Running head: GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Gerontology Nursing Process Paper
William Schmidt
Kent State University
1
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
2
Client Profile
M.B. is a 63 year old Caucasian female initially admitted on August 22, 2012 for a right
thoractomy with exploration and pleural biopsy for right upper lobe cancer. There was extensive
pleural metastasis so the patient was closed up due to the mass being more extensive than
expected so only the biopsy was done .After this she was admitted to the intensive care unit
postoperatively. On the same day the patient had a change in mental status and became hypoxic
which lead to being intubated. M.B. became hypotensive and developed a right pneumothorax
which resulted in the placement of a chest tube. On September 2, 2012 the patient was extubated
along with the chest tube being pulled on September 13, 2012. M.B. underwent a bronchoscopy
to assess for hemoptysis as well as squamous cell lung cancer. After returning from this
procedure she developed high fevers and rigors which she then began pneumonia treatment. On
September 17, 2012 M.B. tested positive for MRSA and Acinetobacter and placed on antibiotic
therapy and contact precautions. On October 2, 2012 M.B. was admitted to the rehab floor to
begin therapy; however on October 4, 2012 she was transferred off the floor to receive packed
red blood cells in which she began to develop a fever, diaphoresis, and shortness of breath. Rapid
response was called and she was once again transferred to the ICU. Chest x-rays showed bilateral
infiltrates worse than previous diagnosis. She was then put on Lasix, 100% non rebreather mask
and later discovered her source of infection was her PICC line which was replaced with a central
line. At this point upon meeting her she is medically stable and anxious to finish therapy and go
home.
Primary Diagnosis
Squamous cell carcinoma, post right thoracotomy, exploration and parietal biopsy.
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
3
Squamous cell carcinoma starts in the large bronchi of the lungs and is the malignant
transformation of lung tissue (B lack & Hawk, 2009). Cigarette smoking as well as people
exposed to second hand smoke are ten times more likely to develop lung cancer than non
smokers. Lung cancer develops when the normal cells of the lung mutate and reproduce
excessively to form masses (Black & Hawk, 2009). Tumor cell growth will begin to inhibit lungs
full expansion capability thus limiting function of the lung or lung. Signs and symptoms may
include but are not limited to hoarseness, change in respiratory pattern, persistent cough, sputum
streaked with blood, frank hemoptysis, and unexplained dyspnea (Black & Hawk,
2009).Thoracotomy is a procedure done by cutting into the pleural membrane of the lungs in this
case to explore and find out the extent of the cancer metastasis.
Secondary Diagnosis(s)
Postoperative hypoxic respiratory failure
Respiratory failure takes place when the body’s mechanism for providing tissues with
oxygen and removing carbon dioxide shuts down. In this particular case the patient has
experienced hypoxemic respiratory failure which can be caused by diffusion problems like
pulmonary edema, adult acute respiratory distress syndrome, or localized problem such as
pneumonia, bleeding into chest or lung tumors. (Black & Hawk, 2009)Signs and symptoms may
includes restlessness, adventitious lung sounds, pulse oximetry readings below 85%, cyanosis,
and elevated blood pressure (Black & Hawk, 2009).
Anemia
According to Black and Hawk (2009) “Anemia is a clinical condition that results from an
insufficient supply of healthy red blood cells (RBCs), the volume of packed RBCs, and/or the
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
4
quantity of hemoglobin” (p.2004).This particular patient may be suffering from defective DNA
synthesis because she is receiving vitamin b12 as a regular medication in order to improve her
anemia. If the number of red blood cells is too low adequate amounts of oxygen cannot be
carried to tissues resulting in hypoxia(Black & Hawk, 2009).Some signs and symptoms
associated with anemia are dyspnea(shortness of breath), palpitations, diaphoresis(profuse
perspiration), and chronic fatigue.
Generalized weakness
Fatigue and generalized weakness is very common in the disease process and in this case
brought on by both the cancer and anemia. Many things can be done to remove contributing for
example b12 will be given to improve the anemia, and therapy programs will be catered to this
particular patient’s ability. It is important as the nurse to recognize signs and symptoms of
weakness and fatigue in order to create a safe and health promoting environment. (Black &
Hawk, 2009)
Surgical History
Patient has history of cardiac catheterization and stenting. It is noted in the chart the
patient has had some type of back surgery but does not list any specifics and patient is unsure of
exact procedure. A notation of bilateral shoulder surgeries has also been listed with no specifics.
Patient’s most recent surgery was a thoracotomy and biopsy of pleura.
