Termite Experiment
advertisement

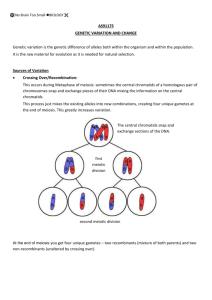
Objectives 1. Model and explain how genetic information is transferred from one generation of cells to the next via the processes of mitosis and meiosis 2. Compare and contrast cell division by mitosis with cell division by meiosis 3. Represent chromosomes containing specific alleles through cell division by mitosis and meiosis Meiosis: sex Last time: Two forms of cell reproduction MITOSIS MEIOSIS • Occurs in somatic (body) cells • Daughter cells? • Ploidy? • Genetically_________ parent cell • Purpose (function): • Occurs in reproductive cells • Daughter cells? • Ploidy? • Genetically_________ parent cell • Purpose (function): Modeling the steps of meiosis Draw a cell containing 2 pairs of unreplicated homologous chromosomes for the individual to the right. She is heterozygous for tongue rolling and earlobe shape. Complete in your groups. Turn in one paper per group at the end of class. DNA replicates G2: Cell DNA is replicated e T e T t E E t Cell Division by Meiosis Two Divisions: 1. Meiosis 1: Homologs separate (crossing over and independent assortment) 2. Meiosis 2: Sister chromatids separate Prophase 1 Homologs align at equatorial plane T T E E t t e e Draw your cell with homologous pairs aligned at the equatorial plane Metaphase 1 Homologs align at equatorial plane How is this different from metaphase of mitosis? T T t t E e e E Crossing-over Metaphase – Anaphase 1: T T E Homologous pairs align, then separate E t t e e First Division (Meiosis 1) Homologs sort into different daughter cells. Draw the products of this division. End of Meiosis 1 2 cells – each with 1 member of homologous pair. T T t t E E e e Are there other possibilities? What is the consequence of separating the homologous pairs? Mendel’s Laws 1. Law of Independent Assortment – Each pair of homologous chromosomes positions independently of all other pairs in Metaphase 1 Metaphase 2: Centromeres of sister chromatids align at equatorial plane. Metaphase 2: T E T t t E e e Second Division (Meiosis 2) Each cell resulting from Meiosis 1 divides. Sister chromatids separate at the centromere and sort into different daughter cells. Draw the products of this division. Metaphase – Anaphase 2: Sister chromatids separate into daughter cells T T t t E E e e Metaphase – Anaphase 2: Sister chromatids separate into daughter cells T T t t E E e e End of Meiosis 2: Daughter cells are “gametes” (eggs and sperm). T T t t E E e e Genotypes of gametes? T T t t E E e e What if homologs lined up differently at Meiosis 1? T T E E t t e e Predict the genotypes of gametes. T T t t e e E E Genotypes of gametes? T T e e t t E E Why are the genotypes different? T T e e t t E E Mendel’s Laws 1. Law of Independent Assortment - Each pair of homologous chromosomes positions independently of all other pairs in Metaphase 1; 2. Law of Segregation - Two alleles of a given gene segregate during gamete formation, in Metaphase 2. What is the consequence of Independent Assortment? T T E E t t e e What would happen if . . .? T E E e e T Why doesn’t this work?? t t Can we predict the number of different types of gametes that could be formed? i.e., How many different allele combinations (genotypes) could you get in the gametes? T E T t t E e e