Oil+Spill+PP9 edited ---- lang arts
advertisement

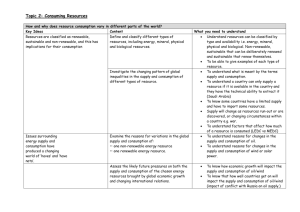
The Benefits and Consequences of Dependency on Non-Renewable Energy Yvonne Alley, Colleen Simpson, Jessica Truett Unit Summary The British Petroleum Oil Spill in the Gulf of Mexico is of high interest to all, especially those located near the Gulf of Mexico. This topic has direct relevance to the students and will allow them the opportunity to become involved within their community. Students will be able to analyze the disaster from several different perspectives to include the economic, environmental, political and social impact this disaster will have in Florida and other regions of the United States. This unit will also allow students to further develop their analytic, evaluative, and problem solving skills in accordance with Florida Sunshine State Standards and Blooms Taxonomy of thinking. Although the spill is happening in the Gulf of Mexico, its effect is not limited to the Gulf's geographic area. This spill will impact many other areas and people around the United States and may also affect the development of new legislation for off shore drilling. As a result, Students will gain a broader understanding of the economic relevance their state has from a national perspective, as well as how the consumption of oil directly affects their lives and communities. By analyzing the need for oil and the consequences of oil dependency on the environment, students will also develop their ability to work collaboratively to create alternative solutions for reducing the consumption of nonrenewable resources that can satisfy demands whilst respecting the limits imposed by nature. There is an abundance of past and current resources that can be used for this thematic unit across several disciplines of study. The theme is sufficiently broad enough to contain many subtopics and allow for student input for the selection of topics relative to each discipline. Students are already motivated to get involved and this thematic unit will allow them to become active participants in this current event and learn that their efforts can make a difference. The unit will also allow students opportunity for introspective global thought as they learn through their research that each individual has a civic responsibility for stewardship of the environment. Major Concepts Social Studies • • • • • • Supply and Demand of Natural Resources Social Responsibility Energy Awareness Geographic data Consequences of changing physical environment Social and economic effects Math • • • • • Data Analysis Estimation Proportions Computations Generalizations Language Arts • • • • • • • • Graphic Organizer Informational/Expository Writing Global Warming Electronic Technology Vocabulary Building Compare/Contrast Non-renwable:Human Cost Inference/Generalizations Info Gathering/ Analyze Science • • • • Oil cleanup methods Disruption of Ecosystems Non-Renewable & Renewable Resources Health Risk towards humans Graphic Organizer Generalizations Estimation Social Responsibility Computations Proportions Data Analysis On the Water On the Beach Supply and Demand of Natural Resources Negative Effects Mathematics Geographic Data Oil Clean Up Methods Food Webs Energy Awareness Social Studies Consequences of Changing Physical Environment Benefits & Consequences of Dependency on Non-Renewable Energy Disruption of Ecosystems Science Terrestrial Habitats Health Risk Toward Humans Social and Economic Effects Graphic Organizers Language Arts/Reading Air Water Marine Habitats Non-Renewable & Renewable Resources Informational/Expository Writing Global Warming Vocabulary Building Inference/Generalizations What the Future Holds Compare/Contrast Electronic Technology Non renewable energy: the Human Cost Information Gathering/Analyze Changing our Lifestyles Focus Questions 1. What are renewable and non-renewable energy resources? 2. What are the environmental/economic consequences of depending on non-renewable resources such as oil? 3. What are the benefits of renewable energy and how could they help reduce oil dependency? 4. How has Gulf oil disaster influenced government responsibility and individual social responsibility relative to energy use? 5. How can disaster such as the Gulf Oil Spill be prevented in the future? Math Learning Goals • To understand the economic and environmental • • • • • • impact of past and present oil spills. To learn how to solve problems related to the use of non-renewable energy resources. To learn how to create various graphs. To demonstrate how to collect and organize information. To learn how to create a survey, analyze data, and make generalizations. To understand and explore the safety of oil rigs. To explore and create a renewable energy source. Social Studies Learning Goals • Extend and Refine use of various map forms and other geographic • • • • representations to acquire, process, and report geographic information. Know ways selected regions are interconnected and interdependent. Extend and refine understanding of environmental consequences of people changing