Muscle contraction and joint movement
advertisement

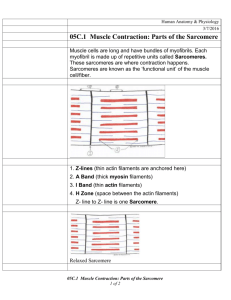
Muscle contraction and joint movement The three types of muscle tissue are: voluntary, involuntary, resting epimysium, perimysium, endomysium skeletal, cardiac, smooth elastic, collagen, fibrous Skeletal muscles are often called voluntary muscles because: they contract when stimulated by motor neurons of the central nervous system ATP activates skeletal muscles for contraction the skeletal muscles contain myoneural junctions connective tissue harnesses generated forces voluntarily The thin filaments consist of: a pair of protein strands wound together to form chains of myosin molecules a helical array of actin molecules a helical array of myosin molecules a pair of protein strands together to form chains of actin molecules The thick filaments consist of: a helical array of myosin molecules a helical array of actin molecules a pair of protein strands wound together to form chains of actin molecules a pair of protein strands wound together to form chains of myosin molecules All of the muscle fibers controlled by a single motor neuron constitute a: sarcomere motor unit crossbridge myoneural junction The sliding filament theory explains that the physical change that takes place during contraction is that: the thick filaments are sliding toward the center of the sarcomere alongside the thin filaments the thin filaments are sliding toward the center of the sarcomere alongside the thick filaments the Z lines are sliding toward the H zone the thick and thin filaments are sliding toward the center of the sarcomere together Troponin and tropomyosin are two proteins that can prevent the contractile process by: inactivating the myosin to prevent cross-bridging causing the release of calcium from the sacs of the sarcoplasmic reticulum covering the active site and blocking the actin-myosin interaction combining with calcium to prevent active site binding The amount of tension produced by an individual muscle fiber ultimately depends on the: number of pivoting crossbridges number of contracting sarcomeres number of calcium ions released all-or-none principle Which type of muscle fiber would be dominant in a muscle like the gastrocnemius, a calf muscle that contracts during standing and walking? intermediate fibers slow fibers fast fibers white fibers Extensive blood vessels, mitochondria, and myoglobin are found in the greatest concentration in: type II fibers fast fibers slow fibers intermediate fibers Which of the following could cause muscle atrophy? wearing a cast on a broken limb a lack of regular stimulation of muscle fibers paralysis all of the above What type(s) of muscle tissue do(es) not contain sarcomeres? cardiac skeletal smooth all of the above The order of the sequential-cyclic reactions that occur at an active site during cross-bridging is: attach, pivot, detach, return attach, return, detach, pivot attach, return, pivot, detach attach, detach, pivot, return The area of the A band in the sarcomere consists of: M line, H band, zone of overlap thin filaments only Z line, H band, M line overlapping thick and thin filaments