6.1 6.2 REviewQs
advertisement

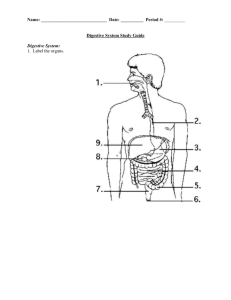
6.1/6.2 REVIEW QUESTIONS P.240-241 GROUP 1: 1. Compare the dehydration synthesis of maltose to the hydrolysis reaction of this macromolecule. Dehydration Synthesis Glucose + Glucose + maltose + water + water Hydrolyis Maltose + water + water glucose + glucose + 5. Describe the function of proteins in the human body. Some proteins function as building blocks for body tissues. Some are enzymes, antibodies, hormones, neurotransmitters or transport molecules such as hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying pigment in blood. 6. Explain the following statement. “The stomach is an organ in which both physical digestion and chemical digestion takes place.” The folds in the stomach allow the stomach to expand as it fills with food. The muscular layers of the stomach churn the food, breaking it into smaller pieces (mechanical or physical digestion) and pushing it into the small intestine. The gastric glands release pepsinogen and hydrochloric acid that activates pepsin for chemical digestion of protein. 7. Use a flow chart to summarize the chemical digestion of the following macromolecules. Include the enzymes (or group of enzymes) that would be involved in this process. a.) starch STARCH MALTOSE GLUCOSE Amylase maltase (carbohydrases) b.) protein PROTIEN POLYPEPTIDES Small PEPTIDES AMINO ACIDS pepsin trypsin peptidase chymotrypsin (proteases) c.) fat EMULSIFIED FAT lipase FATTY ACIDS + GLYCEROL 11. Identify each organ shown in the diagram below and list the digestive process(s) (physical digestion, chemical digestion, or absorption) that takes place in each. A. MOUTH = physical and chemical digestion B. LIVER = none; an accessory organ that produces bile for physical digestion of fats C. GALL BLADDER = none; an accessory organ that stores bile for physical digestion of fats D. LARGE INTESTINE = absorption E. RECTUM = none; elimination of feces F. ESPOPHAGUS = none; carries food from the mouth to the stomach G. STOMACH = physical and chemical digestion H. PANCREAS = none; accessory organ that produces digestive enzymes I. SMALL INTESTINE = chemical and physical digestion, absorption 16. Identify the substances on the diagram indicated by the arrows labeled (i), (j), (k). (i) represents monosaccharides (from carbohydrate digestion) and amino acids (from protein digestion); these are absorbed directly into the bloodstream (j) represents protein-coated triglycerides (from fat digestion); these are absorbed into the lymphatic vessels (k) represents water, minerals (salts), and vitamins produced by bacteria; these are absorbed fro the large intestine into the bloodstream.