the physical environment in selected regions. Understands the basic principles of economic supply and demand and how they apply to various economic systems in selected regions. Extend and refine knowledge of ways current issues affect political, social, and economic systems in selected regions. Science Learning Goals Language Arts Learning Goals • The student uses multiple strategies to develop grade appropriate vocabulary • The student uses a variety of strategies to comprehend grade level text • The student identifies, analyzes, and applies knowledge of a variety of nonfiction, • • • • • • • • • informational and expository texts to demonstrate an understanding of information presented. The student will use prewriting strategies The student will write a draft appropriate to topic, audience, and purpose. The student will write a final product for the intended audience The student develops and demonstrates technical writing that provides information relative to real-world tasks. The student effectively applies listening and speaking strategies The student comprehends the wide array of informational text that is part of our day to day experiences The student uses a systematic process for the collection, processing, and presentation of information The student develops and demonstrates an understanding of media literacy as a life skill that is integral to informed decision making The student develops the essential technology skills for using and understanding conventional and current tools, materials and processes. Student Learning Outcomes Language Arts • • • • • • • • • Students working in pairs will be able to find 8 of 10 meanings for assigned using the internet. Student working in pairs will be able to locate 8 out of 10 real world visual examples of the context vocabulary words are used. Students working in pairs and using assigned materials will create a chart that shows each word’s meaning and Students will each read assigned newspaper article on gulf oil spill and highlight minimum of 80% lesson vocabulary words. Students will each identify 80% of organizational text features used in assigned article. Each student will write a1 paragraph explaining why these organizational features are used and how they help the reader. Students working in pairs will use the internet to locate 3 primary and 4 secondary resources on the Exxon Valdez and Gulf Coast oil disaster Students will each read their primary and secondary sources and identify a minimum of 4 main ideas about the human cost of each disaster from each source and record on assigned graphic organizer. Students working in pairs will create a front page newspaper article using power point, primary and secondary source main points that describes the human cost of oil dependency. Students will incorporate a minimum of 4 organizational text features in their article. Students working in pairs and using assigned internet sources will gather research information on 4 causes and 4 effects of global warming. Students will each select articles that illustrate 4 different types of text format and write 1 paragraph that explains the difference in the characteristics of each format Student Learning Outcomes (continued) Language Arts • • • • • • • • • • Using internet resources and working in pairs students will find 10 possible solutions to help reduce global warming, 1 solution will included reducing carbon footprint and 1 solution will include information on “going green.” Students working in pairs will create a technical booklet that explains 8 steps to take to convert to “going green.” Students working in groups of four and using previous internet research and previous activities will develop an informational documentary report on how non renewable energy use is contributing to global warming. Students in their groups will be able to select correct prewriting strategy to develop documentary main ideas using their primary and secondary sources. Students in their groups will use a minimum of 2 graphic organizers to organize their main ideas and supporting details relevant to their topic. Students in their groups will be able to draft scripts for documentary presentation by organizing information into a logical sequence that divides documentary into 4 distinct segments. Students in their groups will be able to prepare 4 scripts using assigned media technology in a format appropriate to communicate their message to the audience Students in their groups will be able to present a thesis statement, introduction to the problem, examples of effects on human and environment, and concluding predictions of what the future may look like if global warming continues.LA.7.4.2.3 Students in their groups will be able to effectively deliver their speech to inform audience, using appropriate language eye contact, gestures la7.5.2.3 Students in their groups will develop a concluding statement based on their research by making 2 predictions on how continuing dependency on non renewable energy and reluctance to alter lifestyle will affect global warming outcomes for the future. Student Learning