Computer Networks
advertisement

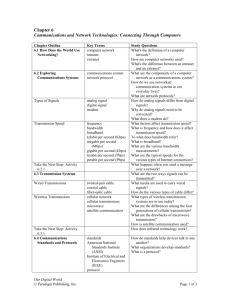
In information technology, a network is a series of points or nodes interconnected by communication paths. In a network, a node is a connection point. In general, a node has programmed or engineered capability to recognize and process or forward transmissions to other nodes. A network is an interconnected system of things or people ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Religions Business contacts Snail Mail Social Media Broadcasting - NBC, CBS, ABC, PBS Transportation (highways & rail) Cellular phone service …and of course computer based (internet) The Internet is a worldwide system of computer networks - a network of networks in which users at any one computer can, if they have permission, get information from any other computer. Intranet ◦ An organizations restricted computer network ◦ Private, yet using WWW software Extranet ◦ Part of a organization‘s intranet that is extended to users outside the organization – usually via WWW. ◦ Customer access Internet ◦ A worldwide computer network using TCP/IP protocol to transmit and exchange data. (TCP/IP is a set of communication protocols used by networks.) Simultaneous Access ◦ Software/Programs ◦ Data Device Sharing ◦ Printers ◦ NAS – Network Access Storage Communication ◦ Email ◦ VOIP – Voice over internet protocol (Skype) Archiving ◦ Backups of multiple clients by a single server In communication networks, a topology is a usually schematic description of the arrangement of a network, including its nodes and connecting lines. There are two ways of defining network geometry: the physical topology and the logical (or signal) topology. Topologies ◦ Physical connectivity Nodes and Addressing Geographical Distribution ◦ Where are the nodes? Work Load ◦ Server networks use the nodes to disperse the workload Network topology is the physical interconnections of the elements (Links, Nodes, Clients, etc.) of a computer network Main Types ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Star Bus Ring Wireless Hybrid Star topology is the most common topology used in today’s workplace. North Greenville University in Tigerville uses star topology. Bus topology is where in a computer network, a bus is a transmission path on which signals are dropped off or picked up at every device attached to the line. WAP (wireless access points) are not necessary needed. A ring is a network topology or circuit arrangement in which each device is attached along the same signal path to two other devices, forming a path in the shape of a ring. A wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider (ISP) that allows subscribers to connect to a server at designated hot spots (access points) using a wireless connection such as Wi-Fi. Standards – IEEE 802.11 ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n 802.11n has a higher frequency and transmits fastest and the longest range Coax cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies between the community antenna and user homes and businesses. ◦ Benefit is one wire for all computers Ethernet is the most widely-installed local area network (LAN) technology. ◦ One wire per node/client Ethernet twisted pair cable is faster than Wireless and is very commonly used in businesses Fiber optic (or "optical fiber") refers to the medium and the technology associated with the transmission of information as light impulses along a glass or plastic wire or fiber. Types ◦ WIMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) ◦ Satellite (Dish Network/Direct TV) High transmission rate (has to be) & latency Each node needs antenna to connect ◦ Low frequency – reliable but slower transmission ◦ High frequency – less reliable but higher speed transmission Fiber is the fastest - pricey Ethernet twisted pair – cheaper and faster COAX – still needed Wireless – price greater than Ethernet twisted pair Node – Client ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Printers Desktops Laptops Copiers Network storage devices Routers Anything that can connect to a network Cell phone GPS device IPOD/PSP/XBOX/PS3/Tivo/DVR/Slingbox… How does the network identify a node? ◦ NIC MAC address – every node’s is unique Format: 01-23-45-67-89-ab, 01:23:45:67:89:ab Each vendor has a pool of addresses Linksys D-Link Etc. Hardware address Translated into a software address (IP address) Two standards for Internet Protocol (IP) IP V4 IP V6 IP Addresses ◦ IP addresses are four octets of the form and range (0-255).