Gamma Rays for Medicine
advertisement

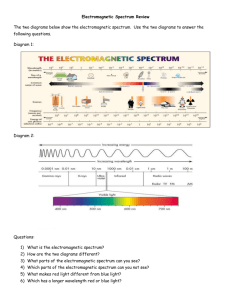
The Basics of Light One thing that all the forms of electromagnetic radiation have in common is that they can travel through empty space. Electromagnetic Radiation • Electromagnetic radiation or “light” is a form of energy. • Has both electric (E) and magnetic (H) components. • Characterized by: –Wavelength (l) –Amplitude (A) Visible light waves are the only electromagnetic waves we can see. We see these waves as the colors of the rainbow. Each color has a different wavelength. Red has the longest wavelength and violet has the shortest wavelength. When all the waves are seen together, they make white light. The Particle/Wave Duality Light is a particle but it has no mass blue light can knock electrons off metal plate red light can’t – has less energy Light is a wave light goes out in all directions light “bends” around corners (like waves around a pier) light reflects (mirrors) light refracts (bends) INTERFERENCE of the light Interference is the interaction between waves traveling in the same medium. Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Radiation (cont.) • We classify electromagnetic radiation by wavelength. • Visible radiation takes up only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio Waves • Created by oscillations (vibrations) of electrons in a conductor. • Very long wavelength (few km to few cm) – low frequency – so low energy waves. • Used to transmit radio and TV signals. • Travel in straight lines, but can be bounced off the upper atmosphere, so can travel around the world. Radio Radio waves are very long compared to waves from the rest of the spectrum Radio telescopes use a large metal dish to help detect radio waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum MICROWAVES • Wavelength from cm to .0001 m • Used for cooking food • Microwaves make water molecules vibrate, which causes food to get very hot very quickly. • Penetrate only a few cm, the heat is then carried inside by conduction MICROWAVES • Microwaves are also used for communication. • Mobile telephones use microwaves. • They are also used to communicate with satellites as they can pass through the upper atmosphere • They also do not spread out much, so they are easy to use with a dish. The Electromagnetic Spectrum INFRA-RED • Everything gives out Infra-red • This allows cameras to use IR instead of visible light for nightvision. • They are also used for thermo-imaging cameras, to find people buried in earthquakes. They will be being used in New York. • They are also used for remote controls Infrared Radiation Wavelength: 1 um – 1000 um We emit IR light. In fact all the objects around us emit IR radiation. Hotter objects emit more IR radiation, which we are warmed by, and which we sense with our skin. IR photo of a man IR photo of the dust in the Solar System The Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Light White light is made up of light from all different colors . Intensity of Light • Intensity is lowered when the light is spread out. The Electromagnetic Spectrum ULTRA VIOLET • Shorter wavelength – 0.000001m to 0.000000001m, frequency higher. • Carry more energy, and can penetrate top layers of skin, damaging the lower layers • This can cause sun burn, and possibly skin cancer of a long period of time. • The eyes are very sensitive to UV, so sunglasses should always be worn in bright sunshine. • Most UV radiation from the sun is filtered by the ozone layer. Ultraviolet Light Some birds & bees can see UV as well as visible light. Ultraviolet light has just the right energy to break molecular bonds apart. For this reason it is detrimental to life. The Earth has a natural shield to Solar UV light in the form of an ozone layer (80 km above the surface). 10% of sunlight is in the UV The Electromagnetic Spectrum X-Rays • Their ability to pass through soft tissue, but not bone, makes them very useful in medicine. • They are completely stopped by metals, making them useful for security scanning at airports. X-Rays • Because they carry a lot of energy they can easily damage or kill cells. • This can lead to cancer if over-exposure occurs. • Very small amounts are used in hospitals and are relatively safe, however the operator will stand behind a lead screen to stop unnecessary exposure • X-rays are also used to treat cancer by killing cancerous cells. The Electromagnetic Spectrum X-Rays and Gamma Rays • X-rays and gamma rays absorbed in the Earth’s atmosphere • observatories must be sent into space • produced by matter heated to millions of degrees • caused by cosmic explosions, high speed collisions X-rays X-rays were discovered 1895 by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (a German scientist) by accident. A week later he took this x-ray of his wife. Gamma Rays for Medicine: • Gamma rays are used in medicine to kill and treat certain types of tumors and cancers. •. RISKS and BENEFITS • X-Rays and Gamma rays are both used in medicine. • Their benefits are they destroy cancer, and avoid surgery, as well as use for diagnostic purposes. • They can also cause cancer, and may cause sickness if exposures are too large. THE COMPLETE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Long WAVELENGTH Short Low FREQUENCY High Low ENERGY High