Outcomes Science • The students will be able to differentiate between renewable energy resources and non• • • • • • • • • • renewable energy resources. With the application of ecological principles, the students will be able to create a specific ecological food web with all the basic components identified. Using their constructed food webs, students will be able to predict how an oil spill will effect their ecosystems. Using knowledge of the environmental impacts that oil has on ecosystems, the students will be able to display how our local ecosystem will be effected by the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. With the aid of CNN's website, the students will be able to create a timeline on the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. The students will be able to explain the different techniques used to clean oil spills. Using knowledge of oil spill clean up methods, the students will be able create a controlled oil spill and test cleanup techniques on a controlled oil spill. The students will be able to invent new techniques to clean up and prevent future oil spills. The students will be able to compare and contrast the benefits and limitations of alternative energy. Using knowledge of alternative energy, the students will be able to build a model that uses alternative energy. Applying all learning experiences from the unit, the students will be able to develop & write a R.A.F.T. to persuade the public to convert to alternative energy resources. Student Learning Outcomes Math • • • • • • • • • The students will identify renewable and non renewable energy, and use this data to create a survey. Students will interpret, explain, and create displays of data in a graph or table with 80% accuracy. Using the information from the graph or table, students will present findings and make generalizations about the general populations. Using collected data, students will calculate with 80% accuracy, the amount of oil spilled in the Valdez oil spill compared to the Gulf oil spill. Students will calculate, compare, and report an estimation of the cost to clean up each oil spill. The students will research and record facts about solar power. Given material and plans, students will calculate and build a solar power oven and cook something in their oven. Students will collect, and analyze information about oil rig safety systems. Using oil rig data, students will design a prototype of an emergency cutoff system. Student Learning Outcomes Social Studies • • • • • • • • • Students working in pairs will be able to identify all the states and capitals of the Gulf Coast region using an atlas. Students working in pairs will be able to label and color each of the states on a blank political map correctly, using colored pencils. Students working in pairs will identify a minimum of 5 resources associated with the gulf coast region. Students working in pairs will be able to label correctly the physical characteristics and natural resources of the Gulf Coast region on a blank physical map from an overhead list using colored pencils. Students working in pairs will be able to create and complete a two page visual information booklet using construction paper and magazines that differentiate renewable and non renewable resources of the Gulf Coast Region. Students will each be able to identify 8 of 10 Physical and Human characteristics of a place, by grouping them into respective categories on a worksheet, from overhead visual examples of characteristics. Students working in pairs will be able to show the interconnected relationship between physical and human characteristics of a place, by creating a collage to represent their information. Students will each be able to write 3 inferences using the information represented in their collage on how a way of life may be affected as a result of changing the physical environment. Students will each be able to use their assigned internet resources to locate a minimum of 4 articles and 1 graph on economic development along the gulf coast over the past five years. Student Learning Outcomes Social Studies (continued) • • • • • • • • • Students working in pairs will be able to create 1 power point comparison chart using their research information that illustrates the economic effects of the Gulf Oil Spill on the economy of the Gulf Coast Region. Students using their comparison chart information will each be able to write an expository essay describing in their own words 3 possible social or economic consequences of how dependency on non renewable energy resources can affect a way of life of any region. Students will each be able to locate research information on the social and economic benefits of 3 renewable energy resources from their assigned internet websites. In pairs students will be able to analyze their research and select a minimum of 6 main points and supporting details to prepare a 5 minute persuasive debate on the economic and social benefits of using renewable energy resources. In pairs students will present their debates to their peers and will be able to defend