Gordon’s Functional Assessment
Gordons
FUNCTIONAL HEALTH PATTERNS
ASSESSMENT TOOL
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Nursing Practicum_____ Student___William Schmidt
Date_10-10-12___
Patient's Initials_MB___ Male____ Female__X___ Age______
Medical Diagnosis___Sauamous cell lung cancer,copd,anemia,Weakness
Reason for seeking health care__Chronic hypoxia secondary to chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease
1. HEALTH PERCEPTION-HEALTH MANAGEMENT
Past medical history:
Illnesses:__Recent polymicrobial sepsis secondary to Enterococcus faecalis Serratia
marcescens and methicillin
resistant staph aureus, Post incision incision and debridement of right lateral
chest wall, moderate copd, hypertension
Surgery:___History of cardiac catheterization, back surgery, bilateral shoulder
surgeries
History of chronic disease_Patient has known about her COPD diagnosis for "around
five year" but has been recently diagnosed
with lung cancer
Immunization History: ____ Tetanus______ Pnemonia_____ Influenza__X___ MMR______
__X__ Polio ______ Hepatitis B
Use of Tobacco:__X__ None -Quit(date_____<1ppd____1-2ppd___ >2pks/day ___Pks/yr
history__ Patient states that her husband has smoked for many years
_____smokeless tobacco)____pipe_____cigar
Alcohol: Amount/type______NOt for many years___ Date of last
drink___Does not recall__
Frequency of use __Never_
Other drugs: Amount/Type :__Denies Use___Freq. Of Use
:________________________
5
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
6
Medication (prescription/Nonprescription)
Page 1
Gordons
Name PLease see medication list
Dose
Frequency of Use
Last Dose
Allergies_Unasyn_NKA_____________
Perception of health:______good__X__ fair________poor
Health Management Habits: Exercise on a regular basis? ___Yes__X_No
Follow prescribed regimen? ___Yes __No X Cannot be assessed at this time
Page 2
Gordons
Safety:__X walker__Special Equipment ___precautions:____Siderails___Restraints
___question for following: use of seat belt, car seats for kids, breasts/testicular
self examination,
safe working conditions._________N/A_____________________________________________
Home Health in last semester safe environment in home i.e.: smoke detectors, access
to home
(stairs), throw rugs/carpets, cleanliness, health issues observed :____Patient
states she lives in a one story home and has
her husband to help care for her
2. NUTRITIONAL-METABOLIC
____Not Assessed
_Unknown Ht._Unknown_Wt._None reported__Weight fluctuations last 6 months
Type of Diet/Restrictions:____ Regular____Lo Salt__X__Diabetic__ Other
Supplements_______
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Appetite_X_Normal___Increased___Decreased___Decreased taste___Food
intolerance:_____
_____Nausea_____Vomiting Describe:_____________________
______Swallowing difficulties_____gag reflex_______chewing difficulties
Feeding _X_self____Assist
Condition of mouth:_X_pink______inflammed__X_moist______dry
_______lesions/ulcerations describe__________________ teeth /gums___Own teeth no
dentures______
______Dentures____upper (partial/full)_______lower(partial/full)
______Intravenous fluids type/amt_____Patient is heplocked________.
Insertion Site:_____PICC Line to right chest triple lumen________
______NG________ Gastrostomy
Skin Condition:_pink___color: pallor,ashen, pink, jaundice, cyanotic, ruddy
_warm___ temperature: warm,cool, hot
_dry___dry, moist, clammy, diaphoretic
Page 3
Gordons
_none___edema:pitting/non-pitting
_good___turgor: good, poor, tenting
_none___pruriitis
_yes_intact
____bruises/lesions describe: (size, location)__Surgical incision site to upper
back 4 inches long well
approximated and healing well. no signs of redness edema or drainage__
Body temperature:______ tympanic _98.2 F_oral _____rectal
3. ELIMINATION
____Not Assessed
7
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Bowel Habits Describe:____Formed brown large__
(consistency, color, amount)
__1_____#BM's/day_10/10/12_____ Date of last BM
_______Constipation_____Diarrhea_______Incontinence
Bladder Habits Describe:___light yellow clear 800cc last shift_____(color, clarity,
amount)
_____Frequency ____Dysuria____Nocturia_____Urgency_______Hematuria
____Retention _____ Burning______Hesitancy________Pressure
Incontinency:_X_No ___Yes______daytime ________nighftime
________occasional______difficulty delaying voiding
Assistive Devices:_____intermittent catheterization______indwelling cath
______external catheter____________ incontinent briefs
Ostomy: type: ________ ____Appliance ______self-care
Inspect Abdomen:_X_ symmetry_____ flat_____ rounded__X_ obese
Auscultate Abdomen:__X__ normal bowel sounds______Hypoactive______ Hyperactive
Palpate abdomen:__X_ soft____ firm_____ tender : describe__Abdomen soft and non
distended bowel sounds present
in all quadrants_____
_____ distention: describe:_____________________________________
Page 4
Gordons
4. ACTIVITY-EXERCISE
______Not Assessed
A. Musculoskeletal:______tremors ____atrophy ______swelling
Self-Care Ability: 0=Independent 1=Assistive device 2=Assistance from others
3=Assistance from person and equipment 4=Dependent/Unable
01234
8
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Eating 0
Bathing 2
Dressing 2
Toileting 1
Page 5
Gordons
Bed Mobility 0
Transferring 2
Ambulating 2
Stairs 2
Shopping 3
Page 6
Gordons
Cooking 2
Home Maint.3
Assistive Devices:___ none____ crutches ______Bedside commode_X__ Walker
____cane_____ splint/brace __X_wheelchair________ other
Gait:__X_normal______abnormaI_______________________________(describe)
Range of Motion__X__normal______limited_______________________(describe)
Posture:__X_normal_______Kyphosis_________Lordosis
Deformities_X_no ______yes:__________________________________(describe)
Amputation________________________Prosthesis_________________________
Physical Development Assessment:_X___normal__________abnormal
describe:______________________________________
B. CV
_____Not Assessed
Pulse:_X__regular ____irregular______strong _____weak
9
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
_____radial rate_76__apical rate
Blood Pressure:______ standing_______lying__141/89__sitting
Extremities: Temperature: ___cold ___cool _X_warm_____hot
Page 7
Gordons
Capillary Refill:_X__brisk ____sluggish
Color:___Normal for race_________(describe)
Homan's Sign:_X__Negative_________Positive
Nails: __X__Normal________ Thickened _______other: ________(describe)
Hair distribution:_X__normal________abnormal________________(describe)
Pulses:__+2___Femoral_______Popliteal_________Post-tibial___+2___Dorsalis
_______Palpable________Doppled
Claudication:______yes__X__no
C. Respiratory
______Not Assessed
Inspect chest:__X__symmetrical ___________asymmetrical
Respirations _22_rate _Shallow_depth (shallow, deep, abdominal, diaphragmatic)
_X_regular ___irregular_______________periods of apnea
____dyspnea at rest____orthopnea__X_dyspnea on exertion
_______Cough:dry/productive describe______Moist productive cough________
_______Sputum: describe_______Thick yellow_____________
Auscultate chest:_X_crackles_X__rhonchi ______friction rub_______wheezing
describe:__Rhonchi heard bilateral with occasional crackles present__
