The database development process and Relational model
advertisement

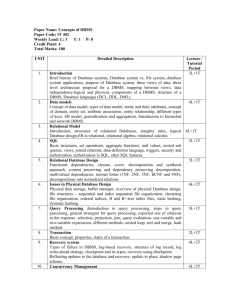
THE RELATIONAL DATABASE MODEL & THE DATABASE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Fact of the Week: According to a Gartner study in ‘06, Microsoft SQL server had the highest annual growth of any proprietary DBMS at 28% increasing market share from 15.6% to 17.4% Learning Objectives Describe the Relational Model Define relational terms and understand the terminology in practice. Understand these relational terms through practice Explain the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Explain the Database Life Cycle (DBLC) Fundamental Axioms of DBMSs Users communicate with computer applications (websites, etc) Computer applications communicate with DBMSs. Users do not communicate with DBMSs directly. As a result DBMSs although they can be used interactively, are not used interactively. A DBMS is not a replacement for sound database design principles. First of many examples for the semester https://labjobs.ischool.syr.edu Website You Web Server (IIS) Web Browser Application Components User Interface and Business Logic (HTML/C#) Db using Relational Model SQL Server Data access logic and Data (SQL) The Relational Database Model Many DBMS applications implement the Relational Model, but none of them enforce it. This permits rookie database designers to shoot themselves in the foot. And many have (including yours truly). The Relational Model has: (Codd’s 3 rules) 1)Data Independence 2) Data Consistency Clear separation between data and metadata Minimal redundancy; the data adopts the “DRY” principle 3) Easy to use You don’t have to understand the implementation to use it. You can build a poorly-designed DB in a DBMS Do you see problems with this database design? Think Codd: Independence? Consistency? Ease-of-Use? Asset# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Resource Sign-out Sheet Item Category Employee Phone Date Out The ABC's of Excel Book Dave Smith 3321 9-Jun InFocus Projector Hardware Sally Jones 4539 2-Jun Prog. for Dummies Book Art Wilson 9091 20-Jun Learning Perl Book Keith Way 3382 Dell Laptop #1 Hardware Sally Jones 4539 20-Jun Windows 2000 Server Solftware Office 2000 Premium Software Dave Smith 3321 12-Jun Dell Laptop #2 Hardware Change Sally Jones’s phone #? How many ‘Software’ in the database? Add New Employee Bob Smith? Delete Dave Smith (no longer works here) Activity: Relational Terminology Identify Each of These : Table Relation Row Column Tuple Attribute Physical Domain Logical Domain Asset Item Category Asset# The ABC's of Excel Book 1 InFocus Projector Hardware 2 Prog. for Dummies Book 3 Learning Perl Book 4 Dell Laptop #1 Hardware 5 Windows 2000 Server Software 6 Office 2000 Premium Software 7 Dell Laptop #2 Hardware 8 Tables are “Buckets for yer data” “Products Appear on Orders” “Customers Place Orders” Orders Customers Tables: • Specialized • Order doesn’t matter • Contain real items Products DBMS : Physical Domain Different “flavors” of DBMSs use different data types. DBMS: Logical Domain / Constraints Default Value – a value entered into an attribute for a row when one isn’t specified. Check Constraint – an expression which must be evaluated prior to the insertion of a row. Eg. Employee_hourly_wage >= 0 Unique Constraint – ensures duplicate values are not inserted into a column. (Secondary Keys should have unique constraints) Lookup table – a separate table containing all of the acceptable values for a given column, typically varchar (Think drop down list) The column you’re trying to constrain is a FK to the lookup table. Activity: The Relational Table Relation Name? Attributes? Physical Domain of Columns? Logical Domain of Columns? Candidate Keys? The Primary Key Constraint Special selected constraint (you choose it) Enforces entity integrity on the table. Must be data unique for each row Should be a candidate key Good PK / Bad PK Good candidate key choices? Customer Name? Email Address? Name and DOB? SSN? Customer Selected value? Random Unique #? Sequential Unique #? Last two are examples of surrogate keys The best PK’s Don’t change … ever! Have no external meaning ... Do not compromise security… Do not hinder performance … Activity: Which of these is a good PK? Candidate keys? Best primary key? Why? Should a Surrogate key be used? The Foreign Key constraint The foreign key is a column added to one relation so that it can be associated with another relation. Foreign keys must have referential integrity – their values must come from the corresponding PK column in the relation. Example of FK: The Lookup Table Asset Item Category Asset# The ABC's of Excel Book 1 InFocus Projector Hardware 2 Prog. for Dummies Book 3 Learning Perl Book 4 Dell Laptop #1 Hardware 5 Windows 2000 Server Software 6 Office 2000 Premium Software 7 Dell Laptop #2 Hardware 8 CategoryID Book Hardware Foreign Key Software Activity: Find the keys Candidate? Primary? Foreign? Secondary? Surrogate? One more time. Tables Rule for joining tables Columns: Physical Domain? Logical Domain? Alllow Null? Keys: Candidate? Primary? Foreign, Surrogate, Secondary? The Natural Join of PK-FK at Work Natural Join FK Example: Implementation of a 1-M Relationship FK Example: Implementation of a M-N Relationship This M-M Relationship has been resolved into two 1-M relationships Example:Null and Flags Nulls typically cause problems in Varchar and Numeric, and bit fields Employee EID 101 102 103 104 105 Ename ETermDate EBenefitPlan Willie Survive BluePoint Mike Rophone 01/01/04 Curt Tens 02/13/04 Sara Doctorintahaus OrangePoint Dustin Dawind 103 and 105 are null for different reasons! Null makes sense for this column Employee EID 101 102 103 104 105 Ename ETermDate EBenefitPlan Willie Survive BluePoint Mike Rophone 01/01/04 Term Curt Tens 02/13/04 Term Sara Doctorintahaus OrangePoint Dustin Dawind Op-Out Flags used to represent different status Data Models: Abstraction Levels Conceptual Logical Internal Highly Abstract Hardware and Software Independent Somewhat Abstract Hardware Independent Software Dependent External Physical Not Abstract (Concrete) Hardware and Software Dependent Systems Development Lifecycle SDLC / DBLC II Analysis III Design IV Implementation Resources I Planning Logical Model Conceptual Model Physical Model Time Internal / External Model V Maintenance & Support THE RELATIONAL DATABASE MODEL & THE DATABASE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Questions?