their argument by answering all questions made by their class peers in a 1 minute question response session. Students using materials provided by teacher will each be able to visually show the relationship between supply and demand by creating 1 cartoon that illustrates one or more examples of how an economy is either supported or diminished by economic supply and demand principles. Students in groups of four will design an energy awareness school wide campaign using computer graphics and software to create posters that show a minimum of 5 ways everyone can conserve energy. Students in groups of four will include at least 2 examples of how renewable energy resources can be used to decrease the demand for non renewable energy consumption. Students will each write a persuasive letter to the Governor using their research information to justify their argument or case either for or against off shore drilling. Language Arts • • • • • • • • Standards LA.7.1.6.1 The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly; LA.7.1.6.5 The student will relate new vocabulary to familiar words; LA.7.1.6.3 The student will use context clues to determine meanings of unfamiliar words LA.7.2.2.1 The student will locate, use, and analyze specific information from organizational text features (table contents, headings, captions, italics, glossaries, indices, key words). LA.7.2.2.2 The Student will use information from the text to state the main idea or provide relevant details LA.7.2.2.3 The student will organize information to show understanding (representing main idea within text through charting, mapping, paraphrasing, summarizing or comparing/contrasting) LA.7.4.2.1 The student will write in a variety of informational/expository forms (e.g., summaries, procedures, instructions, experiments, rubrics, how-to manuals, assembly instructions); LA.7.6.4.1. The student will select and use appropriate available technologies to enhance communication. LA. 7.3.5.1 The Student will prepare writing using technology in a format appropriate to audience and purpose LA. 7.3.5.2 The student will use elements of spacing and design for graphics (tables, drawings, charts, graphics) when applicable to enhance the appearance of the document LA. 7.6.2.1 The student will select a topic, develop a prioritized search plan, and evaluative criteria to select appropriate resources for research. LA. 7.6.2.3 Student will write an informational report that includes a focused topic, appropriate facts and relevant details, a logical sequence, a concluding statement, and a list of sources used. LA.7.3.1.3 The students will prewrite by using organizational strategies and tools (e.g., technology, outline, chart, table, graph, Venn Diagram, web, story map, plot pyramid) to develop a personal organizational style. LA.7.1.7.3 The student will determine the main idea or essential message in grade-level or higher Standards Science • SC.7.E.6.6 Identify the impact that humans have had on Earth, such as deforestation, urbanization, desertification, erosion, air and water qualify, changing the flow of water. • SC.7.E.6.Pa.d Distinguish between clean and dirty water • SC.7.L.12.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web. • SC.7.L.17.3 Describe and investigate various limiting factors in the local ecosystem and their impact on native populations, including food, shelter, water, space, disease, parasitism, predation, and nesting sites. Standards Math • MA.7.S.6.1 Evaluate the reasonableness of a sample to determine the appropriateness of generalization made about the populations. • M.A.7.A.3.3- Formulate and use different strategies to solve one- step and two-step linear equations, including equations with rational coefficients. • MA.7.S.6.2: Construct and analyze histograms, stem-and-leaf plots, and circle graphs. • MA.7.A.1.4: Graph proportional relationships and identify the unit rate as the slope of the related linear function. • MA.7.A.1.1: Distinguish between situations that are proportional or not proportional, and use proportions to solve problems Standards Social Studies • • • • • • Standard 1 Geography: Understand how to use maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technology to report Information. SS.7.G.1.1 Locate the states that constitute the Gulf Coast Region Standard 2 Geography: Understands physical and cultural characteristics of places. SS.7.G.2.3 Explain how major physical characteristics, natural resources and climate have influenced settlement and economy of Gulf Coast region Standard 3 Geography: Understands the relationship between the Earth’s Ecosystems and the populations that dwell within them. SS.7.G.3.1 Use maps to identify location and abundance of natural resources in Gulf Coast region Standard 5 Geography: Understand how human actions can impact the environment. SS.7.G.5.1 Use a choropleth or other map to geographically represent current information about issues of conservation or ecology in the local community Standard 1 Economics: understand the fundamental concepts relevant to the development of a market economy. SS.7.E.1.3. Review