Digital Logic Gate Identification Activity
advertisement

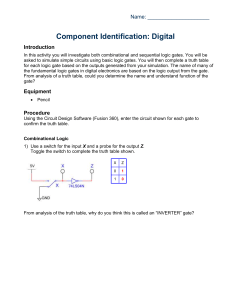
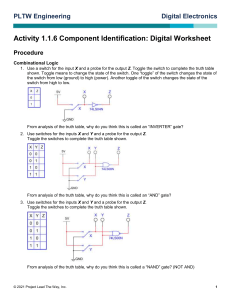
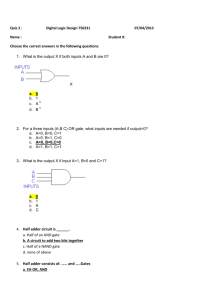
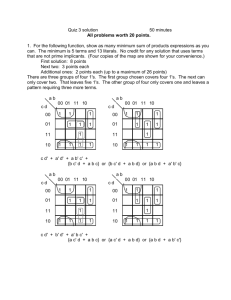
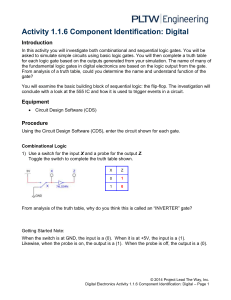
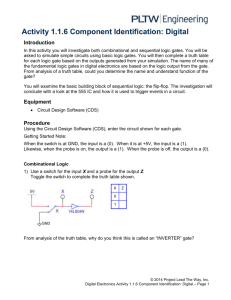
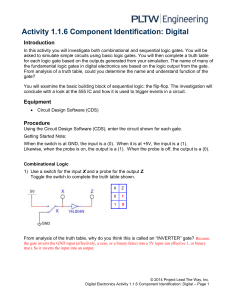
Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital Introduction In this activity you will investigate both combinational and sequential logic gates. You will be asked to simulate simple circuits using basic logic gates. You will then complete a truth table for each logic gate based on the outputs generated from your simulation. The name of many of the fundamental logic gates in digital electronics are based on the logic output from the gate. From analysis of a truth table, could you determine the name and understand function of the gate? You will examine the basic building block of sequential logic: the flip-flop. The investigation will conclude with a look at the 555 IC and how it is used to trigger events in a circuit. Equipment http://www.neuroproductions.be/logic-lab/ Procedure Google search “the logic lab” and click on the first link Getting Started Note: When the switch is RED, the input is a 1. When the input is WHITE, the input is a 0. A light on will mean that the output is 1. A light off will mean that the output is a 0. Combinational Logic 1) Use a switch for the input X and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switch to complete the truth table shown. X Z 0 1 From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “INVERTER or NOT” gate? © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Digital Electronics Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital – Page 1 2) Use switches for the inputs X & Y and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switches to complete the truth table shown. X Y 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 Z From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “AND” gate? 3) Use switches for the inputs X & Y and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switches to complete the truth table shown. X Y Z 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called a “NAND” gate? (NOT AND) 4) Use switches for the inputs X & Y and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switches to complete the truth table shown. X Y Z 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “OR” gate? © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Digital Electronics Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital – Page 2 5) Use switches for the inputs X & Y and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switches to complete the truth table shown. X Y Z 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called a “NOR” gate? (NOT OR) 6) Use switches for the inputs X & Y and a probe for the output Z. Toggle the switches to complete the truth table shown. X Y Z 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “XOR” gate? (EXCLUSIVE OR) Extension: Try creating a logic table for the “XNOR” gate © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Digital Electronics Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital – Page 3