Free Fall - mthslabphysics
advertisement

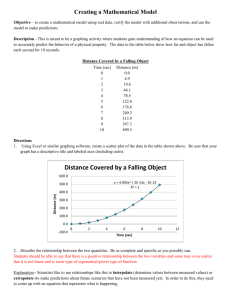
Free Fall Lab Physics Created by K.Rick Essential Question: What may be gained by understanding the effect that gravity has on motion? • Because of gravity, objects accelerate as they fall to the ground. • A free-falling object is an object falling under the sole influence of gravity. a. There is no air resistance acting on a free-falling object. b. A space without air resistance is called a vacuum. • The acceleration due to gravity on earth at sea level in a vacuum is 9.81 m/s2 . a. Acceleration due to gravity is represented by the letter g. b. So, g = 9.81 2 m/s • Air resistance will cause falling objects to accelerate at a slower rate than 9.81 m/s2. Because of air resistance, falling objects will reach a final speed. This is called terminal velocity. Motion Diagrams for Free-Falling Objects What is the initial speed of an object that is dropped? 0 Draw a motion diagram for a dropped falling object for the first 3 seconds of motion. Start with time = 0. Generally down is considered the negative direction (but it doesn’t have to be). t = 0, v = 0 t = 1s, v = -9.81 m/s t = 2s, v = -19.62 m/s t = 3s, v = -29.43 m/s An object is tossed upward with a velocity of 29.43 m/s. Draw a motion diagram for the object for the first 6 seconds of motion. Start with time = 0. t = 2s, v = 9.81 m/s t = 3s, v = 0 t = 4s, v = -9.81 m/s t = 1s, v = 19.62 m/s t = 5s, v = -19.62 m/s t = 0s, v = 29.43 m/s t = 6s, v = -29.43 m/s Because of gravity, objects will slow down as they go up and increase speed as they come back down. The total amount of time in the air is called the hang time. Key Concepts: • For all problems assume it takes place on Earth at sea level in a vacuum unless stated otherwise. This means g = 9.81 m/s2. • Dropped, vi = 0 • At maximum height, v = 0 • Acceleration is usually made negative since gravity pulls down. How Fast? • To find the instantaneous speed of an object in free fall use the following equation: •V = g t Check Your Understanding : • What would be the speedometer reading on a falling rock 4.5 seconds after it drops from rest? • How about 8 seconds? How far? d = ½ g (t2) Find the distance an object will fall after 8 seconds of free fall. Time (s) Distance (m) 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 5 20 45 80 125 How long? d = ½ g (t2) T= 2d/g How long has this skydiver free fallen if he falls for 80 meters? Check Yourself : • An object is dropped from rest and falls freely. After 6 seconds, calculate its instantaneous speed and distance fallen. Instan. Speed Distance V=gt d = ½ g t2 V= 10 m/s2 * 6s d = ½ 10m/s2 * 6s2 V = 60 m/s d = 180 m Double Check Yourself : • An object is dropped from rest and falls freely. After 8 seconds, calculate its instantaneous speed and distance fallen. Instan. Speed Distance V=gt d = ½ g t2 V= 10 m/s2 V = 80 m/s * 8s d = ½ 10m/s2 * 8s2 d = 320 m More Practice • An object falls a distance of 125m. What is its instantaneous speed just before it hits the ground? (hint: find t then find v) FYI: DaVinci’s Parachute His design is highly functional! • This is DaVinci’s 1493 parachute design • This is the modern reproduction of his sketch.