the concepts of supply and demand as they relate to the development of a mixed market economy in the United States Standard 2 Civics and Government: evaluate the roles rights and responsibilities of United States citizens and determine methods of active participation in society, government, and the political system. SS.7.C.2.12 Develop a plan to resolve a state or local problem by researching public policy alternatives, identifying appropriate government agencies to address the issue to. Grade Level Expectations Language Arts • Student will select and use a format for writing which addresses the audience purpose and occasion( including but not limited to narrative, persuasive, and expository). • Uses electronic technology appropriate to writing tasks to create, revise, retrieve, and verify information (for example, Internet, databases and software) • Extend the vocabulary-building expectations of the sixth grade using seventh grade or higher vocabulary • Uses context and word structure clues to interpret words and ideas in text. • Makes inferences and generalizations about what is read Grade Level Expectations Language Arts Con’t • Knows and experiments with possible prewriting strategies for different writing tasks • Uses a prewriting strategy suitable for the task (brainstorming using a graphic organizer) • Gathers information from a variety of sources, including primary sources (for example, letters, magazines, newspapers) • Extends previously learned knowledge and skills of the sixth grade with increasingly complex text assignments and tasks (for example, forming questions for readings, using print and electronic sources to locate information, organizing information from a variety of sources for realworld tasks). Grade Level Expectations Science • • • • • • • • • • • Discuss and test the best techniques for cleaning up oil on a variety of substrates Discuss some of the negative consequences from the oil dispersing techniques. (i.e - CO2 pollution, sinking oil, more toxic oil) Discuss the possible health risks that could result from contaminated air and water. Compare difference in oil polluted water versus clean water Participate in a lab that will illustrate how oil effects bird’s feathers. Create a balanced food web and learn how the disruption or extinction of abiotic or biotic members can impact the other members if the food web. Describe the effects of oil pollution in wildlife Discuss how a limiting facto such as oil can cause dead zones in the Gulf. Simulate what members will be effected and how they will be effected in marine and estuary ecosystems due to the oil spill Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources. Discuss alternative energy technologies and create basic models. Grade Level Expectations Math • Generate and collect data for analysis • Constructs, interprets, and explains displays of data, such as tables • • • • and graphs, and explains how different displays of data lead to different interpretations Predicts outcomes based on a generalization of a pattern or relationship Estimate solutions to real-world problems involving estimations of measurement. Develop an understanding of operations on all rational numbers and solving linear equations. Computes the mathematical odd for and against a specific outcome in given real-world experiments. Grade Level Expectations Social Studies • Extend and refine use of various map forms and other geographic representations to acquire, process, and report geographic information. • Know ways selected regions are interconnected and interdependent. • Extend and refine understanding of environmental consequences of people changing the physical environment in selected regions. • Apply three basic questions to various economic systems in selected regions. • Extend and refine knowledge of ways current issues affect political, social, and economic systems in selected regions. • Know the relative value of primary and secondary sources. Unit Schedule—Week 1 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday • Compile • Create a survey • Complete • Graphing • Graphing renewable/nonrenewable energy data presented in the power point based on compiled data survey in classroom and around school campus Lesson-Circle Graph Lesson-Stem-nLeaf Graph using an estimated number of birds effected by oil •PowerPoint - •LAB – Density of •PowerPoint - •Food Web •PowerPoint – Renewable & Non-renewable energy. •Video: Bill Nye: Energy (Segments 1 & 2) Oil Ch. 16.1 & 16/3 (ecological principles & energy flow) • Video: Oceans Alive – Food Web Projects • Limiting Factors & Relationships Environmental Impacts •LAB : Oily Bird! Social Studies Intro to unit Lesson on Regions and resources Physical & Political map 2 page visual information booklet on renewable – non renewable energy resources quiz Direct Instruction Lesson Physical& Human Characteristics Category worksheet Collage Internet research Economic development Gulf Coast Power point comparison chart economic effects Gulf Oil Spill Language Arts intro to ITU Energy resources Internet Vocabulary Vocabulary