Punnett Squares & Pedigrees Wksht
advertisement

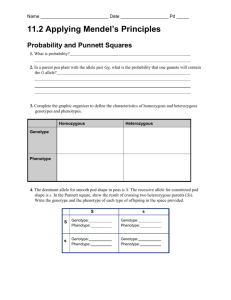
Name: _______________________________ Per. _________ Date: _____________________ Biology Unit 7 – Punnett Squares & Pedigrees Practice Homework 1. The dominant allele for smooth pod shape in peas is S. The recessive allele for constricted pod shape is s. In the Punnett square, show the result of crossing two heterozygous parents (Ss). Write the genotype and the phenotype of each type of offspring in the space provided. S s S Genotype: s Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: For Questions 2–4, refer to the Punnett square above. 2. What is the probability of a heterozygous offspring? Explain your answer. 3. What is the probability of a homozygous offspring? Explain. 4. What is the probability of a homozygous recessive offspring? 5. Using the principle of independent assortment, complete the Punnett square to show the results of an F1 cross between two individuals heterozygous for both pod color (C = green and c = yellow) and pod shape (S = smooth and s + constricted). The gametes and some of the genotypes of the F2 offspring are given. CS cS Cs cs CS CCSS ccSs cS CCss Cs cs ccSs For Questions 6–8, refer to the Punnett square above. 6. Which genotype belongs to an offspring that is homozygous recessive for both traits? What is the probability of that genotype? _______________ 7. What is the phenotype of an individual heterozygous for both traits? _______________ 8. What is the probability of an F2 offspring having the green pod color and smooth pod shape? Explain. (Note: Name: _______________________________ Per. _________ Date: _____________________ Remember that more than one genotype can produce this phenotype.) _______________ _______________ For Questions 9–15, write “T” if the statement is true and “F” if the statement is false. 9. When offspring show a blend of the parents’ traits, one allele is dominant over the other. 10. In complete dominance, the heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes. 11. A heterozygous individual that exhibits the traits of both parents is an example of codominance. 12. Many genes exist in several forms and are said to have codominant alleles. 13. While multiple alleles may exist in a population, an individual usually carries only two alleles for each gene. 14. Traits produced by two or more genes are codominant. _______________ 15. Polygenic traits often show a wide range of phenotypes For each of the following examples, write G if the trait is determined by genotype, and E if it is determined by environment. 16. Turtles whose eggs hatch at higher temperatures tend to be female. 17. A blue-eyed girl is born to two blue-eyed parents. 18. Bees in a colony are assigned different jobs. As they develop, workers begin to look dramatically different. 19. A pair of twins is separated at birth. They grow up in different countries and speak different languages. For Questions 20–25, match the labels to the parts of the pedigree chart shown below. Some of the labels may be used more than once. 20. A person who expresses the trait 21. A male 22. A person who does not express the trait 23. A marriage 24. A female 25. A connection between parents and offspring