Other:_______chest tube_______ tracheostomy Describe:________________________
______________________________________________________________________
Page 8
10
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Gordons
Oxygen:__5 liters nasal cannula__________
5. SLEEP-REST
________Not Assessed
Usual Sleep Habits: _6__hours per night __2__consecutive hours slept per noc
____a.m. nap ________p.m. nap
feel rested after sleep_X yes__no awakening during night __yes _X no
insomnia __yes __no
Methods used to promote sleep: _None_medication:_________________________________
__________warm fluids
_____rituals: (bathing, reading, tv, music)
6. COGNITIVE-PERCEPTUAL
_______Not Assessed
Level of Consciousness:__X_alert___ lethargic___drowsy____stuporous______comatose
Mood (subjective):_X_pleasant___irritable___calm___happy____euphoric
_____ anxious_____ fearful_____ other:_Patient is very pleasant and very tolerant
of student nurse___
Affect (objective):__surprise__anger__sadness__joy___disgust_Xresident is reluctant
to be so far from hospital
upon discharge _fear___ flat__ blunted__
full___
Orientation Level:_X_person_X_place__X_time _X_significant other
Memory: recent:__Xyes _no Remote: _X_yes __no
Pupils:____size _Brisk_Reaction (brisk/sluggish)
Reflexes:__X__normal _____absent
Grasps:__Strong__Right: strong/weak __Strong_left: strong/weak
Push/Pulls:__Weak__right: strong/weak _Weak__left: strong/weak
11
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Other:_____numbness _____tingling
Pain:_X_Denies
____Location: describe: ________________________
____Radiation: describe:________________________
____Intensity: (0-10 scale)
____Timing (how often, events that percipitate)
Page 9
Gordons
When did pain begin?________________________________________
What alleviates pain?________________________________________
What increases pain?________________________________________
Thought Content:___Normal thought content___________________________
Senses: Visual Acuity:_____wnl__X_glasses______ contacts_____blind (R/L)
Prosthesis: (artificial eye) R/L
Hearing:__X_wnl____impaired (R/L)_____deaf(R/L) ______hearing aid
_______tinnitus______drainage from ears
Touch: ___X__wnl______ abnormal: describe________ tingling _____numbness
Smell___X_normal ________ abnormal
Ability to: communicate: language spoken___X_ read__X_clear_X_, articulate_X__
Ability to make decisions_X easy ___moderately easy ___moderately difficult
___difficult
(subjective)
7. SELF-PERCEPTION-SELF-CONCEPT
_______Not Assessed
Appearance:_X_calm____anxious____irritable_____withdrawn_____restless
__X_appropriate dress _______hygiene
Level of anxiety: (subjective) Rate on 0-10 scale____2____
12
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
(objective) face reddened: __X__no _____yes
voice volume changes _X_no ___yes(loud/soft) voice quality
_X_no ___ yes(quavering/hesitation) muscle tenseness: relaxed
fists/teeth clenched
Body language describe____Very calm and cooperative very willing to contribute to
own care____________________
Eye contact: Direct
Answers questions: ___X__readily__________hesitantly
Usual view of self__X_ positive ______neutral _______somewhat negative (subjective)
Level of control in this situation___7____(0-10) (subjective)
Page 10
Gordons
Usual level of assertiveness_____7____(0-10) (subjective)
Body Image: Is current illness going to result in a change in body structure or
function? _____no
___X__unsure _____yes describe: _Patient states she is not sure what procedure will
be next____(subjective)
8. ROLE-RELATIONSHIP
______Not Assessed
Does patient live alone ____yes __X_no: with
whom_____Husband__________________
Married____Yes____ Children_____Unsure__________
Next of Kin______Husband__________________
Occupation:_____None_______________________
Employment Status:___employed ____short-term disability_____long-term disability
__X__retired______unemployed
Support System: _X__spouse ___X__neighbors/friends________none
13
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
_____family in same residence -family in separate residence
Family: Interaction: (describe)_____Patient states she has many family and friends
that live locally that
are very supportive_______ __________
Question patient regarding:
Concerns about illness:_Patient is concerned because she does not know what the next
step will be for her. She
is very nervous about doing cancer treatment in the winter and living an hour from
the hospital_________
_________________________________________________________________________
Will admission cause signifcant changes in usual role?____Resident has been in
hospital for an extended stay and is
anxious to return to role at home after discharge in a few days________
__________________________________________________________________________
Social activities:___X__active ________limited _______none
Activities participated
in:____Church and socializing with friends and family_______________________________
Comfort in social situations (subjective)___X_comfortable___________uncomfortable
**** if patient is dependent on others for care note any evidence of physical or
Page 11
Gordons
psychosocial abuse
9. SEXUALITY-REPRODUCTIVE
______Not Assessed
Female:______date of LMP ___Para ____Gravida_______Pregnant
______Menopause ____no__X__yes __Does not remember__year
Contraception______no_______yes_______________Type
14
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Hx. of vaginal bleeding __X_no ____yes (describe)_____________________
Last Pap Smear___________
History of sexually transmitted disease __X_no
_____yes:_________________
Male: History of Prostate problems _____yes ______no History of penile discharge,
bleeding, lesions; ______no ______yes
describe:_____________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Last prostate exam:_______________________
History of sexually transmitted disease ________no _______yes:
Both: Problems with sexual
functioning?______None______________________
Sexual concerns at this
time?__________None__________________________
1 0. COPING-STRESS TOLERANCE
_________Not Assessed
Overt signs of stress (crying, wringing of hands, clenched fists)
Describe:_________None____________________________________
_
Question patient regarding:
Primary way you deal with
stress?________Patient seems very relaxed and a go with the flow type person. It
seems as thought the patient tries
to hide fears and stress with denial and humor.
___________________________________________________________________________
_
Concerns regarding hospitalizaton/illness: (financial, self-care)______None_________
15
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Page 12
Gordons
Major loss within last year ____yes __X_no
Describe:________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
11. VALUE-BELIEF
_______Not Assessed
Religion:_____Protestant ____Catholic ___ Jewish __Muslim ___Buddhist ___None
_X_other: Cristian non
specific
Question Tatient regarding:
Religious Restrictions:_____None______________________________________________
Religious Practices:____Attends church
regularly_______________________________________
Concerns related to ability to practice usual spiritual or religious customs?
