Free Fall - Western Reserve Public Media
advertisement

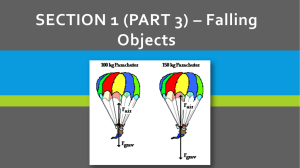
What is free fall? Free fall- objects falling unaffected by air resistance. On Earth we can’t fall without air resistance, but for normal situations the numbers are realistic. When things fall they constantly accelerate. If we can ignore air resistance, all objects accelerate at the same rate. 9.8 m/s2 = g (acceleration due to gravity on Earth at sea level) If everything accelerates at the same rate, does that mean everything falls at the same rate? Even they have a different weight? yes Even if they are different sizes? yes Even if they are different shapes? not if you include air resistance If you put it in a vacuum, then yes Things that increase air resistance. shape- more surface area means more air resistance. velocity- the faster you go, the more air resistance (this is why meteors burn up in the atmosphere) The “thickness” of the air you go through (there is less air resistance higher up in the atmosphere) Terminal Velocity Terminal velocity- the velocity at which the upward force of air resistance equals the downward force of gravity. Once you reach this velocity you will no longer accelerate. (just stay at the same velocity) Parachutes increase your surface area to increase your air resistance in order to reduce your terminal velocity so you don’t die when you hit the ground. International Space Station A joint project from the United States and Russia started in 1998 began construction on the International Space Station. The first crew arrived in 2000. It is a lab, orbiting the planet where crews work and do research. It is the 4th Space Station to orbit the Earth. Weightlessness People aboard the space station appear to be weightless (They float around like there is no gravity). However, they are not out of Earth’s gravitational field (gravity is still pulling on them). Freefall The space station is actually in freefall around the planet. That is what orbit is (constant free fall around the planet). It is moving so quickly forward, it clears the planet. Frame of Reference The “weightlessness” has to do with the frame of reference. If everything is falling at the same rate, it appears as though it is floating with no gravity. Similar to being on an amusement park ride that drops you straight down. Weightless sensation If you put a penny on your knee and ride something that drops you, like the Demon Drop at Cedar Point, it will “float” in front of you, at least from your frame of reference. Really it is falling at the same rate you are. In the case of the space station everything is falling with you (air included), so you can’t tell you are falling.