here
advertisement

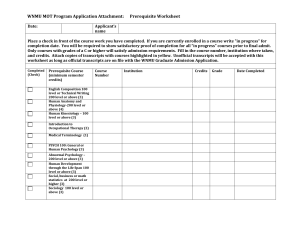
UNIVERSITY OF HAIL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CURRICULUM Degree: Bachelor of Science in MechanicalEngineering <> First Year (Preparatory) Subjects will be allocated on joining the university. Second Year (Freshman) First Term Course Title L T L B Second Term C R Prerequi site Corequi site Cours e Title L T LB C R English Composition II 3 0 3 CHEM 101 Chemistry I 3 4 4 ENGL 102 ENGL 101 English Compositio nI 3 0 3 MATH 102 Calculus II 4 0 4 MATH 101 Calculus I 4 0 4 PHYS 102 Physics II 3 3 4 PHYS 1 01 Physics I 3 3 4 ICS 103 Computer Programmin g in C 2 3 3 IAS 111 Belief and its Consequen ces 2 0 2 IAS 101 Practical Grammar 2 0 2 Prerequi site Corequi site PE 101 Physical Education I TOTAL 0 2 1 1 5 9 1 8 PE102 Physical Education II TOTA L 0 2 1 1 4 8 1 7 Third Year (Sophomore) First Term Second Term Course Title L T L B C R MATH 201 Calculus III 3 0 CE 201 Statics 3 ME 203 Thermodyn amics I ME 210 ME Drawing & Graphics ME 215 Materials Science for ME 3 ENGL 214 Technical Report Writing TOTAL Prerequi site Corequi site Cours e Title L T LB C R 3 ME 201 Dynamics 3 0 3 0 3 ME 20 4 Thermodyna mics II 3 0 3 3 0 3 MATH 202 Elem. Diff. Equations 3 0 3 2 3 3 CE 20 3 Structural Mechanics 3 0 3 3 4 ME 20 6 Manufacturi ng Processes I 3 3 4 3 0 3 IAS 21 1 Ethics in Islam 2 0 2 1 7 6 1 9 TOTA L 1 7 3 1 8 Prerequi site Corequi site Prerequi site Corequi site Fourth Year (Junior) First Term Course Title L T L B Second Term C R Prerequi site Corequi site Cours e Title L T LB C R EE 202 Fund. of Elec. Circuit 2 3 3 ME 306 Manufacturi ng Processes II 2 3 3 Electromech anical Devices 2 3 3 Machine Design II 3 3 4 IAS 201 Objective Writing Terminolog y 2 0 2 EE 306 MATH 303 Methods of Applied Mathemati cs 3 0 3 ME 308 ME 307 Machine Design I 3 0 3 ME 309 Mechanics of Machines 3 0 3 ME 311 Fluid Mechanics 3 0 3 ME 315 Heat Transfer 3 0 3 STAT 319 Probability & Statistics for Eng. 2 3 3 ME 316 ThermoFluids Laboratory 0 3 1 IAS 322 Human Rights in Islam 2 0 2 1 5 12 1 9 1 7 TOTAL 6 1 9 TOTA L Summer Semester Course Title L T L B C R ME 399 Cooperativ e Work Program 0 0 0 Prerequi site Corequi site Fifth Year (Senior) First Term Course Title L T L B Second Term C R Prerequi Corequi Cours e Title L T LB C R Prerequi Corequi site ME 401 Cooperativ e work (Cont.) TOTAL 0 0 0 0 site 9 ME 413 System Dynamics & Control 2 3 3 GS XXX General Studies Elective 3 0 3 ME 4XX ME Elective I 3 0 3 ME 4XX ME Elective II 3 0 3 ME 415 Senior Design Project 1 6 3 IAS 301 Literary Skills 2 0 2 1 4 9 1 7 TOTA L 9 site site Prerequi site Corequi site Total credit hours required in Degree Program: 134 + (Preparatory Year) Elective Courses L T L T LB C R 3 ME 423 Refrigeratio n & Air Conditionin g 3 0 3 0 3 ME 425 Internal Combustion Engines 3 0 3 3 0 3 ME 426 Renewable Energy 3 0 3 3 0 3 ME 427 Turbo machinery 3 0 3 ME 410 Casting And Welding Engineering ME 411 Plastics and Plastics Processing 3 ME 412 Fundament als of Heat Treatment ME 414 Corrosion Engineering I 3 0 C R Corequi site Title Title L B Prerequi site Cours e Course ME 416 Mechanical Vibrations 3 ME 428 Fluid Power Systems 3 0 3 ME 417 Optimizatio n of Mechanical Systems 0 3 ME 429 Fundamenta ls of Aerodynami cs 3 3 0 3 ME 418 Quality in Manufactur ing 3 0 3 ME 430 Energy Conversion 3 0 3 ME 419 Computer Integrated Manufactur ing 0 3 ME 431 Design and Rating of Heat Exchangers 3 3 0 3 ME 420 Iron and Steel Making 3 0 3 ME 435 Thermal power Plants 3 0 3 ME 422 Thermal Desalinatio n Systems 3 0 3 3 0 General Studies Electives (GS XXX) L T L B C R Principles of Human Behavior 3 0 3 GS 423 Industrial Relations 3 0 3 GS 424 Planning and Social Developme nt 3 0 3 GS 427 Man and Environme nt 3 0 3 MGT 301 Manageme nt 3 0 3 Course Title GS 321 Prerequi site Corequi site COURSES DESCRIPTION ME 201: Dynamics: Prerequisite: (Credits 3)CE 201 The course includes the following topics: Kinematics of rectilinear and curvilinear motion of particles. Kinematics of rotation and plane motion of rigid bodies. Dynamics of particles and systems of particles. Work and energy relations. Impulse and momentum principles. Dynamics of rigid bodies in plane motion. ME 203 - Thermodynamics I(Credits 3): Prerequisite: MATH 102, PHYS 102 System and control volume concepts.Properties of a pure substance.Work