___X____no ___________ yes Describe:_______________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Revised 05/00
Four assessment tools
CONFUSION ASSESSMENT METHOD (CAM)
YES NO
1. ACUTE ONSET/FLUCTUATING COURSE
Is there a history of an acute change in mental status with evidence __NO_ ___
of fluctuation in the degree of symptoms?
2. INATTENTION
Does the patient have difficulty focusing attention (e.g., being easily ___ NO___
distractible, or failing to focus on the discussion or sustain an effort)?
3. DISORGANIZED SPEECH
Is the patient's speech disorganized or incoherent, such as rambling or ___ NO__
irrelevant conversation, unclear or illogical flow of ideas, or unpredictable
switching of subjects?
16
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
17
4. ALTERED LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS
Is the patient's level of alertness either hyperalert (e.g., vigilant, overly ___NO___
sensitive to environmental stimuli, easily startles); or hypoalert (e.g.,
lethargic, stuporous, drowsy, difficult to arouse)?
Reproduced from: Confusion Assessm e n t M e t h o d ( C A M ) and CAM-ICU in: Inouye SK.
Delirium in hospitalized older patients. Clin Geriatr Med 1998;
Geriatric Depression Scale: Short Form
Choose the best answer for how you have felt over the past week:
1. Are you basically satisfied with your life? YES
2. Have you dropped many of your activities and interests? NO
3. Do you feel that your life is empty? NO
4. Do you often get bored? NO
5. Are you in good spirits most of the time? YES
6. Are you afraid that something bad is going to happen to you? NO
7. Do you feel happy most of the time? YES
8. Do you often feel helpless? NO
9. Do you prefer to stay at home, rather than going out and doing new things? YES
10. Do you feel you have more problems with memory than most? NO
11. Do you think it is wonderful to be alive now? YES
12. Do you feel pretty worthless the way you are now? NO
13. Do you feel full of energy? NO
14. Do you feel that your situation is hopeless? NO
15. Do you think that most people are better off than you are? NO
Answers in bold indicate depression. Score 1 point for each bolded answer.
A score > 5 points is suggestive of depression.
A score > 10 points is almost always indicative of depression.
A score > 5 points should warrant a follow-up comprehensive assessment.
Source: http://www.stanford.edu/~yesavage/GDS.html
BRADEN SCALE FOR PREDICTING PRESSURE SORE RISK
Sensory
Perception
Ability to
respond
meaningfully to
pressure-related
discomfort
4
1 Point
Completely
limited:
Unresponsive
(does not moan,
flinch, or grasp)
to painful
stimuli because
of diminished
level of
consciousness
or sedation.
2 Points
Very limited:
Responds
only to
painful
stimuli.
Cannot
communicate
discomfort
except by
moaning or
restlessness.
3 Points
Slightly limited:
Responds to
verbal commands
but cannot always
communicate
discomfort or
need to be turned.
OR
Has some sensory
impairment,
which limits
4 Points
No
impairment:
Responds to
verbal
commands.
Has no sensory
deficit that
would limit
ability to feel or
voice pain or
discomfort.
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
OR
Limited ability
to feel pain over
most of body
surface.
Moisture
Degree to which
skin is exposed
to moisture
4
Activity
Degree of
physical activity
3
Mobility
Ability to change
and control body
position
4
Constantly
moist: Skin is
kept moist
almost
constantly by
perspiration,
urine, etc.
Damp-ness is
detected every
time patient is
moved or
turned.
Bedfast:
Confined to
bed.
Completely
immobile:
Does not make
even slight
changes in body
or extremity
position without
assistance.
18
OR
Has a sensory
impairment
that limits the
ability to feel
pain or
discomfort
over half of
body.
Very moist:
Skin is often,
but not
always, moist.
Linen must be
changed at
least once a
shift.
ability to feel pain
or discomfort in 1
or 2 extremities.
Occasionally
moist:
Skin is
occasionally
moist, requiring
an extra linen
change
approximately
once a day.
Rarely moist:
Skin is usually
dry; linen
requires
changing only
at routine
intervals.
Chairfast:
Ability to
walk severely
limited or
nonexistent.
Cannot bear
own weight
and / or must
be assisted
into chair or
wheelchair.
Walks
occasionally:
Walks
occasionally
during day, but
for very short
distances, with or
without
assistance.
Spends majority
of each shift in
bed or chair.
Slightly limited:
Makes frequent
though slight
changes in body
or extremity
position
independently.
Walks
frequently:
Walks outside
the room at
least twice a
day and inside
room at least
once every 2
hours during
waking hours.
Very limited:
Makes
occasional
slight changes
in body or
extremity
position but
unable to
make frequent
or significant
changes
independently
.
No limitations:
Makes major
and frequent
changes in
position without
assistance.
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Nutrition
Usual food
intake pattern
4
Friction and
Shear
3
Very poor:
Never eats a
complete meal.
Rarely eats
more than one
third of any
food offered.
Eats 2 servings
or less of
protein (meat or
dairy products)
per day. Takes
fluids poorly.
Does not take a
liquid dietary
supplement.
OR
Is NPO and / or
maintained on
clear liquids or
IVs for more
than 5 days.
Probably
inadequate:
Rarely eats a
complete
meal and
generally eats
only about
half of any
food offered.
Protein intake
includes only
3 servings of
meat or dairy
products per
day.
Occasionally
will take a
dietary
supplement.
OR
Receives less
than optimal
amount of
liquid diet or
tube feeding.
Problem:
Potential
Requires
problem:
moderate to
Moves feebly
maximal
or requires
assistance in
minimal
moving.
assistance.
