so far is very satisfactory: not “highly satisfactory” but more than just “satisfactory”. Legends and Scales Is there a possibility to divide the ranges and use + and - (e.g. A+ or A)? No, we cannot change the ranges. However, the comments section can be used to further describe the students progress within the range. Legends and Scales Assigning marks does not seem to be consistent with the Portfolio method. A portfolio is more than a collection of material. Selecting material for inclusion in the portfolio is a learning process: students learn how to evaluate their own work and choose their best work to include. This work can be evaluated based upon how well it reflects the development of a specific competency. Portfolios may also be used in subjects like mathematics. Legends and Scales How do you reconcile a letter grade with a range of marks for 7 terms with one End of Cycle mark? Each of the 7 reporting periods allow for reporting the student’s progress in developing the competency. The final mark should clearly represent where the student stands with respect to the End of Cycle Outcomes. Evaluation is based upon a variety of assessment methods and can include tests, assignments, teacher’s judgement, running records, discussions etc. The MELS may propose a ponderation scale for the competencies which may make it easier to determine a final grade. Legends and Scales How do you decide on an End of Cycle mark if the student changes teachers between Year 1 and Year 2? Good communication between members of the Cycle Team is important. The Year 2 teacher will have access to the most recent evidence of the student’s current competency level. Another approach is for teachers to “loop” (teach the same students for both years of the cycle). Legends and Scales How can we compare a child’s performance to his/her peers when a parent wants to know? The Report Card is also accompanied by a Guide for Parents which helps explain the legends and scales. The Comments Section can help a teacher explain this. Student led conferences and portfolios may also help parents understand how their child is doing as compared to his/her cohort. Legends and Scales What is the meaning of NR vs. AR? Does NR mean the competency has not been addressed? NR means Not Reported (as in not reported at this time) AR means Alternate Report (the assessment of this competency will be found in an Alternate Report) NR does not mean that you will not address that competency in future. Legends and Scales Can you enter more than 1 ‘mark’? For example, an E and an AR? No, you cannot enter two different marks. SUBJECT SPECIFIC COMPETENCIES Subject Specific Competencies Is there a limit to the number of characters allotted for personalized teacher comments? Yes, there is a limit. A Word Template is available for use to help you format your comments and keep your comments within the space allotted. Subject Specific Competencies Are the competencies balanced on this report card? It is possible that MELS will announce a weighting or ponderation for different competencies for the end of cycle mark. Subject Specific Competencies Do we need to report on each competency on every communication? Not necessarily. For the most part you should be reporting on all the Subject Competencies, but there may be occasions where you have not addressed and/or evaluated a particular competency during one reporting period. In this case, an NR (Not Reported) may be used. Subject Specific Competencies Do we have to report on Geography & History during every reporting period? Teachers are encouraged to integrate the teaching, and consequently the evaluation, of the two subjects. However, this is the teachers choice. A focus group will be meeting in the fall to address some of these issues. Subject Specific Competencies How does the School Board plan to make teachers comfortable with the new competencies? Cycle I teachers were offered QEP training last year (0405). A plan for Professional Development for 2006-2007 was presented on June 21st. Many ESD Offers of Service relate to the QEP and competency based assessment. August 28th is a full day workshop focused on authentic assessment for school based teams involved in the June 21st workshop. Subject area consultants are available to help you. Subject Specific Competencies Will departments have to meet to create rubrics? Yes. However, there are banks of rubrics already available on the ESD website for the elementary level that could be adjusted, as opposed to starting from scratch. In addition, rubrics are available from other sources and ESD subject consultants are available to help you. Subject Specific Competencies One of the Physical Education and Health Competencies is “adopts a healthy, active lifestyle”. What constitutes a healthy lifestyle and how do we measure it? The Key Features of each Competency are broken down in detail in the QEP and the Evaluation Criteria are listed. In this example, healthy lifestyle indicators are found on page 443. In addition, for this specific competency, one SWLSB school has developed an information sheet which moves between the home and school and helps inform physical education teachers about the healthy, active lifestyle activities of students outside of the classroom. Subject Specific Competencies In the Visual Arts, what does the term ‘appreciates’ mean? Can we change this word to make the meaning clearer? Can you suggest ways to evaluate “appreciation”? The language of the competency cannot be changed. The term “appreciates” can have different meanings in general usage. However, as with the previous question, the QEP describes the Key Features of this competency and provides concrete examples of what appreciation means and how to evaluate it. Subject Specific Competencies Shouldn’t “examines” social phenomena by evaluated a certain way? Examines can have a few different meanings. Referring to the Key Features of the competency will provide a comprehensive explanation of what “examines social phenomena” in QEP terms. (For example: “finds out about the context of the period”; “reflects on social phenomena using chronological reference points” . . . . ) Subject Specific Competencies Why are