and heat. The first law of thermodynamics as applied to a system and a control volume, internal energy, enthalpy. The second law of thermodynamics.Carnot cycle, entropy, reversible and irreversible processes.Applications of steady-state, steady-flow, uniformstate, uniform-flow, and other processes. ME 204 - Thermodynamics II(Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 203 Vapor power cycles, Rankine, reheat, and regenerative cycles. Maxwell relations, ideal and real gases, equations of state, generalized charts. Gas-vapor mixtures, psychrometric charts, ideal solutions. Chemical reactions. Fuels and combustion processes. ME 205 : Materials Science (Credits 3): Prerequisite: CHEM 102, MATH 102 Introduction to the properties of engineering materials: mechanical, electrical and chemical. Fundamentals of crystallography. Impurities and imperfections in solids. Atomic diffusion. Single phase metals and alloys; elastic and plastic deformation, recrystallization and grain growth. Multi-phase materials; phase diagrams with emphasis on iron-iron carbide system. Heat treatment process, such as annealing, normalizing and quenching. Studies of widely used engineering materials; steels, plastics, ceramics, concrete and wood. ME 206 - Manufacturing Processes I(Credits 4): Prerequisite: ME 210, ME 215 Manufacturing methods of metals and plastics including: metal casting, forming, machining, welding, and plastic processing. Laboratory experiments and demonstrations in material behavior, forming, casting, welding and machining operations, metrology and dimensional control. ME 210 : Mechanical Engineering Drawing and Graphics (Credits 3): Pre/Co-Requisites : None The course introduce the student with the basics of Engineering Drawing and Graphics; Topics include: Graphical interpretation of orthographic projection to include auxiliary views, section views, dimensioning, translation of design instructions into detail and assembly drawings, drawing conventions including weldments, piping, referencing and surface finish notation, election of tolerances based on design requirements. Computer Usage of the 75 hours available for this course, 18 hours will be spent on traditional drafting and the remaining 57 hours on computer drafting. Students will use an up to date version of Solid Works to construct orthographic drawings during this course. Students will access models of typical mechanical components and view these models from various directions. These models and viewing techniques will assist students to better visualize in 3-D space. ME 215: Materials Science for Mechanical Engineers (Credits 4): Prerequisite: CHEM 101, MATH 102, PHYS 102 Atomic bonding in solids, bonding forces and energies, primary and secondary bonds. The structure of crystalline solids, lattice, unit cells and crystal systems, density computations, crystal directions and planes, linear and planar atomic densities. Impurities and imperfections in solids: point, line and interfacial defects. Atomic vibration and diffusion. Mechanical properties of materials. Elastic and plastic deformation and recrystallization. Phase diagrams of single and multi-phase materials with emphasis on iron-iron carbide system. Thermal processing of metals and alloys, composite materials, polymers. ME 307 - Machine Design I(Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 206, ME 210, CE 203 Design process, review of stress, strain and deformation analysis as applied to mechanical design; properties of materials; review of static failure theories; designing against fatigue failures; element design; shafts, keys, couplings, power screws, bolted, riveted and welded joints. ME 308 - Machine Design II(Credits 4): Prerequisite: ME 307 Design of elements: bearings (journal and anti-friction), springs, spur, helical, bevel and worm gears; flexible drives (belts and chains); clutches and brakes; design optimization. Laboratory sessions to supplement and to apply the material covered in the lectures. Consideration of manufacturing aspects of the design (limits and fits). Study of projects considering the different stages of their design, manufacturing and assembly. ME 306 Manufacturing Processes II (Credits 3) Principles applied to metal working, casting, welding and machining processes. Design and process considerations.Modern welding