Human Evolution lab
advertisement

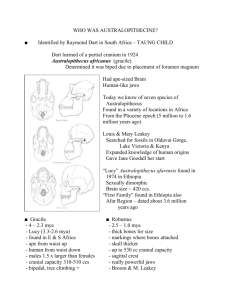
Human Evolution lab Introduction to Paleoanthropology Objectives: • Learn about Primates, hominids and hominoids. • Learn about cladistics and Phylogenies • Create a human Phylogeny using the fossil reproductions in lab by – Collecting data from the skulls – Learning significant characters for comparison – Construct a cladogram from your data • Observe how different conclusions may be made from the same data set. • View a video recreation of significant stages of human evolution Orangutan and Gorilla Characters 1. Facial Slope Angle 2. Supraorbital Browridge (large, small, or medium) 3. Forehead (large, small, or medium) 4. Sagittal Crest (absent, small, medium, or large) 5. Foramen Magnum (rear or forward) Brain case features 6. Cranial Module 7. Nasal Bones (arched or flat) 8. Prognathism (present or absent) Facial features 9. Postorbital Constriction 10. Facial Width 11. Dental Arcade (Box, U, or intermediate) 12. Incisors (angled or vertical) 13. Canines (above or below) 14. Diastema (present or absent) 15. Tooth Row Length Dental features Geographic Regions and Ages of the Fossils: • • • • • 1- East Africa, 3.9-3.0 MYA 2 – East Africa, 1.9-1.7 MYA 3 – Africa, Asia, and Europe, 1.8 MYA-0.3 MYA 4 – East Africa, 2.3-1.6 MYA 5 – Europe and the Middle East (West Asia), 0.2 0.03 MYA • 6 – Africa, Asia, and Europe, 0.6-0.1 MYA • 7 – South Africa, 3.0-2.3 MYA • 8 – Africa, Asia, and Europe (and later worldwide), 0.15 MYA-present Australopithecus bosie & Homo erectus Neanderthal FACIAL SLOPE Facial slope Facial slope Supraorbital bridge Supraorbital bridge Forehead Forehead Sagittal crest Foramen magnum CRANIAL MODULE Cranial Module- length Cranial Module- depth Cranial Module- width Nasal bones - arched Nasal bones - flat Prognathism Postorbital constriction Facial width Zygomatic arch Shape of Dental Arcade Canines - above chewing surface Canines - below chewing surface Incisors – angled out Incisors- vertical Tooth row length 2 premolars + 3 molars Diastema – gap for long canine