there three competencies in French at the Secondary level compared to only two at the elementary level? Lire des textes variés en français (base) ou Lire des testes courants et littéraires en français (enrichi) was added so that students can develop their abilities to assimilate content read, heard or produced (base) OR to read and interpret more complex literary texts (enrichi). Some expectations of this competency are to analyse various types of texts and to recognize the different intentions those texts carry. This competency implies the development of critical thinking and of the appreciation for the cultural aspects of the language. CROSS CURRICULAR COMPETENCIES Cross-Curricular Competencies Are the CCCs evaluated every term or only at the end of cycle? You are only required to report on the CCCs at the End of the Cycle. However, you will have to observe and assess the CCCs throughout the cycle in order to report on their development at the end of the cycle. Consequently, your Cycle Team may decide to report on them more frequently than at the end of the cycle. Cross-Curricular Competencies Who fills in this form? Is it done as a team of teachers? Does the student get one over-all evaluation or 1 per teacher? Evaluation and reporting of the CCCs is decided by the Cycle Team and approved by the Principal. The QEP warns against limiting the evaluation of a CCC to one subject area (e.g. limiting “solves problems” to solving situation problems in Mathematics). The CCC are necessary skills for learning in all of the subject areas and will be needed for work in most employment areas. The CCCs very similar to the Conference Board of Canada’s list of Essential Work Skills. Cross-Curricular Competencies Where will the time necessary for the completion of CCCs be taken from? Who evaluates the CCCs in a school of 1300 students? The good news for teachers adjusting to the new report card is that reporting on the CCCs will be implemented slowly. For the year 2006-2007 teachers are not required to report on the CCCs. By July 1, 2007, Cycle I Secondary teachers will be required to report on a minimum of one of the nine CCCs. The addition of the Cross Curricular Competencies may seem to add to the teacher’s workload, but the QEP notes that there is really nothing new about teachers observing how a student learns, works, interacts with others and achieves his/her potential. Cross Curricular Competencies How can the CCCs be evaluated? The QEP refers to both teacher assessment and student assessment for evaluating the CCCs (QEP pg. 34). The Student Self Evaluation Sheet, available for use with the report card, may be helpful for this. The exact evaluation and reporting process for the CCCs is determined by the Cycle Team and approved by the Principal. For more information about the CCCs refer to the document: L’Évaluation des Compétences Transversales at: http://www.mels.gouv.qc.ca/dgfj/comitepea.htm Students with Special Needs If a student receives a 60% (C) in Term 1 and a 70% in Term 2 (also a C) there is no progression in the letter value of the grade. This is not motivating for the child. The teacher can indicate the progress made by the student through the comments on the report card and also explain this to the parent(s) at parent/teacher interviews. Students with Special Needs Is there a place in the report card to mention that a student is following a modified program? The anecdotal report would describe the modified program in detail. Students with Special Needs Are special needs students still evaluated on the competencies or just on the content of the program through an anecdotal report? Special needs students can still develop competencies and teachers can still evaluate competency development. Which competencies are evaluated and how they are evaluated depend upon the modifications to the program and teacher judgment. OTHER QUESTIONS Other Questions Is the reason why the report looks so busy because it is bilingual? And, if so, is this necessary if it is not a legal requirement? A bilingual report is not legally necessary, but will be very helpful to parents who read more fluently in French. The purpose of the report card is to report to parents. The elementary report card currently in use is also bilingual. Other Questions PAPER! What about the environmental implications of a multi-page report? It is true that the report card uses a lot of paper. However, we must report on all competencies. In the future, there may be the possibility of using the portal and PDF files. Other Questions Is the expectation that this report be applied to all of Cycle I? Yes. Are absences/lates to be recorded by the teacher? These can be recorded through GPI in a similar manner as they are now. Other Questions Can we use the assignment part of the GPI to generate results and transfer them to GPI, as is done today? We are not sure this approach will work with letter grades. The evaluation of a competency is based upon progress made in the development of the competency; it is not the same as the average of all the marks gathered throughout term. Other Questions Does the reporting coincide with the terms? Terms and communications are not necessarily the same thing. The report card as a communication tool does not determine the number of terms in a school year. Other Questions Are teacher's comments expected to be as extensive as at the elementary level? Teachers can choose how to approach the comments section for their subject area. Other Questions May we resort to using the “3” classes of comments: for example, context; “canned” comments; and anecdotal comments? You can access a bank of comments, create your own standardized message, or use a combination of standardized and personal messages. Other Questions Who places students for Cycle II? The final decision for placement is the responsibility of the school principal. This decision is made in consultation with the team of teachers and parents. The Cycle Team will have to discuss criteria for retention. More information about the three pathways for Secondary Cycle II will be available in August. Secondary Cycle I Report Card School Team Workshop Questions and Answers from June 21, 2006