processes. Non-traditional material removal processes. Powder and metal processing.Automation.Numerical control machining.Introduction to statistical manufacturing process control.Laboratory demonstrations and experiments on these principles and processes. Prerequisite: ICS 101, ME 206 ME 309 - Mechanics of Machines(Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 201 Kinematics of mechanisms, vector method of analysis of plane mechanisms.Static and dynamic analysis of machines, inertia forces, gyroscopic forces.Static and dynamic balancing, balancing machines.Dynamics and balancing of reciprocating engines.Flywheels, kinematic and dynamic analysis of cam mechanisms.Elements of mechanical vibrations, critical speeds and torsional vibrations. ME 311: Fluid Mechanics (Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 201, ME 203, MATH 201 Definition and properties of fluids. Fluid statics with applications. Basic fluid dynamic equations of continuity, energy and momentum, with applications to different flow situations and flow measurement. Viscous effects, boundary layer concepts, laminar and turbulent flow in pipes, open channel flow, fluid dynamics, forces on immersed bodies. Modeling and dimensional similarity. Introduction to turbomachinery. ME 315: Heat Transfer. (Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 311 An introduction to heat transfer by conduction, radiation and convection. Steady-state analysis of heat transfer through composite plane, cylindrical and spherical walls with convection and radiation boundary conditions, internal energy generation and extended surfaces (fins). Significance of multidimensional effects. Unsteady heat transfer in plates, cylinders and spheres. Numerical solution of heat conduction problems. Practical analysis of convection with application to heat exchangers. Blackbody and graybody radiation systems.. Students will be assigned several homework problems that will involve the use of the computer to solve practical problems. ME 316: Thermo-Fluid Lab (Credit 1): Prerequisite:ME 311andCo-requisite:ME 315 This lab course deals with fluid mechanics and heat transfer. All experiments conducted in this lab combine elements of theory and practice. Many of the concepts and basic theories which the students learns in the lectures of ME 311 and ME 315 are demonstrated and confirmed in the lab through different experiments. ME 413: System Dynamics and Control (Credits 3): Prerequisite: ME 201, MATH 202 Dynamics of mechanical, fluid, electrical and thermal systems. Equations of motion. Dynamic response of elementary systems. Transfer functions and pole-zero diagrams. Simulation of dynamics of complex systems. Dynamic stability of systems. Open and closed-loop systems. Basic control actions. Laboratory sessions involving use of computers for simulation of dynamic systems and analysis of control systems. ME 399 Cooperative Work(Credits 0): Prerequisites: ENGL 214, junior standing and approval of the Department. A continuous period of 8 weeks of summer training spent in the industry working in any of the fields of mechanical engineering. The training should be carried out in an organization with an interest in one or more of these fields. On completion of the program, the student is required to submit a formal written report of his work. ME 401 - Mechanical Engineering Cooperative Work(credits 9): Prerequisite: ENGL 214, ME 307, ME 309, ME 315 A period of 28 weeks of industrial employment for Mechanical Engineering students to work in appropriate industries or firms. Students are evaluated on their performance on the job and are required to submit an extensive formal report on their experience. ME 410 Casting And Welding Engineering (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 206, ME315 Metallurgical and engineering principles applied to melting, casting and solidification. Testing and evaluation of castings. Foundry processes. Introduction to metallurgy of welding.Materials and process selection, codes and specifications, weldment design and testing.Welding defects. Analysis of industrial welding processes ME 411 Plastics and Plastics Processing (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite:ME 306 Thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers, their properties and engineering applications. Plastic