Econ Chapter 2 Guided Reading Name 2.1 Objectives
advertisement

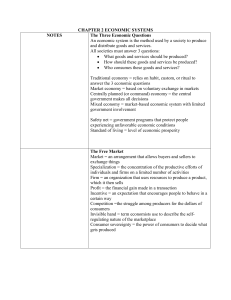
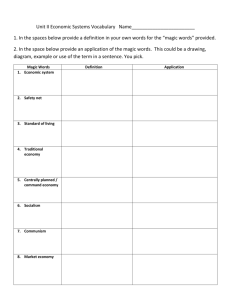
Econ Chapter 2 Guided Reading Name _____________________________ 2.1 Objectives -Identify the 3 key economic questions - Analyze societal values that determine how a country answers the economic questions - Explain the characteristics of traditional, command, and market economies Define the following vocab words 1. Economic System 2. Factor Payments 3. Patriotism 4. Safety Net 5. Standard of Living 6. Traditional Economy 7. Market Economy 8. Centrally Planned Economy 9. Command Economy 10. Mixed Economy Answer the following questions 1. What are the three economic questions? 2. What is the function of an economic system? 3. Why have different economic systems developed? 4. List and explain the goals that each economic system tries to address. 5. List the four economic systems that have developed. 6. Explain how the four economic systems differ from each other. 7. Centrally planned economies are sometimes called _________________________. 8. Market or Free Market economies are sometimes referred to as __________________. 9. Why aren’t all people paid the same amount in factor payments for the resources they provide? Provide your own example of two unequal factor payments. 10. Why do governments provide safety nets? 11. What are four situations in which governments usually provide safety nets? 12. Give at least one example of a traditional, a command, and a market economic system. SECTION 2 2.2 Objectives - Explain why markets exist - Analyze a circular flow model of a free market economy - Understand the self-regulating nature of the marketplace - Identify the advantages of a free market economy. Define the following vocab words 1. Market 2. Specialization 3. Household 4. Firm 5. Factor Market 6. Profit 7. Product Market 8. Self-Interest 9. Incentive 10. Competition 11. Invisible Hand 12. Consumer Sovereignty Answer the following questions 1. Describe how a free market economic system operates. 2. What is the struggle among various producers for the consumer’s business called? 3. What is the motivating force in the market place? 4. What is the regulating force in the market place? 5. Explain what Adam Smith meant by the “invisible hand”. 6. List the advantages of a Free Market System. 7. What is the most important advantage of a free market system? 8. Explain the difference between product market and factor market. 9. Explain what motivates a seller to sell a product. 10. What is the most effective way for consumers to make their desires known to sellers? 11. Draw and explain the circular flow diagram on page 30. SECTION 3 2.3 Objectives - Describe how a centrally planned economy is organized - Analyze the centrally planned economy of the former Soviet Union - Identify problems with centrally planned economy. Define the following vocab words. 1. Socialism 2. Communism 3. Authoritarian 4. Collective 5. Heavy Industry Answer the following questions 1. How do communism and socialism differ? 2. What characterizes an authoritarian government 3. Why do Soviet collectives offer little incentives to farmers? 4. In the Soviet Union, what was the opportunity cost of the emphasis on heavy industry? 5. Of the economic goals discussed in section 1, which is the most difficult for a command economy to achieve? 6. Who were the two socialist philosophers that wrote the Communist Manifesto? 7. What group adopted the term Communism and who was their leader? 8. Explain why centrally planned economies have a difficult time meeting consumer needs. 9. What year did the Soviet Union collapse? SECTION 4 2.4 Objectives - Explain the rise of mixed economic systems - Interpret a circular flow model of mixed economy - Compare the mixed economies of various nations along a continuum between centrally planned and free market systems Define the following vocab words. 1. Laissez Faire 2. Private Property 3. Free Enterprise 4. Continuum 5. Transition 6. Privatize Answer the following questions. 1. Explain why some nations have transitioned to a free enterprise system. 2. Explain the mixed economy is Sweden? (pg 41) 3. Explain why centrally planned nations are slow to succeed when they privatize industry. 4. Explain how Hong Kong, which is part of China, is so far right on the continuum. 5. According to the continuum, which country has the highest level of central planning? 6. Explain how government actions affect the circular flow model in a mixed economy. 7. What does it mean to privatize? List an example. 8. Why do all countries fall onto a continuum? DRAW AND EXPLAIN THE CONTIUNUUM ON PAGE 43