Ch. 1
advertisement

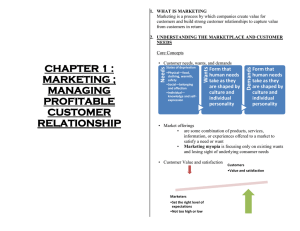
1 Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships ROAD MAP: Previewing the Concepts • Define marketing and outline the steps in the marketing • • • • process. Explain the importance of understanding customers and the marketplace, and identify the five core marketplace concepts. Identify the key elements of a customer-driven marketing strategy and discuss the marketing management orientations that guide marketing strategy. Discuss customer relationship management and strategies for building lasting customer relationships. Describe the major trends and forces that are changing the marketing landscape in this new age of relationships. 1-2 What Is Marketing? • Simple Definition: Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. Goals: 1. Attract new customers by promising superior value. 2. Keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction. 1-3 Marketing Old vs. New Old view of marketing: Making a sale -- “Telling and Selling” New view of marketing: Satisfying customer needs 1-4 Marketing Defined A social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. 1-5 A Simple Model of the Marketing Process Create value for customers and build customer relationships Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants Design a customerdriven marketing strategy Construct a marketing program that delivers superior value Capture value from customers in return Build profitable relationships and create customer delight Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity 1-6 What are Consumers’ Needs, Wants, and Demands? This Is a Need Needs - state of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs. 1-8 Types of Needs • Physical: – Food, clothing, shelter, safety • Social: – Belonging, affection • Individual: – Learning, knowledge, self-expression 1-9 This Is a Want Wants - form that a human need takes, as shaped by culture and individual personality. 1-10 This Is Demand Wants Buying Power “Demand” 1-11 Need / Want Fulfillment • Needs and Wants Fulfilled through a Marketing Offer : – Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want. 1-12 What Satisfies Consumers’ Needs and Wants? Products Anything that can be Offered to a Market to Satisfy a Need or Want Persons Places Information Organizations Ideas Services Activity or Benefit Offered for Sale That is Essentially Intangible and Does Not Result in the Ownership of Anything 1-13 Product as an Idea Products do not have to be physical objects. Here the “product” is an idea—protecting animals. 1-14 Marketing Myopia • Sellers pay more • attention to the specific products they offer than to the benefits and experiences produced by the products. They focus on the “wants” and lose sight of the “needs.” 1-15 Value and Satisfaction Expectation 8 Performance 10 Expectation Performance 10 8 If performance is lower than expectations, satisfaction is low. If performance is higher than expectations, satisfaction is high. 1-16 Exchange vs. Transaction • Exchange: – Act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return. • Transaction: – A trade of values between two parties. – One party gives X to another party and gets Y in return. Can include cash, credit, check, or barter. 1-17 What is a Market? • The set of actual and potential buyers of a product. • These people share a need or want that can be satisfied through exchange relationships. 1-18 Elements of a Modern Marketing System 1-19 Marketing Management • The art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. Questions to ask: 1. What customers will we serve? What is our target market? 2. How can we best serve these customers? What is our value proposition? 1-20 Segmentation and Target Marketing #1 #2 Market Segmentation: Divide the market into segments of customers Target Marketing: Select the segment to cultivate 1-21 Marketing Management Demand Management Demarketing Finding and increasing demand, also changing or reducing demand, such as in demarketing. Temporarily or permanently reducing the number of customers or shifting their demand. 1-22 Value Proposition • The set of benefits or values a company promises to deliver to consumers to satisfy their needs. It cleans and freshens like sunshine! www.gainlaundry.com 1-23 Marketing Management Philosophies Societal Marketing Concept Marketing Concept Selling Concept Product Concept Production Concept 1-24 Marketing and Sales Concepts Contrasted 1-25 Customer-Driven Marketing How many of us would have thought to ask for a “wearable” PC? Marketers must often understand customer needs even better than customers themselves do. 1-26 The Marketing Mix Product Price Customer Needs Promotion Distribution 1-27 Customer Relationship Management • The process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction. 1-28 Customer Perceived Value • Customer’s evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and all the costs of a marketing offer relative to those of competing offers. 1-29 Customer Perceived Value Is FedEx’s service worth the higher price? FedEx thinks so. It promises reliability, speed, and peace of mind. FedEx ads say “Need to get it there or else? Don’t worry. There’s a FedEx for that.” 1-30 Customer Satisfaction • Dependent on the product’s perceived performance relative to a buyer’s expectations. 