Unit 1: Medicinal Plants - askmrspierce
advertisement

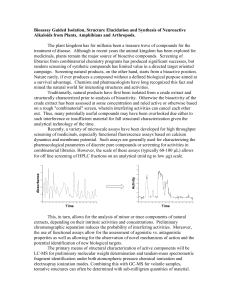
Unit 1: Medicinal Plants 9 days Read on your own: Introduction to Pharmacology Course Goals • Help scholars obtain an understanding of how drugs and medicines are – Found – Isolated – Produced – Abused • Help scholars understand different classes of drugs and how they work in the body Course Structure • • • • Unit 1 – Medicinal Plants Unit 2 – Psychopharmacology Unit 3 – Depressants and Stimulants Unit 4 – Drugs that relieve Pain • 11 Lab Activities and/or Case Studies • 3 Research Projects Classroom Policies • School rules apply • Respect the space, manager, and your peers • All deadlines are final – work should be submitted electronically if the scholar is not present Test Format • 30 multiple choice questions • Choice of 6 free response questions Pharmacology Reference Book • No textbook available • Lecture materials were primarily pulled from the following textbooks – A Primer of Drug Action 9th edition: Julien – Economic Botany 3rd edition: Simpson and Ogorzaly Website, Notes, Projects • All notes, lectures, and activities are available on the class website • askmrspierce.pbworks.com January 6th: Medicine throughout History History of Medicine • 75% of world’s population still depends on traditional herbal medicine • 10% of major medical drugs in the U.S. have a primary ingredient extracted from plants today • 25% of common medicines contain some compounds from plants History of Medicine • Fungi are the source of penicillin (discovered 1941) • Many plant compounds have provided blue prints for synthetic drugs History of Medicine • Early drugs were found by trial and error • Passed by word of mouth History of Medicine • Sumerian drawings of opium poppy (2500 B.C.) History of Medicine • Code of Hammurabi (1770 B.C.) • Tablets carved under the direction of the King of Babylon • Mention many plant medicines History of Medicine • Egyptians recorded knowledge of illness and cures on temple walls • Also on the Ebers papyrus (1550 B.C.) • Contains over 700 medicinal recipes • Include – cannabis, aloe, castor, mandrake, and several gum and resin producing shrubs • Mandrake was used as an anesthetic (contains atropine and scopolamine) History of Medicine • Golden Age of Greece had many major advancements in the field of pharmacology • Hippocrates (460 – 377 B.C.) • Father of Medicine • Illness caused by bodily problems, not evil spirits • Discussed between 300 and 400 species of plants that provided medicinal drugs History of Medicine • Aristotle – compiled a list of medicinal plants • Theophrastus – Father of Botany – Provided first account of opium poppy and its effects • Dioscorides – 5 volume work titled De Materia medica – Described preparation of 1000 simple drugs History of Medicine • Middle Ages saw little advancement • Not much academic interest in Europe • Monks used early Greek writings to produce herbals • Printing press in 1439 made herbals more wide spread Renaissance • Study of human anatomy renewed • Surgical procedures were improved • Paracelsus (1493 – 1541) – – – – Publicly burned Greek works Said God put plants on Earth to be used by humans Said plants had signs of what they were useful for Doctrine of Signatures • Red sap = treatment for blood disorder • Brain-like convolutions of walnut = good for brain 17th and 18th Centuries • Edward Jenner – Vaccination in 1796 • William Withering – Foxglove extracts as remedies for heart problems in 1775 19th Century • Progress was made in surgical procedures • Joseph Lister – Promoted the use of chemicals to prevent infection 20th Century • ‘miracle’ drugs produced • Morphine, quinine, ephedrine • Chemists began task of determining the structures of these compounds • Determined how to synthesize them Natural Medicines • Less studied in the U.S. than elsewhere over the last 50 years • Old fashioned or folkloric • Biochemistry can synthetically make compounds Plant Biodiversity • Only 1 in 10,000 randomly screened plants make it to market • National Cancer Institute is expanding its testing program for natural products • Currently has teams in all major rainforest areas of the world • In many parts of the world illness is treated holistically • Illness is viewed as an imbalance January 7th: Chemistry of Plant Derived Medicines Chemistry of Plant Medicines • • • • Two major classes Alkaloids Steroids Often the medicinally active compound occurs with one or more sugar molecules attached • Called glycosides Steroids • Four carbon rings = backbone • Addition of diverse chemical groups at different places on the backbone leads to diversity of compounds • Adding sugar = steroidal glycosides Steroids • Occur in several groups of angiosperms • Secondary products (no direct physiological function) • Often have pronounced effect on animals (especially vertebrates) • Herbivory deterrent Milkweed and Monarchs • • • • • Asclepias is toxic to humans Contains abundant steroidal glycosides Eaten by monarch caterpillars Store compound in their body Butterflies are toxic to vertebrate predators (birds) Alkaloids • • • • • Diverse group Multi-cyclic chemicals Contain nitrogen Usually exhibit alkaline reaction Occasionally enter into primary metabolism of plants, so may not be a secondary product Alkaloids • Many are extremely poisonous to humans – Locoweed – Nightshade – Hemlock – Nicotine • Can alleviate physiological problems when ingested in small quantities • Important to standardize safe dose January 8th: Plants that were formerly