Application chart Discussion on disasters Newspaper article Organizational features Primary and secondary resources Internet research Exxon Valdez & Gulf Oil Spill Prepare power point Newspaper article on the human cost of oil disasters Math Science Unit Schedule—Week 2 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday • Graphing • Create graph • Research • Calculate • Incorporate your LessonHistograms using the number of sea life animals effected by the oil. using data from survey-share results • Quiz on graphs Valdez oil spill and Gulf oil spill amount spilled in each oil spill and compare/contrast amount and cost of clean up findings into the oil cleanup methods PowerPoint that you will create in science • Food Web • PowerPoint - • Video: Bill Nye: • LAB - •PowerPoint – Oil Presentations (simulated with oil spill) • Present ideas of how the local ecosystem is effected by oil. Alternative Energy Energy (segments 3-11) Alternative Energy Simulations cleanup methods. •LAB – Simulated Oil Spill & Testing Methods Social Studies Presentation power point chart Assessment: Expository essay economic effects non renewable energy resources Internet research benefits renewable energy resources Start preparing debate Finish persuasive economic debate preparation Practice Debate presentations Economic consequences Lesson, supply & demand Create cartoon showing supply & demand relationship (finish at home) Language Arts Presentation of newspaper article How non renewable energy contributes to global warming Internet research Causes & Effects Continue Internet research Cause and effects Internet research solutions to global warming Create “how to” booklet Reduce energy consumption Math Science Unit Schedule—Week 3 Monday Math Science Social Studies Language Arts Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday • Video about • Calculate • Collect, • Design and • Presentations renewable energy resources materials and build a solar oven • Quiz organize, and analyze oil rig safety information sketch a prototype of an emergency cutoff system and Test • Explore CNN’s • Create •Field Trip – •Present RAFT’s • Jeopardy Oil Spill Web Page Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Timeline Beach/Bay •Homework – Persuasive RAFT paper Introduce Energy Awareness campaign Internet research Energy awareness campaign internet research Start preparing posters Energy awareness campaign Finish posters Write scripts introduction Develop point of Documentary video Informational Documentary on Global warming develop outline main points view Review Game • Unit Test Energy awareness poster presentations Peer evaluations Documentary video Review what has been learned Explain government responsibilities Assessment: Persuasive letter to Governor on off shore drilling Presentations Daily Schedule • First Bell: 9:04 A.M. • HR/First Period: 9:10 – 10:04 • Second Period: 10:07 – 10:56 • Third Period: 10:59 – 11:48 • 7th Grade Lunch: 11:48 – 12:17 • Fourth Period: 12:20 – 1:09 • Fifth Period: 1:12 – 2:01 • Sixth Period: 2:04 – 2:53 • Seventh Period: 2:56 – 3:45 Media List • LCD Projector & Screen • Laptop Computer • Internet Access • DVD Player • Computer Speakers • LAB equipment • Computer Lab Access • Textbooks • Microsoft Programs • Document Camera Lesson Plan Overview Language Arts • The focus of the theme for students is to develop their literary skills through real world application by taking on the role of investigative Journalists reporting on how energy use contributes to the problem of global warming. In week one students will be working on the vocabulary associated with energy use to establish basic knowledge and contexts in which the words apply. They will be applying reading and analysis skills to a variety of different text formats in their research to develop inferring paraphrasing and summarizing skills as well as understand how text structure affects overall meaning. They will focus their investigation on the human tragedy resulting from dependency on non renewable energy by examining the Exxon Valdez and Gulf Oil disasters and presenting their opinions in a front page news article. • Week two they will focus on causes and effects, analysis of text, development of point of view, and possible solutions. Students will be using the topic of global warming to investigate how non renewable energy contributes to the problem and investigate the ways in which individuals can help alleviate global warming through simple modifications in energy habits. Students will demonstrate and develop their writing skills by creating an informational “how to” booklet that addresses ways in which individuals can become good consumers of energy. • Week three is a culminating activity in which students will create an informative documentary from their research in week one and two that demonstrate their comprehension, analysis, perspective, inferring and communication skills relative to energy use and why it is important for society to alter lifestyles now to secure their quality of life in the future. Lesson Plan Overview • Science Lesson Plan