Experiment 25:
advertisement

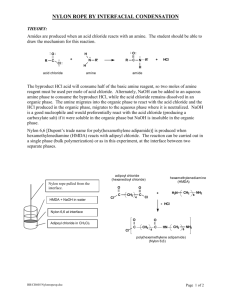
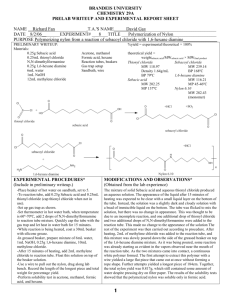
Experiment 25: ORGANIC POLYMERS: THE SYNTHESIS OF NYLON Objectives: To synthesize Nylon 6,10 from hexamethylene diamine and sebacoyl chloride. To determine the length of the Nylon formed using a simple mathematical calculation. SYNTHESIS OF AN AMIDE O H R + N H amine C R catalyst R H O N C R + H2O HO Carboxylic Acid amide Reacting a carboxylic acid with an amine yields an amide. Water is a by-product, and this reaction is slow without a catalyst. SYNTHESIS OF AN AMIDE O H R + N H amine C R R H O N C R + HCl Cl Acid chloride amide By using a carboxylic acid chloride, a more reactive carboxylic acid derivative, the rate of reaction can be increased. In this reaction, HCl is the by-product. MECHANISM O + C R Cl R' H O N C H R O + OH Cl N R' H C R Cl N R' H H O C R H N R' SYNTHESIS OF NYLON 6,10 H H N H O CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 N Hexamethylene diamine O C H Cl CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 C Sebacoyl chloride Cl In order to make a polyamide, such as Nylon 6,10, the amine molecule must have a –NH2 group at each end, and the acid chloride must have a –COCl group at each end. The diamine and the diacid chloride bond together, end-on-end, to form very long chains. Nylon 6,10 is made from hexamethylene diamine (the diamine) and sebacoyl chloride (the diacid chloride). SYNTHESIS OF NYLON 6,10 O H H N CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 N C + H H O CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 C Cl Cl Hexamethylene diamine Sebacoyl chloride O H N CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 H N C Nylon 6,10 = O CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 H N H (CH2)6 N n C H N CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 O O C (CH2)8 C n H N + HCl CLASSIFICATIONS OF SYNTHETIC POLYMERS Synthetic polymers are classified by their method of synthesis. Synthetic Method Chain-growth Step-growth polystyrene Polyamides (nylon) NATURAL ORGANIC POLYMERS Proteins Polysaccharides hair, skin, tissue cellulose, starch Polynucleotides DNA, RNA SYNTHETIC ORGANIC POLYMERS Nylons Polyesters Acrylics Polyvinyls Plastic sheeting and plumbing materials Polystyrenes Insulating materials EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis) Pour diamine solution and diacid chloride in separate beakers. Using forceps, grasp the film that forms at the interface of the two liquids. Pull up slowly and wrap end of nylon string around a test tube. Rotate the tube and count the number of revolutions made before no more nylon can be produced. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Analysis) Calculate the length of the nylon string produced (in meters) using the following equation: Nylon produced (m) = (test tube diameter (m)) X (p) X (# test tube revolutions ) Table 25.1 Test tube diameter (mm) # of test tube revolutions Length of nylon (m) SAFETY CONCERNS CAUTION: All chemicals are hazardous to the skin and eyes. Safety goggles and gloves are required during the experiment!!! WASTE MANAGEMENT Pour all waste from synthesis and solubility tests into container labeled “ORGANIC WASTE (Polymers)” CLEANING Clean all glassware with soap, water, brush, and rinse with wash acetone before returning to lab drawer! DO NOT return any glassware to lab drawer dirty or wet!