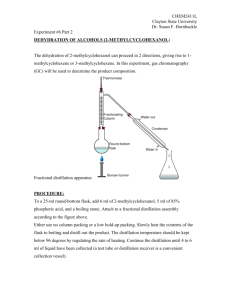
Simple Distillation
advertisement
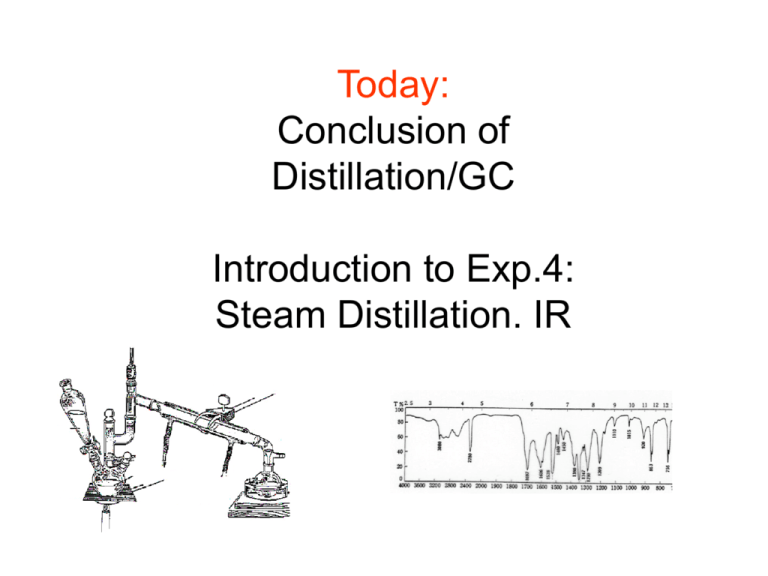
Today: Conclusion of Distillation/GC Introduction to Exp.4: Steam Distillation. IR Simple & Fractional Distillation Curve GC conditions for your EA and EP Analysis: Sample injection volume: 0.5 mL GC column: 15 m x 0.53 mm (I.D.) PhMe-silicone stationary phase, Rtx-50 column Initial oven temperature = 35oC Initial time = 0.75 min Temperature ramp = 35oC/min Final Temperature = 70oC Final time = 1.0 min Column head pressure = 20 psi or more (He as Mobile Phase) Injector Temperature = 225oC Detector Temperature = 250oC Detector: thermal conductivity (TCD) GC Chromatogram solvent RT EA EP Area Type Width Area% (min) .210 333265 12.35 .506 1103207 40.88 1.061 1261972 46.77 Area ratio = mole ratio AEA/ AEP = nEA/nEP Task: Determine the amount of EA as mole % EA in sample S1 and also in sample F1 Step 1: analyze the standard mixture (50:50 v/v) of EA and EP for calibration of the GC instrument AEA AEP = nEA x C nEP calculate where k = 1 C A = GC peak Area n = moles Step 2: Calculate the mole ratio of your sample using the correction factor obtained from the standard nEA nEP k x for samples S1 and F1 AEA AEP = nEA nEP Mole ratio → mole fraction → mole % Exp.4: Steam Distillation. IR Exp. 4: Isolation of a Natural Product CH3O Eugenol HO CH2CH CH2 A “phenolic”. CH3 CH3 Caryophyllene CH3 H2C CH3O Eugenol Acetate CH3C-O O CH2CH CH2 Steam Distillation 1. What types of mixtures can be separated by steam distillation? 2. The vapor pressure of water at 99oC is 733 torr. What is the vapor pressure of eugenol that codistills at this temperature? 3. During a steam distillation the mole ratio of two immiscible liquids is equal to the ratio of ...... ? n1/n2 = Po1/Po2 Steam Distillation Dalton’s Law: P1V1 = n1RT1 and V1 = V2 and T1 = T2 P1V1 P2V2 = P2V2 = n2RT2 n = moles, n1RT1 therefore n1 = P1 n2RT2 n2 P2 where 1= water and 2 =compound steam-distilled Steam Distillation n1/n2 = Po1/Po2 (mass1/MW1) / (mass2/MW2) = Po1/Po2 Steam distillation problem: Benzene and water mixture boils at 69oC. The MW of benzene is 78.11. MW of water is 18.01 How many grams of water are required to steam distil 1 gram of benzene? Use this Table 6.1 for Interpolation Steam Distillation Which of the following boiling points are EQUAL TO 100 degrees C, which are BELOW, and which are ABOVE ? 1. A water - eugenol mixture 2. A water- acetic acid mixture (bp. of pure acetic acid: 120 degrees C; it is miscible with water) 3. A sand-water mixture 4. A solution of NaCl in water Direct Steam Distillation Set-up Macro-scale Thermometer Separatory Funnel water 150 mL water & 7g Clove buds Bunsen burner H2O Ice bath Use a lab-jack Liquid-Liquid Extraction of steam distillate with methylene chloride Which layer is methylene chloride (CH2Cl2)? Which layer is going to contain the eugenol? Aqu. layer CH2Cl2 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Anhydrous Na2SO4 Plug of cotton “Tare” 50-mL E-flask with ** one boiling chip Collect both MeCl layers, then boil off solvent Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) 1) What is the approximate range of wavelengths visible to humans? And where would you find the range of IR light? How about its energy compared to visible light? 2) What are the "wavenumbers", commonly used in IR to define absorptions? 3) What type of information do we obtain from an IR spectrum? 4) How can we identify a compound from its IR, e.g. how can we know that we obtained eugenol? 5) How will your IR tell you if your eugenol sample contains impurities? Our next Experiment: Exp. 10: Caffeine!