Overview Math • • • • • Survey Says Students will learn about renewable and non-renewable energy sources. Using the collected information, students will create a survey that will be conducted in the classroom and throughout the school. Graphing Students will learn how to create and read three different types of graphs. Students will learn how to create a circle graph, stem-n-leaf graph and histogram. Using the data compiled from the survey and two science lessons, student will use the graphs to display and present their findings to the rest of the class and make generalizations based on their findings. Valdez vs. Gulf Students will collect and organize information pertaining to the Valdez and Gulf oil spill. Student will then use the collected information to calculate, compare, and report an estimation of the cost to clean up each oil spill. Soak up the Sun Students will research and learn about solar power. Students will further their understanding by planning and calculating the amount of materials needed to build a solar oven. Students will build a solar oven that can be used to warm cookies. Safety First Students will learn how to compile information about oil rig safety systems. Using the compiled information, students will work in groups to design and sketch an emergency cutoff system for an Lesson Plans • Social Studies Culminating Activities Assessments • Rubrics • Test • Peer Evaluations • Internet Logs • • • • • • • • Quizzes Worksheets Oral Presentations Self Evaluations Pretests Video Worksheets LABS R.A.F.T. Paper Social Studies Assessments • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Quiz on states and capitals and resources Map rubric Product rubric visual resource booklet Quiz human & physical characteristics Collage rubric relationship between physical & human characteristics of a place Internet Research log Oral presentation rubric Power point comparison chart rubric Writing rubric for expository essay on social economic consequences dependency non renewable energy Persuasive debate writing rubric Oral debate rubric Product rubric for supply demand cartoon Oral presentation rubric for cartoon Product rubric for energy awareness poster Peer evaluations of posters Oral presentation rubric for posters Persuasive Writing rubric letter to Governor (summative) References Science • • • • • • • • • • • http://edition.cnn.com/SPECIALS/2010/gulf.coast.oil.spill/ Science, (Print, Audio, Video), (Verbal, Visual, Vicarious, Simulation) http://www.the-scientist.com/blog/display/57448/ Science, Print, Visual, Verbal Biggs, Alton, et al. (2006). Glencoe / McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Science, Print, Verbal, Visual, Direct (Ch. 16, Sec. 1-3 & Ch.19, Sec. 1) **http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2010/05/26/gulf-oil-spill-cleanup-wo_n_591346.html** Science, Print, Visual, Verbal http://www.nytimes.com/2010/05/02/us/02oil.html Science, Print ,Visual, Verbal http://library.thinkquest.org/10867/cleanup/methods/index.shtml Science, Print, Visual, Verbal Dr. Richard Snyder, director of UWF's Center for Environmental Diagnostics and Bioremediation Science, Audio, Verbal, Simulated **http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm** Science, Audio, Visual, Vicarious, Simulated, Direct **http://news.discovery.com/animals/gulf-dead-zone-oil-spill.html** Science, Print, Visual, Verbal http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=spill-clean-up-chemicals Science, Print, Visual http://www.altenergy.org/ Science, Print, Visual, Verbal References Language Arts Math References • Forcefield. (2010). Wind Power. Retrieved June 20, 2010, from http://www.otherpower.com/otherpower_wind.shtml • Home Science Tools. (2010). Retrieved June 20, 2010, from • Martinello, M. L. & Gillian, C. E. (2000). Interdisciplinary Inquiry in Teaching and Learning. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall • Non-Renewable Resources. (2006). Retrieved June 20, 2010, from http://www.eco- • Perez, J. (2007). Dale Resources. Retrieved June 17, 2010, from http://www.daleenergy.com/flash/fromdale/index.html • Powell, C.S. (n.d). We Did the Math: BP Oil Spill is Worse Than the Exxon Valdez. Retrieved June 17, 2010, from http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/80beats/2010/05/27/we-did-the-mathbp-oil-spill-is-now-worse-than-the-exxon-valdez • Roberts, P.L. & Kellough, R. D. (2008). A Guide For Developing Interdisplinary Thematic Units. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall • State of Oregon. (2009). Retrieved June 20, 2010, from • The New York Times. (2010). How Much Oil is on the Gulf Coast. Retrieved June 17, 2010, from http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2010/05/27/us/20100527-oil-landfall.html • United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2009). Environmental Kids Club. Retrieved June, 17, 2010, from http://www.epa.gov/kids/game.htm http://www.hometrainingtools.com/build-a-solar-oven-project/a/1237/ pros.com/non-renew.htm http://www.oregon.gov/ENERGY/RENEW/index.shtml References Social Studies •