World War II and Post War Georgia
advertisement

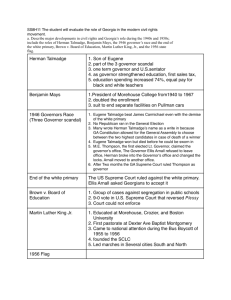
America and Georgia In World War II What started WWII? Germany- WWI treaty punished the country, economic problems Hitler- came to power, promised a return to German greatness Rebuilding a German Empire Japan- wanted an empire, land in southeast Asia and coast of China Where the war was fought: European Theater: Eastern Europe and then throughout Europe -GERMANY and Italy invade the entire European continent Pacific Theater: Asia, Pacific, Islands, China- JAPAN Axis Powers Allied Powers FDR, Josef Stalin, and Winston Churchill Harry Truman, Stalin and Churchill US Involvement Isolationism: US belief/strategy to keep to itself- not involve itself in world issues and affairs. Stayed out of WWII for quite awhile(until the bombing at Pearl Harbor) Lend Lease Act FDR and Congress passed act to be able to lend war materials to countries that were important to our interests. German u-boats began sinking American merchant ships.- (several off GA- SSI and Cumberland) FDR ordered to “shoot on sight” Attack on Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Brought US into the war- became part of the ALLIES Over 2,300 killed and 19 ships destroyed “A date which will live in infamy” The end of the depression Men in the Military Women were in the workforce Factories making war products The European Theater The Holocaust and Liberating the Concentration Camps Hitler’s plan was to “purify” the German race by removing undesirables. concentration camps and then • killed them in gas chambers Over 6 million Jews died An estimated 11 million people died in the camps This was the Holocaust Allied forces liberated a number of the camps Georgia and World War II 1940-still in depression, most still work on farms War Effort: 1- Servicemen 2-Manufacturing/War Supplies 3-Military Training 4-Crops and Supplies Economy Improves! Georgia’s Military Over 300,000 Georgia men and women served in the military during the war. Almost 7,000 of them died. Liberty Ships Brunswick and Savannah Between 1943-44 99 built in Bwk Employed 16,000 people Quickly built, assembly line “throwaways”, “ugly ducklings” Cargo ships- supplies, men, weapons Famous people: • Henry Grady • Howard Coffin Glynco Naval Air Station This area is now known as FLETC. Only Naval station to house every type of aircraft Largest blimp base in the world Blimps looked for German U-boats and escorted Allied ships Bell Bomber Aircraft Company Marietta, GA 1943 Largest aircraft assembly plant in world Built B-29 bombers (665 of them) Employed: from 1,179 to over 17,000 by the end of the war Women- Rosie the Riveter Major defense plant in US Now Lockheed Martin Training Allied Troops in GA GA and Texas had the most training facilities Camp Stewart Camp Gordon Fort Benning Warner Robbins Southern Fields How GA got so many military camps: Lots of open unused land, good climate Active and powerful leaders: Carl Vinson- US Congressman from Georgia for over 50 yrs, helped create US AIR FORCE and Navy in the Pacific, helped bring military to GA Richard Russell- US Senator from GA: over 40 yrs, past governor of GA, supported strong military, supported federal farm relief, rural electrification, National School Lunch Act Leaders saw this as a way to help Ga. economically Camp Stewart Now called Fort Stewart Near Savannah Anti-aircraft training Lots of land- live ammunition 50,000 troops 280,000 acres- 5 counties Camp Gordon Augusta Largest communication center in the world Fort Benning Columbus, GA Largest infantry training post in the world Warner Robins Air Force Base 15,000 civilian employees Southern Fields Western GA- near Americus German Prisoner of War Camp Propaganda Georgia’s Wartime Economy Economy is still rooted in agriculturediversified a little- dairy, food crops Largest form of manufacturing is textiles Coca-Cola won a government contract to supply Coke to the soldiers in Europe • Bottling plants were built in Europe and the Pacific Social and Economic Impact of the War Two oil tankers were sunk off the coast of SSI by German u-boats People collected and donated items like scrap metal and rubber to help make weapons and other equipment. Victory gardens were planted to help families at home and troops overseas Ration cards were issued by the government on such items as gas, rubber tires, and meat & sugar. V-E Day Victory in Europe Day Germany surrenders May 8, 1945 The Atomic Bomb The B-29 bomber known as the Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima in Japan Three days later, a second a-bomb was dropped on Nagasaki, also in Japan Over 110,000 people were killed immediately and more than 100,000 others died within a few months from radiation exposure Hiroshima Nagasaki V-J Day Victory over Japan Day Japan surrenders August 14, 1945 After Hiroshima and Nagasaki Postwar Georgia Baby Boom – A period in time of major increases in the number of births. Usually happens after wars. (1946-1964) Men coming home from war looking for jobs. Moved to cities for more opportunities. Population Trends in GA Between the 1930s and 1960s the population in the rural areas dropped significantly as more people moved into the cities looking for good paying jobs. Folks that came from other states to GA, moved into the urban areas due to the industries that were springing up. Changes in Business & Industry The average GA yearly income tripled from 1940-1950 The number of white collar workers grew from 20% in 1940 to 33% in 1960 The 3 major counties of metropolitan Atlanta grew as did Savannah (due to the port) The automobile industry grew as did the textile industry Labor unions began to form after WWII to make sure people had good working conditions Changes in Agriculture Mechanization • Tractors replaced sharecroppers Dairy & Livestock • Increase in meat and dairy products during WWII • Poultry is the largest industry in GA Poultry accounts for half of the state's $4 billion farm income. Its economic impact in Georgia is $13.5 billion. On an average day, the state produces 24.7 million pounds of chicken meat and 8.2 million table eggs. Improved Farming Methods • New crops that produced better • New chemicals to control weeds & pests • Better organization of farms Crop Diversity • Peanuts, soybeans, & tobacco = 27% • Cotton = 2.5% • Poultry farming and livestock = 50% Growth of Atlanta Transportation • Atlanta Hub for railroads I-75, I-20, & I-85 all intersected here • Interstate highway system Hartsfield Airport • Home of Delta Airlines MARTA (Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority) Lake Sidney Lanier • New source of water for Atlanta area Major League Sports Falcons, Hawks, Braves Huge VENUE- brings in people Shows that city is large enough to support sports and therefore large enough to support industry, visitors, economy Atlanta’s Political Leadership William Hartsfield • Atlanta’s longest serving mayor • Developed the Atlanta airport Serves more than 78 million passengers annually • Supported the Atlanta zoo • Reformed the city’s police and fire departments Politics in WWII Georgia Board of Regents Controversy- “Cocking Affair” • Involved Governor Eugene Talmadge • He tried to get rid of educators that promoted integrating the state’s schools • The Board of Regents would not fire people just because Talmadge said so • Talmadge then forced two members of the board to resign and replaced them with people who did what he said • Due to Talmadge’s involvement and the firing of two college professors, the Southern Association of Colleges and Secondary Schools took away GA’s accreditation in the public school system Governor Ellis Arnall • Replaced Talmadge • Promised to reform state government • Established the Dept. of Corrections Abolished chain gangs and severe punishment • Formed the Board of Pardons and Paroles • Changed the voting age from 21 to 18 GA was the first state to let 18-yearolds vote Three Governor’s Controversy Eugene Talmadge ran for governor again in 1946 • Campaigned on a white supremacy platform • Talmadge won the election but died before taking office Herman Talmadge, Eugene’s son, received a number of write-in votes and declared himself the new governor M.E. Thompson, the Lieutenant Governor declared himself the governor Ellis Arnall said he was still the governor since no one had been sworn in yet Controversy Continued Herman’s supporters broke into the governor’s office and changed the locks • Ellis couldn’t get into his office • Herman’s supporters said he was the new governor and gave him the keys to the office Ellis set up a temporary office at the information booth of the Capitol building Lt. Governor Thompson set up a governor’s office in a nearby building The GA Supreme Court ruled Thompson the official governor Upon a new election, Herman Talmadge beat Thompson and became the governor Politics The county unit system, that favored the small rural counties, was ruled unconstitutional in the early 60s. • This changed the face of GA politics