Complete lifting During a
without sliding move skin
against sheets is probably
impossible.
slides to some
Frequently
extent against
slides down in
sheets, chair,
bed or chair,
restraints, or
requiring
other devices.
frequent
Maintains
repositioning
relatively
with maximal
good position
assistance.
in chair or
Spasticity,
bed most of
contractions, or the time but
agitation leads
occasionally
19
Adequate: Eats
over half of most
meals. Eats a
total of 4 servings
of protein (meat,
dairy products)
each day.
Occasionally will
refuse a meal, but
will usually take a
supplement if
offered.
OR
Is on a tubefeeding or TPN
regimen that
probably meets
most of
nutritional needs.
No apparent
problem: Moves
in bed and in
chair
independently and
has sufficient
muscle strength to
sit up completely
during move.
Maintains good
position in bed or
chair at all times.
Excellent: Eats
most of every
meal. Never
refuses a meal.
Usually eats a
total of 4 or
more servings
of meat and
dairy products.
Occasionally
eats between
meals. Does
not require
supplements.
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
to almost
constant
friction.
20
slides down.
Instructions: Score client in each of the six subscales. Maximum score is 23, indicating little or
no risk. A score of < 16 indicates “at risk”, a score <9 indicates high risk.
From Perry and Potter 4th Edition of Basic Nursing. Used with permission of Nancy Bergstrom
and Barbara Braden, PhD, RN, Professor, Creighton University School of Nursing, Omaha,
Nebraska.
FALL RISK ASSESSMENT
Resident Name: MB Date: _10/10/12_________
X Admission
Post-Fall
Quarterly
Parameter
A
0.
Level of
Consciousness/
Mental Status
Readmission
Change in Condition
Score Patient Status/Condition
0
Alert and oriented X3
2
Disoriented X 3 at all times
4
Intermittent confusion
B.
History of Falls
0
No falls
0
(past 3 months)
2
1-2 falls
4
3 or more falls
0
Ambulatory & continent
2
Chair bound & requires assist w/ toileting
4
Ambulatory & incontinent
0
Adequate (w/ or w/o glasses)
2
Poor (w/ or w/o glasses)
C.
0
D.
0
Ambulation/
Elimination
Status
Vision Status
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
4
E.
Gait and Balance
------
1
F.
Orthostatic
0
Changes
G.
21
Legally blind
Have resident stand on both feet w/o any type of assist then
have walk: forward, thru a doorway, then make a turn.
(Mark all that apply.)
0
Normal/safe gait and balance.
1
Balance problem while standing.
1
Balance problem while walking.
1
Decreased muscular coordination.
1
Change in gait pattern when walking through doorway.
1
Jerking or unstable when making turns.
1
Requires assistance (person, furniture/walls or device).
0
No noted drop in blood pressure between lying and standing.
No change to cardiac rhythm.
Take resident’s
blood pressure
and pulse lying
down, then
again after
standing up.
2
Medications
------
Based upon the following types of medications: anesthetics,
antihistamines, cathartics, diuretics, antihypertensives,
antiseizure, benzodiazepines, hypoglycemics, psychotropics,
sedative/hypnotics.
0
None of these medications taken currently or w/in past 7 days.
2
Takes 1-2 of these medications currently or w/in past 7 days.
4
Takes 3-4 of these medications currently or w/in past 7 days.
1
Mark additional point if patient has had a change in these
medications or doses in past 5 days.
Drop<20mmHg in BP between lying and standing.
Increase of cardiac rhythm <20.
4
Drop >20mmHg in BP between lying and standing.
Increase of cardiac rhythm >20.
2
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
H.
Predisposing
------
Diseases
2
I.
Equipment Issues
22
Based upon the following conditions: hypotension, vertigo,
CVA, Parkinson’s Disease, loss of limb(s), seizures,
arthritis, osteoporosis, fractures
0
None present.
2
1-2 present.
4
3 or more present.
O
No risk factors noted.
1
Oxygen tubing.
1
Inappropriate use of or resident does not consistently use
assistive device.
1
Equipment needs:
1
Other:
1
TOTAL SCORE
6
A score of 10 or more indicates high risk for falls. If score is
10 or more, complete page 2.
Discharge Planning/Education Needs
I would educate the patient on proper diabetic monitoring and proper foods to eat.
According to her HGBA1C it appears that the patient has not been properly managing her
diabetes. I could use many different techniques to demonstrate proper insulin technique, storage
and how to notice if she is becoming hypoglycemic or hypoglycemic. I could give her written
information on blood glucose monitoring and actually observe the patient checking her blood
sugar and administering insulin. The patient would also be provided a list of appropriate diabetic
foods and asked to give me an example of a daily meal plan. These are just a few ways to assess
her understanding of diabetes (Craven & Hirnle, 2009).
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
23
I would also want to answer any questions she has related to her diagnosis of cancer. I
would provide information that would ease her mind but also be very truthful in describing the
battle she faces. It appeared to me that she was reluctant to speak of it and joked a lot when
questioned about the diagnosis around family. This questioning would have to occur
independently from family and friends. As the nurse I would want to assess the family’s feelings
of this potential terminal diagnosis as well, I would provide contact information of local support
groups and possible meeting times.
Labs
Test
Result
Possible reason for abnormal
result
PCO2
59.9 H
Altered gas exchange
PO2
57 L
Altered gas exchange
HCO3
34.2 H
Altered gas exchange
BE
7.5 H
Altered gas exchange
O2HB SAT
85.1 L
Altered gas exchange
Glucose
173 H
Diabetes diagnosis
BUN
30 H
Poor excretion function
Albumin
2.5 L
Poor kidney function
Globulin
4.5 H
Poor kidney function
Triglycerides
326 H
Poor diet
HDL
23 L
Poor diet
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
24
Iron
17 L
Anemia
INR
1.0 C
Blood thinning products
PTT
25.7 C
Blood thinning products
HGB
10.5 L
Anemia
HCT
33.9 L
Anemia
NEUT %
87.3 H
Defense against bacteria
Sed rate
C
Blood thinning products
HGB A1C
H
Poor diabetes regulation
Sputum Culture
Acinetobacter Baumannii
/Haemol (rare gram positive
cocci) present in sputum
Contracted bacteria
Medications
Medication Name
Dose,
Route
Purpose/Action
Side Effects
Novolog 70/30
24 units
subcutane
ous once
daily
Antidiabetic that
decreases blood
glucose by transport
into cells
Hypoglycemia,
anaphylaxis,
blurred vision,
dry mouth
Fluticasone/Salmeterol
1 puff 2
Decreases
times daily inflammation by
inhibiting mast cells.
