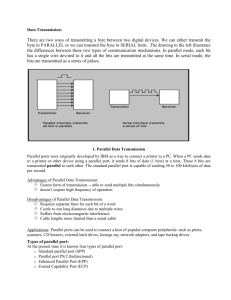
Setting up Putty for Terminal Use: First identify the COMM port on the
advertisement

Setting up Putty for Terminal Use: First identify the COMM port on the computer on the PC you are using. The serial port may be a physical port on the workstation, which typically uses COM 1 or COM2. It may also be an emulated serial port via a USB adapter. In which case the “COM” port will be identified under devices and printers as shown by the orange arrow in Figure 1. Figure 1: Identifying Com port Next, Connect the Serial Cable to the network device’s console port. Finally, make sure the settings on Putty are correct Launch Putty and under Session >> Connection Type: Choose Serial as show in Figure 2. Figure 2: Choosing Serial Connection Type Next, go to the last Category on the left column and Choose Serial. Verify the Serial Port you are using as well as the Connection Settings as shown in Figure 3. Since you’ve identified the Com port number you can update it on the Putty configuration under the Serial settings Fig.2: Verify Serial Settings Typical Settings are listed below in Table 1. Typical Serial Settings: Brand Speed (Baud) Data Bits Stop Bits Parity Flow Control Cisco 2950 HP 2524 HP 2615 9600 9600 19200 8 8 8 1 1 1 None None None None None None Table 1: Typical Console settings for networking devices Setting up Putty for CLI Using Telnet: Setting up Putty for CLI use is very straight forward. Simply select Telnet for connection type and type in the IP address of the device. Figure 3 shows a typical connection setup. Figure 3: Typical Telnet setup Navigating CLI Configuration When the window opens up it will prompt you with the switch name. It looks like the figure below. Figure 4: Initial CLI window There are some basic functions that most CLI share regardless of the brand. One is displaying a list of available commands when you enter either question mark (?) or type in help. Try this with to When you hit question mark on the HP switches you will see that it displays a list of available commands. This is a great way to navigate around without needing to be an expert with a specific brand. Figure 5 shows an output window of what you should expect to see after performing the command: Figure 5: Help command output Another useful command to start off with is “show config”. With this command the switch will display the entire configuration. Figure 6 shows the command executed. Figure 6: Show config command In this case the vlan1 or (default vlan) is the only one configured on the switch. If other vlans were configured in this switch they would be displayed here. The arrow indicates where the command was typed in. To make any changes to the current configuration you must enter configuration mode. To do so, simply enter “config”. After doing so you will notice that the word config appears in brackets after the name of the switch. Figure 7 shows a switch in config mode. You will notice that the options are different here if you enter (?) Figure 7: Configuration Mode To get a look that is closer to a Graphical UI use the “menu” command. This will change the look from a CLI to a context menu display. This style is better suited for beginners that don’t have most of the commands memorized yet. Figure 8 shows the menu mode. Figure 8: Menu Mode