important to medicine Human Diseases • Leprosy – Disfiguring • Painful death • Malaria – Killed more people throughout recorded history than all other diseases and wars combined • First drugs used to treat these diseases came from plants Leprosy • • • • • Leprosy was long considered to be incurable Leper colonies Caused by bacterium Similar to tuberculosis The Vedas mentioned over 2000 years ago an oil (chaulmoogra) that helped in curing leprosy • Europeans did not pay serious attention Leprosy • Source of chaulmoogra oil was unknown to western medicine • Joseph Rock led expedition to find the species of plant that produced the chaulmoogra fruit in the 1920’s • Found trees in India that produced chaulmoogra, and sent seeds to Hawaii where cultivation began Leprosy • Chaulmoogra was only successful treatment until sulfa drugs were produced in 1946 Malaria • Bronze Age Greek skulls show evidence of malaria • Well documented throughout history • During WWI more people died from malaria than from enemy fire • In 1999, CDC estimated that 310-500 million people were infected with malaria worldwide • ~1 million people died in 1999 (primarily kids) Malaria • • • • Believed to be transmitted through the air Root of name Actually transmitted by a mosquito vector Infectious agent is a protozoa called Plasmodium • Fever, chills, anemia, and spleen enlargement Malaria • In the middle of the 17th century Jesuits in South America found that local people had a remedy • Steeped bark of Cinchona trees in water • Indian name for this drink was ‘quina’ • Protestants believed that the Jesuits were trying to poison them, and would not try the drug Malaria • Oliver Cromwell died of malaria rather than take the “Jesuits’ powder” • Cinchona was not universally accepted until 1681 • Quinine (the active ingredient) was not isolated until 1820 Malaria • The Dutch finally established productive plantation in Java of a particularly potent species • Gave them a monopoly on the world supply of quinine • During WWII the U.S. and Europe were cut off from supplies • U.S. sent expeditions to Bolivia Malaria • One of these expeditions was successful • Quinine was successfully synthesized in 1944 • This reduced the need for natural quinine • Some Plasmodium strains are becoming resistant to synthetic compounds • Renewed interest in natural compounds Malaria • Original basis for drinking gin and tonic in the evenings • British originated the drink because the bitter component of tonic water in quinine • Served as a prophylactic dose Malaria • New antimalarial compound has been recently found in Artemisia annua (Asteraceae) • A wormwood related to the plant used to make absinthe • Has been used in China since 168 B.C. Ephedrine • Originally made by soaking the dried stems of ma-huang, Ephedra sinica (a gymnosperm) • Prescribed in China for centuries as a stimulant, and treatment for high blood pressure, asthma, and hay fever Ephedrine • After 1920 western medicine accepted Ephedra as a decongestant • Bronchodilator • Similar structure to adrenaline • Initially caused the death of many children from cardiac arrest White Willow • Salix alba (Salicaceae) • Soaked leaves of this plant were often placed on body parts to relieve aches • Salicin (the active ingredient) was isolated in 1827 • Salicin and salicylic acid are stomach irritants • Acetylsalicylic acid, produced in Germany in 1898, can be ingested easily White Willow • This compound, called Aspirin, is the most widely used medicine in the world • New physiological actions are being discovered and described even today Cocaine • Not often thought of as a medicine • Has historically been used as a calmative and local anesthetic • Coca, Erythroxylum coca, is native to the Andes • Indians have chewed the leaves for thousands of years Cocaine • Reduces feelings of hunger, pain, and fatigue • First used as a medicine in 1884 when one of Freud’s assistants found that a cocaine solution numbed his tongue • Used as local anesthetic in eye surgery and dentistry • Cocaine has never been synthesized • Lidocaine and procaine (Novocain) have January 12th: Plants that are important in medicine today Steroids • Many animal hormones are steroids • To produce hormones for therapy can be expensive and labor intensive • Between 1936 and 1940 it was discovered that certain yam plants had steroids called saponins • These looked almost identical to human sex hormones, with only 1 additional ring added Saponins • These tubers can be collected and used to produce large amounts of saponins • Then microorganisms are added that cleave off side groups and add others • This produces synthetic hormones at a relatively inexpensive price Saponins • Most of these hormones are used in birth control pills and fertility drugs Digitalis • 2 of every 5 American dies from heart related illness • Dropsy used to be a disease caused by retention of fluid in the tissues, likely cause by congestive heart failure • William Withering is credited with finding purple foxglove (Digitalis purpurea) compounds that cured this type of disease. Digitalis • The two active compounds were isolated in 1928 • They are still used in heart treatment today Alkaloids • Pain is a necessary warning • Drugs that numb pain, without causing unconsciousness, are called analgesics • One of the oldest and best sources of analgesics is the opium poppy Opium • Fossilized poppy capsules have been found in prehistoric settlements around the Mediterranean • Representations of the poppy appear in ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman artwork • Used as a calming agent for at least 2600 years Opium • Most opium production is in Nepal, India, Laos, and Cambodia • Only about 4% of the crop is harvested for legitimate medical uses • Cultivation is illegal in most countries (including ours) • High amounts of opium are currently being grown in Afghanistan Opium • Harvested by slashing capsule and collecting the latex • Used to be used in powdered form • Now subjected to chromatography to separate the chemical components • Over 26 different alkaloids have been seperated from the opium poppy • Only 3 are commonly used in medicine – Morphine, Codeine, Papaverine Morphine • • • • Most abundant in the opium poppy VERY addictive Most potent painkiller Very helpful during early times when no anesthetic was available for surgery • Often given during labor and delivery during the 1930’s and 1940’s Codeine and Papaverine • Less habit forming • Often over the counter • Used for the treatment of internal spasms • Traditionally used for treatment of diarrhea • Also used for cramping January 13th: Tropane alkaloids and Balladonna Tropane Alkaloids • First isolated from Atropa belladonna • Atropine, scopolamine, and hyoscyamine • All have similar complex nitrogen ring structure • Nightshade has been used since the time of the Ancient Greeks • Named for Atropos (one of the fates who cut the thread of life) Tropane Alkaloids • Belladonna is the common name which was derived from the medieval practice of putting drops into the eyes • This dilated the pupil, and made women look charming Tropane Alkaloids • Soothe the smooth muscle system and relieve cramping • Also has some cardiac physiological effect • Dilate pupils • Relieve pain and infection in the urinary tract Hellebore • Not all alkaloids come from the potato family • A lily species indigenous to North America • Have two compounds used to decrease blood pressure • Used by Native Americans • Adopted by Europeans January 14th: Cinchona, Rauwolfia, Snakeroot, and Cancer Drugs Cinchona • • • • • Known primarily as a source of quinine Produces about 30 other alkaloids Quinidine Useful in treating heart disease Helps regulate irregular rhythyms Rauwolfa • Mentioned in the Vedas of India • Noted that snakeroot was used to treat hypertension • Indian people have chewed on snakeroot for centuries for its calming effect • Can also be used to treat mental illness Rauwolfia • Most important chemical obtained from snakeroot is reserpine • Replaced electric shock and injections of insulin as a replacement for schizophrenia treatment • Also helpful for its calming effects in other mental disorders • Mostly obtains from crops in India, Pakistan, and Java Cancer Drugs • Many have proved to be plant alkaloids • Work by interfering with cell mitotic division Common Periwinkle • Used in its native region for centuries to treat diabetes • In 1957 was found to be effective in treating and curing some forms of childhood leukemia Mayapple • Found in forests of Canada and the Eastern United States • Used by native Americans to treat skin disorders, tumorous growths, and as a purgative • Used today to treat testicular, lung, and breast cancers Autumn Crocus • Mainly used to alleviate pain from gout • Also interferes with mitotic cell division Pacific Yew • Yews are commonly know as ‘trees of death’ • Genus name Taxus is derived from the Greek word for toxin • Used to treat ovarian cancer • Not cost effective to synthesize, but Taxol, a multicyclical alcohol, can be extracted from yew bark • Trees were being lost to deforestation • Became #1 selling cancer drug in 2000, sales over $3 billion January 15th: Other Plants of Medicinal Use Plantain • 2 species have psyllium in their seed husks • A colloid mucilage used for intestinal problems • Ground powder pulls water out of the intestinal tract which forms a smooth, bulky mass that is unaffected by bacteria • Relieves irritations caused by diarrhea and constipation Aloe • A member of the liliaceae • Soothing gels • Used for skin conditions Ipecac Syrup • Used in many households to induce vomiting • Member of the coffee family • Used in poison control kits Chymopapain • From papayas • Sister enzyme to papain (meat tenderizer) • Injected into slipped disks, dissolves disk and alleviates pressure • Prevents surgery January 20th: Dietary Supplements Herbal Medicine • Use of herbs to treat illness, fatigue, and depression has increased dramatically in the last 40 years • Several contributing factors: • Prescription drugs are expensive • Aura of being more natural and less invasive • Don’t need a physician to purchase Regulation • Cons: – Increase expense – Deprive some people of medicine – Claim they are already safe – Claim they are already extensively used • Pros: – Differ widely in content – Contain contradicting compounds Herbiogenic Death • Serious complications, underscore the major concern with consuming unregulated bioactive compounds • Several deaths have occurred from ephedra being used as a diet Interactions • St. John’s Wort reduces the efficacy of birth control pills Germany • Has regulation of all bioactive compounds that has been shown to be very effective • Makes herbal use safe for public • Still available and inexpensive China • Herbal medicines have been used for thousands of years • Chinese scientists are currently attempting to isolate and test these compounds • Looking to folk medicine for new cures U.S.A. • Private and governmental agencies are conducting screening process for new drugs • Conservation concerns