Tiotropium Bromide
18mcg
inhale
daily
Inhibits
acetylcholine at
receptor sites to
cause
Bronchospasm,
angioedema,
Churg-Strauss
syndrome, upper
respiratory
infections
Bronchoconstrict
ion, increased
heart rate, chest
pain, upper
Nursing
Consideration
s
Monitor for
hypoglycemic
reaction,
Change in
level of
consciousness
or confusion.
Lung sounds,
BP
monitoring
Monitor lung
sounds and
heart rate.
Observe for
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
25
bronchodilation
Albuterol 2 Puff
Linezolid(Zyvox)
Lisinopril
Prednisone
Acidophilus
Amiodarone HCL
Cyanocobalamin(Vitam
in B12)
Doxepin
HCL(Sinequan)
respiratory
infections
Bronchospasm,
palpitations,
restlessness,
anxiety
respiratory
distress
Inhale 4
Bronchodilates by
Respiratory
times daily acting on B2
function,
receptor to relax
Monitor heart
smooth muscle
rate and
rhythm
600mg PO Broad spectrum anti Nausea,
CBC with
every 12
infective that inhibits vomiting,
diff, monitor
hours
protein synthesis
diarrhea, lactic
for CNS
acidosis
symptoms,
allergic
reaction
2.5mg PO Antihypertensive ace Stroke,
Monitor heart
2 times
inhibitor
angioedema,
rate and
daily
chest pain,
rhythm, blood
hypotension
pressure,
blood studies
5mg PO
Corticosteroid
Circulatory
Monitor all
daily with suppresses migration collapse,
vitals, daily
meal
of inflammation
thrombophlebitis weights, I&O
causers
, embolism, g.i.
hemorrhage,
hypertension
1pkt PO 3 Natural bacteria
Nausea,
Observe for
times daily supplement given to difficulty
g.i. distress,
regulate appropriate breathing,
respiratory
bacteria levels
swelling of
distress
throat
200mg PO Antiarrhythmic
Irregular
Monitor heart
daily
heartbeat,
rate and
blurred vision,
rhythm
chest pains
1000mcg
Water soluble
CHF, pulmonary GI function,
PO daily
vitamin used for
edema,
nutritional
RBC development
anaphylaxis,
status,
diarrhea
worsening of
CHF in
cardiac
patients
100mg PO Antidepressant and
Suicidal ideation Monitor BP ,
at bedtime antihistamine
, hypertension,
withdrawal
dysrhythmias,
symptoms,
hepatitis, renal
constipation,
failure
mental/emoti
onal status
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
26
Enoxaparin
40mg
subcutane
ous daily
Anticoagulant binds
to antithrombin 3
Hemorrhage,
thrombocytopeni
a, bleeding
Ezetimibe(Zetia)
10mg PO
at bedtime
Fatigue ,
diarrhea, chest
pain
Furosemide(Lasix)
40mg Po
once daily
before
meals
Antilipidemic
inhibits the
absorption of
cholesterol
Loop diuretic that
inhibits reabsorbtion
of sodium and
chloride
Gabapentin(Neurontin)
600mg PO
3 times
daily
Hydrochlorothiazide
25mg PO
daily
Levothyroxine Sodium
0.025mg
PO daily
before
meals
10mg PO
daily
before
meals
Thyroid hormone
Metoprolol Tartate
50mg PO
2 times
daily
Antihypertensive
lowers BP by
blocking B2
receptors
Multivitamin
1 tab PO
daily
Vitamin
Loratidine
Circulatroy
collapse, loss of
hearing, renal
failure, Stevens
Johnsons
syndrome,
Anticonvulsant
Drowsiness ,
mechanism unknown seizures,
vasodilation,
constipation
Diuretic acts on the
Drowsiness,
distal tubule
irregular pulse,
hepatitis,
anemia, blurred
vision
Antihistamine binds
to histamine
receptors
Thyroid storm,
cardiac arrest,
tachycardia ,
palpitations
Sedation,
headache, acute
asthma attacks
Depression,
bradycardia,
CHF, cardiac
arrest, edema,
chest pain
None known at
recommended
dosage
Blood studies
and
coagulation
studies, occult
blood and
stool
Lipid levels,
evaluate
therapeutic
response
Signs of
hypokalemia,
rash,
confusion,
weight daily,
I&O rate and
rhythm of
heart, BP
Seizures aura,
renal studies,
mental status,
do not crush
Weight daily,
I&O, Monitor
BP and
respirations,
electrolyte
studies
BP, pulse,
Daily weight,
General
cardiac status
Allergic
reaction,
monitor
respiratory
status
I&O, daily
weigths, BP,
apical pulse,
skin turgor
and edema
Assess
vitamin
deficiency,
chew tabs
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Pantoprazole
27
40mg Po
daily
before
meals
80mg PO
at bedtime
Proton pump
inhibitor suppresses
gas secretion
Aspirin
81mg PO
daily with
meals
Nonopiod analgesic
blocks pain impulses
in CNS
Cyclobenzaprine
HCL(Flexeril)
10mg PO
3 times
daily as
needed
Skeletal muscle
relaxant reduces
tonic muscle activity
Hydroxyzine
HCL(Atarax)
10mg PO
4 times
daily as
needed
0.5 mg PO
q 6 as
needed
Antianxiety/antihista
mine depresses
subcortical levels of
the CNS
Hypnotic antianxiety
potentiates the
actions of GABA
Acetaminophen
650mg q 4
as needed
Nonopiod analgesic
blocks pain impulses
peripherally
Cefepime HCL 2 gram
in Sodium Chloride
0.9% 50ml
100 mls/hr
IV every
12 hrs
Broad spectrum
antibiotic inhibits
bacterial cell wall
synthesis
Novolog 70/30
16units
See above
Pravastatin Sodium
Lorazepam(Ativan)
Antilipidemic
inhibits HMG-CoA
reductase enzyme
should be
chewed not
swallowed
Headache,
Monitor GI
Diarrhea,
system,
abdominal pain, Hepatic
hyperglycemia
studies
Hepatic
Fasting lipid
dysfunction,
panel, hepatic
myositis, nausea, studies, renal
hepatitis
studies,