manufacturing processes, equipment and mold design. Plastic materials and process selection. ME 412 Fundamentals of Heat Treatment (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 206, ME315 Principles of phase, transformations, heat treatment. Mechanical properties as applied to ferrous and non-ferrous metals and alloys. Heat treatment processes, including normalizing, hardening, tempering, annealing, surface hardening. Applications of heat treatment and surface hardening techniques ME 413: System Dynamics and Control (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 201, MATH 202 Dynamics of mechanical, fluid, electrical and thermal systems. Equations of motion. Dynamic response of elementary systems. Transfer functions and pole-zero diagrams. Simulation of dynamics of complex systems. Dynamic stability of systems. Open and closed-loop systems. Basic control actions. Laboratory sessions involving use of computers for simulation of dynamic systems and analysis of control systems. ME 414 Corrosion Engineering I (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 215, EE 306 Corrosion is concerned with the degradation and failure over time of all engineering materials due to their exposure to various environments such as seawater, atmosphere and chemicals. Apart from the high cost of repair, the corroded structures may also endanger people’s safety and result in loss of life. This course will expose prospective materials engineers on the importance of understanding the principles and mechanisms of corrosion and methods to control corrosion. ME 416 Mechanical Vibrations (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 201, ME 309 Free and forced vibrations; Applications to systems with one-, two-, and multi-degree of freedom; Viscous, hysteretic, and Coulomb damping; Response to general periodic excitations; Transient vibration and the phase method; Principal and coupled coordinates; Dynamic vibration absorbers; Energy methods and Rayleigh’s principle; Laboratory sessions on vibration measuring instruments, vibration measurement techniques, and experiments to illustrate various vibration phenomena studied. ME 417 Optimization of Mechanical Systems (3-0-3): Prerequisites: ME 307 Formulation and simulation of mechanical engineering systems involving dynamics, kinematics, and machine design and thermo-fluid systems; The concept of optimization; Analytical and numerical methods such as unconstrained and constrained optimization, Lagrange multipliers, linear programming for optimum design of mechanical systems. Lab demonstration sessions involve formulation and solution of optimization problems using computers and existing software packages during the design process. ME 418 Quality Improvement in Manufacturing (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: STAT 319 Introduction to principles and philosophies of total quality management; Advance methods for process control, Six sigma approach to quality, Quality function deployment (QFD) and Taguchi approach to quality, and Parameter Optimization. ME 419 Computer Integrated Manufacturing (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 306 and ICS 103 High volume discrete parts production systems; CAD/CAM fundamentals; Numerical Control (NC) manufacturing systems. Part Programming; NC justification, advances in NC (CNC, DNC, adaptive control); Tooling for NC and CNC; Overview of group technology, flexible manufacturing systems (FMS), and robotics in manufacturing. Related laboratory experiments, CNC Programming, and projects will be done on CNC machines and associates CAD/CAM software available in ME Workshop. ME 420 Iron and Steel Making (Credits 3,0,3):Prerequisite: ME 215 Introduction to extractive metallurgy and iron ore dressing including the following topics: iron ores, mining, and ore dressing. Production of pig iron.The blast furnace.Production of steel. Bessemer process, basic oxygen process, open-hearth process, direct reduction process, and electric-furnace process. Continuous casting. ME 422 Thermal Desalination Systems(3-0-3): Prerequisite: ME 315, ME204 Seawater composition.The need for water desalination. Classification of desalination processes. Single effect evaporation.Thermal vapor compression systems.Multiple effect evaporation.Multistage flash distillation, once through MSF, Brine