Sedimentary Rocks
advertisement

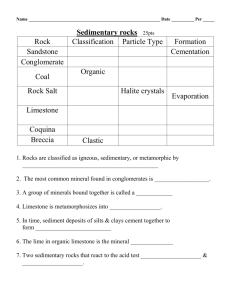
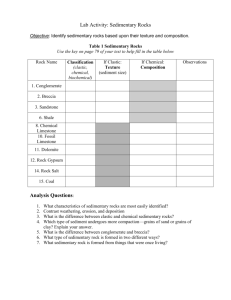
Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rocks • Formed by the compaction and cementation of sediments (small pieces of rock and living things). Depositional Environment • Sedimentary rocks can tell you what the environment was like when they formed. This is called the “Depositional Environment.” For example, a sandstone’s depositional environment was likely a beach or a desert since that is where you find sand today. Where did these rocks form? Sandstone with cross-bedding Fossil Fish Mudstone with ripple marks Fossil Plant Impressions Types • 2 major types: – A. Clastic: Made of smaller pieces of rocks called clasts. (sandstone for example) – B. Nonclastic (Either Chemical or Organic): Made of once living things or from evaporated/precipitated minerals. (Coal and Limestone for example). Examples of Clastic Sediments Breccia Sandstone Conglomerate Shale Texture of Sedimentary Rocks • • • • Grain Size Grain Type Sorting Grain Shape Clastic • Clastics - made from fragments of other rocks called clasts. These clasts are either compacted when sediments build up on top of them or they are cemented together by some sort of solution that acts like glue. Form layers that are easily seen with the naked eye. Size • Fine grained: Small, can’t see individual grains • Medium grained: Sand sized, can see grains • Coarse grained: Pebble sized, can easily see individual grains Grain Shape Sorting • Well Sorted: Grains are similar shape and size • Poorly Sorted: Grains are all shapes and sizes Well or poorly sorted? Well or Poorly Sorted? Fossils • Sedimentary rocks are the most likely rock to have fossils. The fossil can tell you where the rock formed. Brachiopod fossils in limestone Imprint of a leaf Trilobites Trilobite fossils – over 250 MILLION years old!!! Nonclastics • Made from chemical or organic processes • A. Chemical: Precipitates - Minerals combine and settle out in the ocean. • Examples include: limestone (CaCO3), dolomite (MgCO3), and chert (SiO2) & some ores like hematite concretions. • -Limestone and Dolomite form in shallow, warm, tropical oceans. Chert forms in colder, deeper ocean waters. • Evaporites - left behind when water evaporates. Rock Salt (NaCl) Rock Salt Nonclastics • B. Organic: • Limestone – Formed in shallow, warm, tropical oceans from shells of organisms and corals reefs that are cemented or compacted together. • Bituminous coal – Form from build up of dead plants. Formed in swamps and marshes. • Coquina – Formed from cemented shells. Likely formed in a beach environment. Coal Limestone Coquina Tectonic Boundaries • Sedimentary rocks form in areas that lack tectonic plate boundaries (passive margins) like the east coast of the United States, including Virginia.