(0-255).(0-255).(0-255) ◦ Data is routed between nodes based on IP addresses ◦ Each domain name translates to a unique IP address www.google.com translates to 208.67.217.231 i.e. try Ping www.google.com from DOS prompt ICANN.org is in charge of DNS Maintains Internic.org to provide info about domain names ◦ A profound shortage of addresses with IP V4 4.3 billion addresses with some reserved Usefulness of static addresses How many nodes in the world? IP Addresses ◦ Addresses structure:(8 groups of 4 base16 digits) 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 ◦ Version 6 provides enough addresses for every atom in the universe - provided they buy a computer ◦ Supports 2128 (about 3.4×1038) addresses. ◦ Currently used at main WWW routing points ◦ Advantages of having your own address? Your are known wherever your node physically resides LAN – Local Area Network ◦ Ex. – NGU VLAN – Virtual LAN (act as a LAN due to common set of needs - collaboration) MAN – Metropolitan Area Network ◦ Ex. - City of Greenville WAN – Wide Area Network ◦ Ex. – Internet Server Based ◦ Thin client - relies heavily on server processing ◦ Ex. – NGU email server Client Server Based ◦ Fat client – shares in the work load with less expensive server ◦ Ex. – NGU CAMS (clients process the reports) Peer to Peer Based ◦ Each computer can act as client or server ◦ Ex. - Home network All networks ◦ Authentication User name and password ◦ Encryption https – encrypts credit card account #s, email ◦ Firewall Software What can network users get to on your machine ◦ Anti-virus Software Protect against malware Vendors – McAfee, Symantec, AVG, etc… ◦ Finger Print Scanner ◦ Contingency planning – what if the unexpected happens Backups, backups, backups Wireless ◦ WEP – Wired Equivalency Protocol NOT secure (Google “breaking wep encryption”) ◦ WPA – Wireless Protected Access WPA & WPA2 – secure provided you use good pass phrases What do we transmit/exchange? ◦ Text Emails Print jobs Chat ◦ Graphics Pictures ◦ Video Movies Live Streaming ◦ Audio Songs Voice How is it transmitted? ◦ Broken into packets Header – Packet 1 Trailer – Last Packet Those in between ◦ Not all packets take the same route ◦ Reassembled on receipt to match that sent Who owns the internet? ◦ Many companies – Sprint, Verizon, Time-Warner, etc. We’re just renting space ◦ Transmission is not perfect Must have schemes for re-sending dropped packets What about audio & video – is there any reason to resend? What about your debit card atm transmission Easier to resend the whole thing or just what’s missing? TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol ◦ Standard network data exchange protocol(standard) ◦ TCP applications FTP – File transfer protocol (transfer files) Telnet – Terminal connections SMTP – email transmission POP3 – email transmission ◦ IP applications HTTP – Hypertext transfer protocol VOIP – Voice over IP ISP – Internet service provider ◦ Types of connection for the home Cable Modem DSL Modem ISDN Modem 56K Dial-up Modem Home satellite Cable Modem – higher capacity than home DSL Modem – “ “ “ DS1/T1 High speed line (DS3 /T3 even better) Satellite ◦ Types of connection for business ◦ Businesses concerned with throughput ◦ Become a node on ISP’s network Domains ◦ Common .com, .net, .org, .edu, .gov ◦ Not so common .uk, .us, .tv, .biz, info (checkout godaddy.com) Sub Domains ◦ Part of the larger domain ◦ Ex. www.ngu.blackboard.com Domain is www.blackboard.com Sub domain is ngu Accessed via ngu.blackboard.com Websites are designed using html (hypertext markup language) ◦ Easy enough for anyone to create Write html Use applications like Dreamweaver or Microsoft Expression Can save MS Office 2007 files as web pages ◦ Store cookies Ease of use User names Passwords (not so good if not secure – https) ◦ Store temporary files Faster browsing Fills up hard drive Fragmentation ◦ Your browser will let you purge cookies and files. Data specific Websites are encoded using XML (Extensible Markup Language) Example – see notes Standard for data exchange ◦ MS Access can import XML Microsoft Office 2007 file naming ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Word “Document.docx” Excel “Spreadsheet.xlsx” PowerPoint “Presentation.pptx” Access – “Database.accdb” ????? http://wordnetweb.princeton.edu http://compnetworking.about.com http://en.wikipedia.org/ http://www.emailclients.net/