B. Characteristics of a contract
advertisement

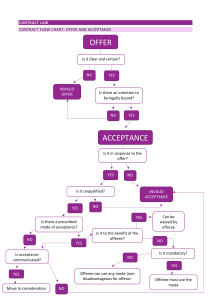
Chapter 5—Contracts I. Contract-It is any agreement enforceable by law. A. Elements of a contract- 1. Offer--A proposal by one party (offeror) to another (offeree) intended to create a legally binding agreement. 2. Acceptance—The second party’s unqualified willingness to go along with the first party’s proposal. 3. Genuine agreement—A valid offer and acceptance 4. Capacity—The legal ability to enter into a contract. 5. Consideration--The exchange of things of value 6. Legality—People can’t enter into contracts to commit exists. illegal acts. B. Characteristics of a contract-1. Valid, void, voidable, unenforceable. a. Valid—this means legally good or binding b. Void—no legal effect c. Voidable—A party who is able to cancel a contract for some legal reason d. Unenforceable—This is one the court will not uphold. ex. because the Statute of Limitations has run out. 1 2. 3. Express or Implied a. Express—It is stated in words b. Implied—It is shown by the actions of the parties. Bilateral or Unilateral a. Bilateral—it contains two promises b. Unilateral—there is a promise only by one person to do something 4. Oral or written a. Oral—Two or more people are speaking to each other *most contracts are of this type b. Written—Certain contracts must be in writing to be enforceable. For ex. sale of land, or those that will take more than one year to perform, sale of goods >$500 C. Offer and Acceptance— 1. Requirements of an offer: a. anger or as a joke. Serious intent—It can’t be made in the heat of 1. Invitations to negotiate—most ads in newspapers, magazines, or in catalogs are not offers since the seller couldn’t possible have enough products if everyone who sees the ad wants to purchase. There are exceptions—if the seller says, “first come, first served” or something to that effect 2 b. Definiteness and certainty—Use exact terms, not just words like “a share” or “a reasonable” amount. c. Communicated to the offeree—Offers can be made by telephone, fax, e-mail, telegram, letter, etc. However, someone can’t accept your offer if they didn’t know about it. For example, a reward. You can’t get a reward if you didn’t know about it. 2. Requirements of an acceptance— a. Unconditional-the acceptance must not change the terms of the original offer. This is called the “mirror image rule.” 1. There are some exceptions-non merchants b. Methods of acceptance—if face to face, there is no problem. There are special rules that govern acceptances separated by distances. 1. effective when sent 2. if address is faulty, the acceptance is not complete until delivered to the right place. Silence is not acceptance unless the offeree has previously agreed to this condition. 3. Termination of offer a. revocation—taking back of the offer b. rejection—refusal of an offer by the offeree c. counteroffer—changing the original offer d. on the acceptance expiration of time—if offeror has set a time limit 3 e. death or insanity 4 5