2.2A Trig Ratios (Defind in terms of x,y,r)
advertisement

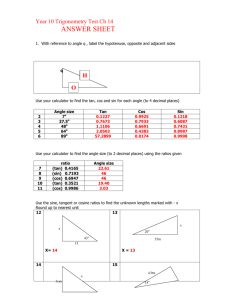
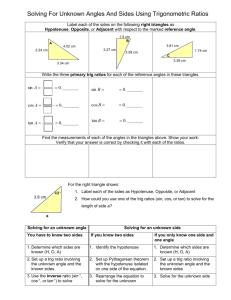
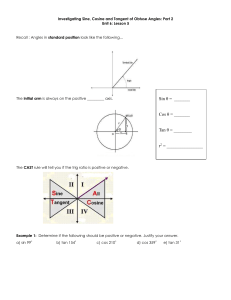
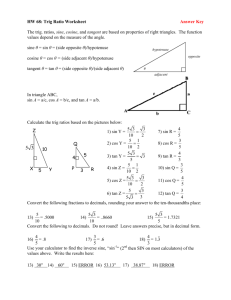
Math 20-1 Chapter 2 Trigonometry 2.2 A Trig Ratios of Any Angle Teacher Notes Math 20-1 Chapter 1 Sequences and Series 2.2A Trig Ratios of Any Angle (x, y, r) Label the two special Triangles 300 2 3 1 2 450 450 600 1 1 2.2.1 Finding the Trig Ratios of an Angle in Standard Position Suppose angle is an angle in standard position. Choose a point (x, y) on the terminal arm, at a distance r from the origin. r P(x, y) y sin r y x cos r x r2 x2 y2 = + r = √x2 + y2 y tan x What is the relationship between x, y, and r? 2.2.2 Finding the Trig Ratios of an Angle in Standard Position Suppose angle is an angle in standard position. How are the ratios affected if we choose the point (-x, y) on the terminal arm? y sin r P(-x, y) r y Ref -x x cos r y tan x r2 = (-x)2 + y2 The horizontal and vertical lengths are considered as directed distances. 2.2.3 How can you tell if the ratios will be positive or negative? ( -, + ) y r cos All Tangent Cosine ( +, + ) ( -, - ) sin Sine ( +, - ) x r tan y x 2.2.4 Finding Trigonometric Ratios of Angles in Standard Position y sin r cos y sin r x r y tan x Sine is positive. cos x r y tan x All are positive. y sin r sin x cos r x cos r y tan x tan Tan is positive. y r y x Cos is positive. 2.2.5 The Cast Rule Determine the sign of the ratio. 1. sin 1270 Positive 2. tan 240 Positive 3. cos 2600 Negative 4. tan 1450 Negative 5. cos 970 Negative 6. cos 450 Positive 7. sin 3140 Negative 8. cos 3150 Positive 2.2.6 The Cast Rule I and _____ II . i ) Sine ratios have positive values in quadrants _____ I and _____ IV . ii) Cosine ratios have positive values in quadrants _____ III . I and _____ iii) Tangent ratios have positive values in quadrants _____ iv) sin > 0 and cos < 0 II ______ v) tan < 0 and sin < 0 IV ______ 2.2.7 Finding the Exact Trig Ratios of an Angle in Standard Position Given point P(5, 12) on the terminal arm calculate the exact values of the primary trig ratios. r = √52 + 122 r =13 P(5, 12) 13 5 12 12 y sin sin 13 r x 5 cos r cos 13 y 12 tan x tan 5 2.2.8 Finding the Trig Ratios of an Angle in Standard Position The point P(-2, 3) is on the terminal arm of .in standard position. Determine the exact value of the trigonometric ratios for angle . 3 sin 13 P(-2, 3) 13 3 R -2 r2 x2 y2 = + r2 = (-2)2 + (3)2 r2 = 4 + 9 r2 = 13 r = √ 13 2 cos 13 3 tan 2 2.2.9 Challenging: Determine the exact value of the trig ratios given 5 sin , tan 0 7 Must be in Quad III sin cos tan x -5 7 5 7 2 6 7 5 2 6 x 2 72 52 x 72 52 x 24 x 2 6 2.2.10 Calculator: Determine Approximate Trig Ratios (four decimal places) 1. sin 250 = 0.4226 2. cos 1210 = 0.5150 3. tan 3350 = 0.4663 4. sin 00 = 0 5. tan 900 = undefined 2.2.11 Page 96: 1c, 2a,b, 3a,c, 4, 5d, 6 explain, 8a,b,e, 11a, 18b, 20 2.2.12