mixing and recirculation MSF. Reverse osmosis. Desalination using renewable energy sources. Economic analysis of desalination processes ME 423 Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 315, ME204 Simple and compound refrigeration cycle, Compressors capacity and dimensions, Actual cycle, Review of moist air, Psychrometric and air conditioning processes. Summer and winter air conditioning cycles, ventilation, classification of central air conditioning systems, cooling load calculation, air duct design, air fan power and selection. ME 425 Internal Combustion Engines (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 204 Types of engines and their operation; Four and two stroke engines; Thermodynamics of engine cycles; Engine design and performance parameters; Operating characteristics of spark and compression ignition engines; Thermochemistry in-cylinder combustion and combustion abnormalities; Analysis of fuel-air cycles; Analysis of intake, fuel and exhaust systems; Turbocharging and supercharging; Performance characteristics of actual engines. ME 426 Renewable Energy (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 204 Reserves of non-renewable fuels; Prospects of renewable energy, and its sources and pattern of usage; characteristics of renewable sources: intermittent, low power density etc.; use of renewables in small scale systems. Current technology: wind wave, tidal, passive and active solar, biological and examples of devices; Energy management, interaction of nontechnical requirements (social, economic, political, environment) in engineering design and innovation; case-study. ME 427 Turbo machinery (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 204, ME 311 Thermo-fluid dynamics aspects of fluid flow, kinematic relations and efficiencies of turbomachines. Two dimensional cascades; Turbine and Compressor cascade correlations and performance. Axial Turbines (two dimensional analysis), Axial Flow Compressors and Fans (two dimensional analysis), Centrifugal Compressors and Fans, Radial Flow Turbines, and preliminary design fundamentals of turbomachines and three dimensional considerations. ME 428 Fluid Power Systems (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 311 Study of fluid power systems as used in industrial applications to transmit power by the flow of hydraulic fluids. Fluid power circuit diagrams including components such as valves, pumps, motors, filters, reservoirs and accumulators. Analysis of fluid leakage, hydrostatic transmissions, hydraulic stiffness, and performance of positive displacement pumps and motors. ME 429 Fundamentals of Aerodynamics (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 311 Inviscid incompressible flow to include potential function, stream function, circulation and basic flows; KuttaJoukowski theorem.Aerofoil theory and wing theory. Drag, aircraft propulsion and propeller; Static performance problem; Special performance problem; Introduction to stability and control, Longitudinal stability and control; Lateral and directional stability and control. ME 430 Energy Conversion (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 204, ME 315 Introduces basic background, terminology, and fundamentals of energy conversion.Discusses current and emerging technologies for production of thermal, mechanical, and electrical energy. Topics include fossil and nuclear fuels, solar energy, wind energy, fuel cells, and energy storage. Thermodynamic power cycles for power production: Rankine and Brayton; internal combustion power cycles. Introduction to exergy. ME 431 Design and Rating of Heat Exchangers (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 315 Heat transfer mechanism leading to basic heat exchanger equations; classification and analyses of heat exchangers including geometry; heat transfer and flow friction characteristics; compact and shell and tube heat exchanger application and design procedures; fouling and its effect on life cycle analysis; maintenance methodology; flow induced vibration and noise in heat exchangers. ME 435 Thermal Power Plants (Credits 3,0,3): Prerequisite: ME 204, ME 315 Forms of energy, oil, gas and coal. Combustion processes, energy cycles. Steam generators and their component design. Turbines. Load curves. Field trips to power plants and other energy installations.