Animal Biotechnology
advertisement

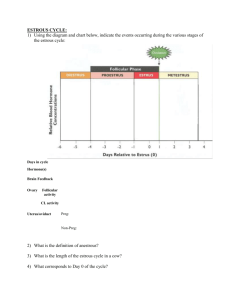
Animal Biotechnology Animal Biotech • Animals provide a number of products we use in every day life. • Milk • Leather • Wool Animal Biotech • Eggs •Meat Roles of Animals in Biotech • Animals are involved in lab experiments. • Without the use of animals humans might be in danger. Animal Models • 4 models apply for the use of animals. • Living animals • Living animal tissues or systems • Non-Living systems Animal Models • Computer and Mathematical approaches Living Animals • These animals are living and usually have no threat to their well being. • Such animals may be known as laboratory or scientific animals. Living Animals • Agricultural Research often uses experimental groups of animals. Living animal tissues or systems • Animal tissues can be cultured in a lab. • This saves the use of animals as well as the expense of feeding, housing, and cleaning up after the animals. Non-Living Systems • Involves using non living mechanical models that reflect animal activity. • These often relate to skeletal movement and locomotion Non-Living Systems • Artificial replacement parts, such as hip joints can be studied using non living systems. Computer and mathematical approaches • Computer simulations with virtual reality and other uses help in biotechnology. • Computer modeling may be done with a propose biotechnology practice before it is tested with animals. Laboratory animals • A laboratory animal is an animal used for laboratory or research purpose. • Good tending is needed to assume that the research is properly carried out. Laboratory animals • Without research involving animals, scientists would not have a base. Animal Species • Most animals are subjects of study at one time or another. • Most common species used in research laboratories are mice, rats, and hamsters. Animal Species • A primate is an animal with thumb and forefinger opposition. • A non human primate is similar to humans but is not a human. Animal Reproduction • Reproduction is a process by which offspring are produced. • Sexual Reproduction is the union of a sperm and egg to ultimately produce a new individual. Animal Reproduction • The union of the sperm and egg is called fertilization. • Semen- the fluid produced by the male reproductive organs, contains sperm. Animal Reproduction • Copulation- is the sexual uniting of animals so the male can ejaculate semen near the eggs in the reproductive tract of the female. Reproductive Development • Puberty-is the time at which an animal is capable of reproduction. • Fertilization- union of the sperm and egg results in the formation of a zygote Reproductive Development • Gestation- is the period of pregnancy in animals. • Parturition- is the birthing process. • Lactation- is the secretion of milk by the mammary glands. Reproductive Development • Dry time is a time when mammals are not lactating. The Estrous Cycle • Estrous is a time when a female is fertile and receptive to a male. • The estrous cycle is the time between the estrous. The Estrous Cycle • The three periods in the estrous cycle that follow estrous are metestrus, diestrus, and proestrus. Artificial Insemination • Artificial insemination is the transfer if collected semen to a recipient female. It is used with sheep, beef cattle, turkeys, and swine. • Generally female estrous cycles are regulated with hormone Artificial Insemination • Sperm are collected from males by artificially promoting ejaculation. Gender Preselection • Gender preselection is choosing the gender of a potential offspring. • Gender preselection may be done by sorting sperm. Gender Preselection • The DNA content of sperm varies slightly based on the gender of the offspring that would result from conception. Embryo Transfer • Embryo transfer is the harvesting of fertilized ova from a donor and implanting them into a recipient. • The harvested embyros are transferred to a recipient. Embryo Transfer • Non surgical transfer involves flushing the embryos from the uterine horn. Bovine Somatotropin • Bovine somatotropin is a natural occurring growth hormone produced in the pituitary gland in the endocrine system. • By treating dairy cattle with the hormone, milk production is Bovine Somatotropin • Some small dairy producers do not use BST and incorporate that fact in their advertising. Transgenic Animals and Products • Pigs- have been used to manufacture human hemoglobin. • A xenograft is the practice of grafting an organ or a tissue from one species into another. Transgenic Animals and Products • Mice- transgenetic mice have been used in several ways. • One of the best known is to produce human antibodies. • Cattle- are used to control disease such as mastitis in dairy cows. Methods of creating transgenetic animals • Step One- collect embryos • With proper stimulation far more embryos can be obtained than would be the natural result of the reproductive process. Methods of creating transgenetic animals • Step Two- Inject embyros. • A pro nucleus is the haploid nucleus of the sperm or ovum that have united in fertilization to form a zygote. Methods of creating transgenetic animals • Step Three- Zygote Culture • The zygotes are placed in the oviduct of a recipient female.