Physics 1161 Lecture 2 Electric Fields
advertisement
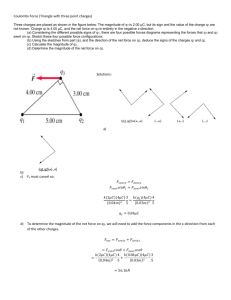
Physics 1161 Lecture 2 Electric Fields Three Charges • Calculate force on +2mC charge due to other two charges Q=+2.0mC 4m – Calculate force from +7mC charge – Calculate force from –3.5mC charge – Add (VECTORS!) Q=+7.0mC Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 2 6m Q=-3.5 mC Electric Force on Electron by Proton • What are the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron by the proton? q=1.6x10-19 C + r = 1x10-10 m Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 3 e- Comparison: Electric Force vs. Electric Field • Electric Force (F) - the actual force felt by a charge at some location. • Electric Field (E) - found for a location only – tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there: F = qE • Both are vectors, with magnitude and direction Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 4 Electric Field • Charged particles create electric fields. – Direction is the same as for the force that a + charge would feel at that location. E F/q – Magnitude given by: • Field at A due to proton? q=1.6x10-19 C + r = 1x10-10 m Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 5 A What is the direction of the electric field at point A, if the two positive charges have equal magnitude? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Up Down Right Left Zero A y + + B x Preflight 2.2 What is the direction of the electric field at point A? 1) Up 2) Down 3) Left 4) Right 5) Zero Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 7 A + y B x Preflight 2.3 What is the direction of the electric field at point B? 1) Left 2) Right 3) Zero A + Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 8 y B x What is the direction of the electric field at point C? 1. Left 2. Right 3. zero y + C - x Preflight 2.5 X A Y B Charge A is 1) positive Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 10 2) negative 3) unknown Preflight 2.6 X A Y B Compare the ratio of charges QA/ QB 1) QA= 0.5QB Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 11 2) QA= QB 3) QA= 2 QB Preflight 2.8 X A Y B The magnitude of the electric field at point X is greater than at point Y 1) True Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 12 2) False Compare the magnitude of the electric field at point A and B 1. EA> EB 2. EA= EB 3. EA< EB B A E inside of conductor • Conductor electrons free to move – Electrons feels electric force - will move until they feel no more force (F=0) – F=qE: if F=0 then E=0 • E=0 inside a conductor (Always!) Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 14 E inside of conductor • Conductor electrons free to move – Electrons feel electric force - will move until they feel no more force (F=0) – F=qE: if F=0 then E=0 • E=0 inside a conductor (Always!) Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 15 Preflight 2.10 X A Y B "Charge A" is actually a small, charged metal ball (a conductor). The magnitude of the electric field inside the ball is: (1) Negative Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 16 (2) Zero (3) Positive Recap • E Field has magnitude and direction: – EF/q – Calculate just like Coulomb’s law – Careful when adding vectors • Electric Field Lines – Density gives strength (# proportional to charge.) – Arrow gives direction (Start + end on -) • Conductors – Electrons free to move E=0 Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 17 To Do • ActivPhysics 11.1 – 11.3 – On the MasteringPhysics website • Read sections 19-6 & 19-7 • Do Prelecture 03 & Preflight 03. See you next Wednesday! Remember no class Fri or Mon! Physics 1161: Lecture 2, Slide 18