observe for
muscle
tenderness
Seizures, GI
Assess pain,
bleeding,
renal studies,
hepatitis, Reyes
hepatotoxicity
syndrome
, blood
studies
Dysrhythmias,
Assess pain
dizziness,
level, allergic
weakness,
reaction,
postural
assist in
hypotension
ambulation
Dizziness,
BP, Mental
seizures,
status,
hypotension, dry administer
mouth
with food
Tachycardia,
BP, blood
dizziness, apnea, studies,
cardiac arrest,
hepatic
orthostatic
studies,
hypotension
mental status
Hepatotoxicity,
Hepatic
renal failure,
studies, renal
anemia,
studies, blood
cyanosis,
studies, I&O,
vascular collapse allergic
reaction
Seizures, heart
C&S,
failure, bleeding, nephrotoxicit
anaphylaxis,
y,
electrolytes,
bowel pattern,
blood studies
See above
See above
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Heparin Sodium
subcutane
ous PM
300900units
IV every
12 hrs
Insulin Human Lispro
3-15units
subcutane
ous 4
times daily
per sliding
scale
Apap/Hydrocodone(Vic 1-2
odin)
UDTAB
PO every
4-6hrs as
needed
28
Anticoagulant
prevents the
conversion of
fibrinogen to fibrin
Antidiabetic
decreases blood
glucose by transport
into cells
Nonopiod analgesic
binds to opiate
receptors in CNS to
reduce pain
Bisacodyl
10mg
Laxative/stimulant
rectal
acts on intestine to
suppositor increase motor
y every
activity
day as
needed
All medications provided by Mosby’s Nursing Drug Reference
Hematuria,
hemorrhage,
anemia,
thrombocytopeni
a, anaphylaxis
Blurred vision,
flushing,
anaphylaxis,
hypoglycemia
Bleeding,
blood studies,
pt-inr, platelet
count
Seizures,
circulatory
depression,
respiratory
distress,
palpitations,
drowsiness
Muscle
weakness,
tetany, nausea,
vomiting ,
diarrhea
Pain level,
CNS changes,
allergic
reaction,
respiratory
dysfunction
Urine
ketones,
hyper or hypo
glycemic
reactions
I&O, cause of
constipation,
cramping
and/or rectal
bleeding
Critical Thinking Map
Please refer to end of paper
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing
Diagnosis
1.Impaired
gas
exchange
related to
altered
oxygen
supply as
evidenced
by blood
gas values
secondary
Supporting
Data
1.Dyspnea
upon
exertion
Shortterm Goal
Patient
will be
free of
respirator
y distress
until the
end of
shift today
Long-term
Goal
Patient will
demonstrate
improved
ventilation
and
adequate
oxygenatio
n of tissues
by arterial
blood gases
within
Intervention
s
1. Assess
client’s
response to
activity.
Encourage
rest periods,
limiting
activities to
client
tolerance
Rationales
Evaluation
Increased
oxygen
consumption
and demand
and stress of
surgery may
result in
increased
dyspnea and
changes in
vital signs
Goal met
patient
presented
with no
sign of
respiratory
distress
during
shift.
Patient is
very aware
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
29
client’s
normal
range by
discharge
date
to chronic
obstructiv
e
pulmonary
disease,
and lung
cancer
diagnosis
of her
respiratory
issues and
is very
open to
pulse
oximetry
checks and
frequent
respiratory
monitoring
. Long
term goal
cannot be
evaluated
at this
time.
Continue
plan of
care
2.Labored
work of
breathing
2.Ausculate
lung sounds
for air
movement
and
abnormal
breath
sounds
3.Oxygen
saturation
of 96% on
5 liters of
oxygen
3.Maintain
patent
airway by
positioning,
suctioning,
and use of
airway
adjuncts
4.Encourage
and assist
with deepbreathing
exercises
and pursed
lip breathing
as
4.CO2 of
33 on
blood gas
values
Lack of air
movement
and
adventitious
breath
sounds can
indicate
consolidatio
n in lung
fields
Airway
obstruction
impedes
ventilation,
impairing
gas
exchange
Promotes
maximal
ventilation
and
oxygenation
and reduces
or prevents
atelactasis
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
30
appropriate
5. Monitor
and graph
ABGs and
pulse
oximetry
readings.
Note
hemoglobin
levels
Monitoring
ABG values
can be
critical in
noticing a
decline or
improvement
of patient’s
gas levels
Long-term
Goal
Interventions
Rationales
Evaluatio
n
Patient
will
demonstrat
e patent
airway
with no
respiratory
distress
until
discharge
1.Auscultate
chest for
character of
breath sounds
and presence
of secretions
Noisy
respirations,
rhonchi, and
wheezes are
indicative of
retained
secretions or
airway
obstructions
Short
term goal
met.
Patient is
able to
describe
how to
use
incentive
spiromete
r, how to
deep
breathe
and
cough,
and what
she uses
albuterol
inhaler
for. Long
term goal
cannot be
evaluated
at this
time
continue
plan of
care
2. Observe
amount and
character of
Presence of
thick,
tenacious,
5.Resident
states “it is
difficult to
catch my
breath
sometimes
”
Nursing
Diagnosis
Supporting
Data
2.Inefectiv
e airway
clearance
related to
increased
amount of
secretions
as
evidenced
by
abnormal
breath
sounds
1.Cough
with
productive
yellow
sputum
2.Rhonchi
heard in both
lungs on
Shortterm
Goal
Patient
will
verbalize
three
technique
s to
maintain
patent
airway
by the
end of
shift
today
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
31
inspiration
expiration
sputum and
aspirated
secretions.