1-31 Customer Relationship Levels Basic Relationship Continuum Full Partnership 1-32 Loyalty and Retention Social Benefits Financial Benefits Structural Ties 1-33 Partner Relationship Marketing Partners Inside the Firm 1. All employees customer focused 2. Teams coordinate efforts toward customers Partners Outside the Firm 1. Supply chain management 2. Strategic alliances 1-34 Customer Loyalty & Retention • Customer Lifetime Value – The entire stream of purchases that the customer would make over a lifetime of patronage. • Share of Customer – The share a company gets of the customers purchasing in their product categories. 1-35 Customer Lifetime Value To keep customers coming back, Stew Leonard’s has created the “Disneyland of dairy stores.” Rule #1—the customer is always right. Rule #2—if the customer is ever wrong, reread Rule #1. 1-36 Customer Equity • Customer equity is the total combined customer lifetime values of all the company’s customers. 1-37 Customer Relationship Groups Butterflies High Good fit between company’s offerings and customer’s needs; high profit potential True Friends Good fit between company’s offerings and customer’s needs; highest profit potential Profitability Strangers Low Little fit between company’s offerings and customer’s needs; lowest profit potential Barnacles Limited fit between company’s offerings and customer’s needs; low profit potential Short-term customers Long-term customers Projected loyalty 1-38 The Internet • The Internet has been hailed as the technology behind a New Economy. • Marketing applications include: – “Click-and-mortar” companies – “Click-only” companies – Business-to-business e-commerce • Business-to-business transactions online are expected to reach $4.3 trillion in 2005. • By 2005, 500,000 companies will use the Internet to do business. 1-39 The New Digital Age The recent technology boom has had a major impact on the ways marketers connect with and bring value to their customers. 1-40 New Marketing Landscape Rapid Globalization Not-for-Profit Marketing Ethics & Social Responsibility New World of Marketing Relationships 1-41 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts 1. Define marketing and outline the steps in the 2. 3. 4. 5. marketing process. Explain the importance of understanding customers and the marketplace, and identify the five core marketplace concepts. Identify the key elements of a customer-driven marketing strategy and discuss marketing management orientations that guide marketing strategy. Discuss customer relationship management and strategies for building lasting customer relationships. Describe the major trends and forces that are changing the marketing landscape in this new age of relationships. 1-42 Q: Your marketing campaigns appeal to your customers' desire to be perceived as owning the best in bicycle technology. Your marketing campaigns successfully appeal to consumers': 1. needs. 2. wants. 3. satisfactions. 4. demands. AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-43 Q: Your company is also successful because you offer free maintenance and repair for the first two years after the purchase of a bicycle. Therefore, along with the physical product, you offer an attractive package of: 1. values. 2. ideas. 3. events. 4. services. AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-44 Q: As a campaign manager for a candidate to your county's legislature, you are defining the candidate’s positioning among voters and are working on a pre-election rally during which your candidate and several prominent supporters will deliver speeches. You are planning a: 1. 2. 3. 4. product. service. satisfaction. promotional campaign AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-45 Q: Your firm has perfected a process that reduces the overall cost of producing custom-made bikes. As a result, you adopt the ________ concept of marketing, whereby you offer your products to consumers at prices well below those of your competitors. 1. 2. 3. 4. production product marketing societal marketing AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-46 Q: You favor a marketing approach that emphasizes the quality and new features of your bicycles, yet your assistant prefers an approach that emphasizes innovative promotion strategies. Which of the two following marketing concepts are exhibited here? 1. 2. 3. 4. Marketing and selling Production and societal marketing Product and marketing Product and selling AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-47 Q: To reduce the large capacity of bikes in your warehouse, you adopt the _________ concept and attempt to push your products into the market through heavy advertising. 1. production 2. product 3. selling 4. marketing AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-48 Q: In anticipation of high demand, you build a factory in Mexico, where you can save on labor and production costs. However, you still provide benefits to the Mexican workers comparable to those many American workers receive, illustrating that you have successfully practiced the: 1. 2. 3. 4. marketing concept. product concept. societal marketing concept. selling concept. AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-49 Q: Are you more inclined to buy from a company that is socially responsible? 1. Yes 2. No AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-50 Q: Would you be willing to pay more for a product because it was from a sociallyresponsible company? 1. Yes 2. No AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-51 Q: The most important new technology for connecting is: 1. 2. 3. 4. the the the the Internet. database. laptop computer. fiber optic telephone. AK, 7e – Chapter 1 1-52