m - Deans Community High School
advertisement
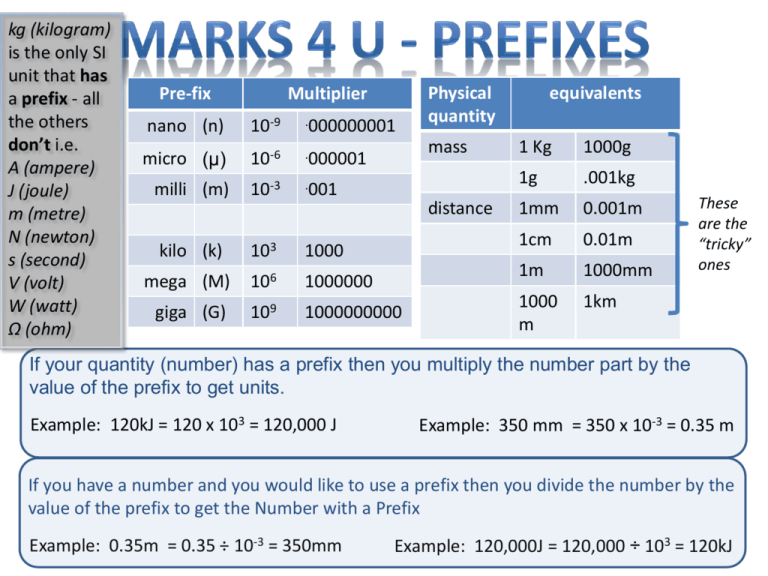
kg (kilogram) is the only SI unit that has a prefix - all the others don’t i.e. A (ampere) J (joule) m (metre) N (newton) s (second) V (volt) W (watt) Ω (ohm) Pre-fix Multiplier nano (n) 10-9 .000000001 micro (μ) 10-6 .000001 milli (m) 10-3 .001 kilo (k) 103 1000 mega (M) 106 1000000 giga (G) 109 1000000000 Physical quantity mass distance equivalents 1 Kg 1000g 1g .001kg 1mm 0.001m 1cm 0.01m 1m 1000mm 1000 m 1km These are the “tricky” ones If your quantity (number) has a prefix then you multiply the number part by the value of the prefix to get units. Example: 120kJ = 120 x 103 = 120,000 J Example: 350 mm = 350 x 10-3 = 0.35 m If you have a number and you would like to use a prefix then you divide the number by the value of the prefix to get the Number with a Prefix Example: 0.35m = 0.35 ÷ 10-3 = 350mm Example: 120,000J = 120,000 ÷ 103 = 120kJ Divide you page down the middle and label Before and After (collision). Draw a diagram! Write down your formulas Use “u” for velocity before and use “v” for velocity after collision Substitute values: Remember to look for stationary objects - their velocity is zero and that part of the equation goes away! Now let LHS (before) = RHS (after) Then solve for unknown value (i.e. what the question asked you to find) Note : the unit of momentum is kgm/s or kgms-1 Note : the formula for momentum is given as p=mv in the Data Booklet Draw diagram or sketch On LHS write Horizontal Constant Velocity s vt List known and unknown quantities Draw line down centre of page On RHS write Vertical Constant Acceleration v u a t Time (t) is common to both horizontal and vertical motion Constant Acceleration due to gravity Constant Velocity … (Newton’s 1st Law) Speed or Velocity (ms-1) constant speed acceleration deceleration constant speed deceleration Distance travelled = Area under graph time (s) NOTE: v > u gives acceleration; v < u gives deceleration or negative acceleration Before you begin. Remember that VS= V1 + V2 Now write down what you know and don’t know ! R1 V1 Vs R2 V2 Use this formula if you can’t use formula 1. Look for VS in the question. There are two formulas associated with Voltage Dividers Try to use formula 1 first. You need 3 of the 4 terms V1, V2, R1 or R2. (VS is not required) Again, remember that VS= V1 + V2 … you don’t need to use formula 2 twice! The question will indicate whether the temperature (Thermistor) or light (LDR) is increasing or decreasing. Use this information to start your answer e.g “As the light level falls the resistance of the LDR increases …” Explain the Science of the LDR (L.U.R.D.) or Thermistor (T.U.R.D.) The LDR or Thermistor may be placed here – you need to think how this affects step 2 This could be any output device, e.g. relay, bell, buzzer etc. LDR1 Vs R2 V2 Explain How the Transistor works:Switches ON at the threshold voltage 0.7 V for npn transistor 1.0 – 2.0 volts for MOSFET Copy this from the Physics data booklet Cross multiply to simplify then solve for the unknown term.. Read the question carefully and select two of the three terms (ratios) shown in the formula – you should end up with a simpler relationship containing two terms (ratios). Transformers are not 100% efficient due to • Heat loss • Magnetising currents • Sound (vibrations) Temperature(T) Gas Cooling Curve Liquid Solid time(t) When material is cooling it gives off heat energy When its temperature is increasing the material is absorbing heat energy LED numerical questions are usually worth three marks. The question usually gives the operational or working voltage of the LED … and the operational or operating current of the LED. Then it asks you to calculate R R Vs This is where you get the extra mark The current through R is the same as the operating current of the LED Remember to include unit Ω If the question asks you to find a “half life” or “how long a sample takes to decay” or “the initial or final level of Activity” then it’s a good bet that you need a ………….. Fill in the initial Activity Divide previous Activity by 2 Divide previous Activity by 2 Until you reach your Final Activity Activity (units) Time (units) Initial time = 0 0 Add one ½ Life to previous time Add one ½ Life to previous time Until your reach your Final time You will get the Units from the question To find the number of half lives – count the number of entries you have Made in the time row, but don’t count the first one (the zero value). To find the Half Life divide the final time by the number of half lives ½ mark Initially Vc = Logic 0 (0V) R1 Not gates inverts Logic to Logic 1 (5v) This is applied to top of R1 Capacitor charge up to Logic 1 (5v) ½ mark Not gates inverts Logic to Logic 0 (0v) This is applied to top of R1 Capacitor discharges to Logic 0 (0v) ½ mark The process repeats ½ mark Logic 0 = 0V Logic 1 = 5V Timing/ Frequency determined by R1 and C