Investigate
changes
bloody, or
purulent
sputum may
suggest
development
of secondary
problem
3.Encourage
Adequate
oral fluid
hydration
intake within
aids in
cardiac
keeping
tolerance
secretions
loose and
enhances
expectoratio
n
4.Provide and Improves
assist client
lung
with incentive expansion
spirometer and and
postural
ventilation
drainage
facilitates
techniques
removal of
secretions
5.Administer
Relieves
bronchodilator bronchospas
s,
m to
expectorants,
improve
and
airflow.
analgesics, as Expectorants
indicated
increase
mucous
production
and reduce
viscosity of
secretions.
3.Respiratio
ns of 22 a
minute on
5L of
oxygen
4.Diagnosis
of small cell
lung
carcinoma
5.Shallow
breaths
noted upon
assessment
Nursing
Diagnosi
s
3.Fear
related to
situationa
l crisis as
evidence
Supporting
Data
Short-term
Goal
Long-term
Goal
Interventions
Rationales
Evaluatio
n
1.Exploratio
n has lead
the doctors
to discover
disease is
Patient will
acknowledg
e and
discuss
fears and
Patient
will begin
use of
individuall
y
1.Acknowled
ge reality of
client’s fears
and concerns
and encourage
Support
may enable
client to
begin
exploring
Client’s
goals
were
partially
met. It
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
d by
expressio
n of
denial
and
worry
not
surgically
resectable
2.Patient
beginning
possible
chemotherap
y which she
has never
endured
before
concerns by appropriat
the end of
e coping
shift today
strategies
32
expression of
feelings
and dealing
with the
reality of
cancer and
its treatment
2.Note
comments and
behaviors
indicative of
beginning
acceptance or
use of
effective
strategies to
Fear and
anxiety will
diminish as
client begins
to accept
and deal
positively
with reality
was very
hard to
observe
client’s
true
feelings
because a
family
friend
was
present
during
whole
shift. The
only
thing I
would
change
regarding
both
goals
would be
to try and
evaluate
when
patient
does not
have
friends
from
their
immediat
e circle
present.
Continue
plan of
care
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
3.Patient
jokes every
time she
discusses her
potential
outcome
which could
represent a
state of
denial
4.Patient
verbalizes
concern with
driving “so
far” in the
winter to
undergo
chemotherap
y
5.Patient
states “I
don’t really
know what
my husband
will do if
I’m not here
anymore”
33
deal with
situation
3.Accept, but
do not
reinforce,
client’s denial
of the
situation
4.Provide for
client’s
physical
comfort
5.Involve
client and
significant
other in care
planning
When
extreme
denial or
anxiety is
interfering
with
progress of
recovery,
the issues
facing client
need to be
explained
and
resolutions
explored
It is difficult
to deal with
emotional
issues when
experiencin
g extreme or
persistent
physical
comfort
This may
help restore
some
feeling of
control and
independenc
e to a client
who feels
powerless in
dealing with
diagnosis
and
treatment
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
34
References
Black, J.M., & Hawks, H.H. (2009). Medical-Surgical Nursing: Clinical Management for
Positive Outcomes (8th ed.) St. Louis, MO: Sauders Elsevier
Camporeale, J, Huhmann, M. (May 2012). Supportive Care in Lung Cancer: Clinical Update.
Seminars in Oncology Nursing Vol28, pp e1-e10. doi:10.1016/j.soncn.2012.03.009
Craven, R.F., & Hirnle, C.J. (2009). Fundamentals of Nursing: Human Health and Function (6th
ed.) Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health
Doenges, M.E., Moorhouse, M.F., Murr, A.C. (Eds). (2010) Nursing Care Plans Guidelines For
Individualizing Client Care Across the Life Span (8th ed.) Philadelphia, PA F.A. Davis Company
Eggert, J. (Februaury 2010). The Biology of Cancer: What Do Oncology Nurse Really Need to
Know. Seminars in Oncology Nursing, Vol.27, pp 3-12. Doi:
10.1016/j.soncn.2010.11.002
Esper, P. (August 2010). System Cluster of Individuals Living With Advanced Cancer. Seminars
in Oncology Nursing, Vol.26, pp 168-174. Doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2010.05.002
Hogan, M.A., Davenport, J, Estridge, S, & Zygmont, D. (Eds.). (2008) Medical-Surgical Nursing
Reviews & Rationales. Upper Sadle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall
Skidmore-Roth, L (Ed.). (2009) 2009 Mosby’s Nursing Drug Reference. St. Louis, Mo: Sauders
Elsevier
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
Link to nursing journal used in paper
http://journals.ohiolink.edu/ejc/article.cgi?issn=07492081&issue=v24i0001&article=57_scilc
35
GERONTOLOGY NURSING PROCESS PAPER
36
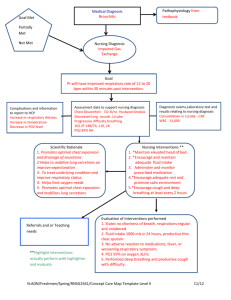
SQUAMOUS
CELL LUNG
CANCER
COPD
Tumor growth commonly begins in the bronchus then
migrates to upper lobes. (Med Surg 80)Tumor
formation can cause restricted inhalation and
exhalation leading to inadequate gas exchange.
Dyspnea
Progressive deconstruction of alveoli, decreased
surface area of respiratory bronchioles, alveoli, and
alveolar ducts available for gas exchange(MED SURG
64)
Impaired gas exchange related
to altered oxygen supply as
evidenced by blood gas values
secondary to chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease, and lung
cancer diagnosis
Altered
blood gas
levels
Cyanosis
Restlessness
Altered level of
consciousness
Anxiety/panic