Data - Adypato
advertisement

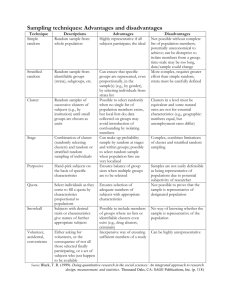
Data Why Collect Data? Obtain input to a research study (Memperoleh suatu masukan tentang penelitian) Measure performance (mendapatkan performance) Assist in formulating decision alternatives (Membantu merumuskan alternatif keputusan) Satisfy curiosity (Menjawab tentang keraguan) Knowledge for the sake of knowledge (mendapatkan suatu pengetahuan yang baru) Data Types Data Numerical Categorical (Quantitative) (Qualitative) Discrete Continuous Data Type Examples Numerical Discrete To how many magazines do you subscribe currently? ___ (Number) Continuous How tall are you? ___ (Inches) Categorical Do you own savings bonds? __ Yes __ No How Are Data Measured? (Pengukuran data) Nominal scale Categories e.g., Male-female Count Ordinal scale Categories Ordering implied e.g., High-low Count Skala nominal hanya bisa membedakan sesuatu yang bersifat kualitatif (misalnya: jenis kelamin, agama, warna kulit). Skala ordinal selain membedakan juga menunjukkan tingkatan (misalnya: pendidikan, tingkat kepuasan). How Are Data Measured? Interval scale Equal intervals No true 0 e.g., Degrees Celsius Measurement Ratio scale Equal intervals True 0 Meaningful ratios e.g., Height in inches Skala interval berupa angka kuantitatif namun tidak memiliki nilai nol mutlak (misalnya: tahun, suhu dalam Celcius). Sedangkan skala rasio berupa angka kuantitatif yang memiliki nilai nol mutlak Data Sources Data Sources Data Sources Data Sources Data Sources Primary Data Sources Data Sources Primary Secondary Data Sources Data Sources Primary Experiment Secondary Data Sources Data Sources Primary Experiment Survey Secondary Data Sources Data Sources Primary Experiment Survey Secondary Observation Data Sources Data Sources Primary Experiment Survey Secondary Observation Published (& On-Line) Surveys Survey Steps Define purpose Design questionnaire Select sample design Sample type Sample size Survey Steps Define purpose Design questionnaire Select sample design Sample type Sample size Collect data (field work) Prepare data Edit Code Analyze data Interpret findings Report results Questionnaire Design Question content Mode of response Question wording Question sequence Layout Pilot testing © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Samples Why Sample? Destruction of test units Quality control Accurate & reliable results Pragmatic reasons Time Cost Types of Samples Types of Samples Type of Sample Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Judgment Probability Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Judgment Quota Probability Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Judgment Quota Probability Chunk Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Simple Random Sample Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Simple Random Sample Each population element has an equal chance of being selected Selecting 1 subject does not affect selecting others May use random number table, lottery, ‘fish bowl’ © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Random Number Table Column Row 00000 12345 00001 67890 11111 12345 11111 67890 01 49280 88924 35779 00283 02 61870 41657 07468 08612 03 43898 65923 25078 86129 Systematic Sample Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Systematic Sample Every kth element Is selected after a random start within the first k elements Skip interval, k, is Population size Sample size Used in telephone surveys © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Stratified Sample Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Stratified Sample Divide population into subgroups Mutually exclusive Exhaustive At least 1 common characteristic of interest All Students Commuter s Residents Select simple random samples from subgroups Sample Cluster Sample Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Cluster Sample Divide population into clusters If managers are elements then companies are clusters Select clusters randomly Survey all or a random sample of elements in cluster Companies (Clusters) Sample Nonprobability Samples Types of Samples Type of Sample Non Probability Probability Simple Random Judgment Quota Chunk Systematic Stratified Cluster Nonprobability Samples Judgment Use experience to select sample Example: Test markets Quota Similar to stratified sampling except no random sampling Chunk (convenience) Use elements most available Errors Due to Sampling Errors Due to Sampling Total Population (Students) Errors Due to Sampling Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Errors Due to Sampling Coverage (Frame) Error Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Errors Due to Sampling Coverage (Frame) Error Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Planned Sample (Selected Students) Errors Due to Sampling Coverage (Frame) Error Sampling Error Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Planned Sample (Selected Students) Errors Due to Sampling Coverage (Frame) Error Sampling Error Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Planned Sample (Selected Students) Actual Sample Errors Due to Sampling Coverage (Frame) Error Sampling Error Nonresponse & Measurement Error Total Population (Students) Sample Frame (Students in Phone Book) Planned Sample (Selected Students) Actual Sample Conclusion Defined statistics Distinguished descriptive & inferential statistics Summarized the sources of data Described the types of data & scales Explained the types of samples Described survey process & errors This Class... Please take a moment to answer the following questions in writing: What was the most important thing you learned in class today? What do you still have questions about? How can today’s class be improved? End of Chapter Any blank slides that follow are blank intentionally.